STM32F4Dis Board using with Cygwin - I2C
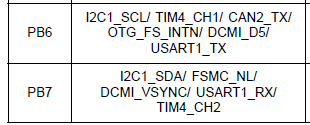
1 Pin Description
REF: Discovery kit with STM32F407VG MCU--UM1472 User manual
I2C对应的Pin:
micropython-1.12\ports\stm32\boards\STM32F4DISC
mpconfigboard.h
// I2C busses
#define MICROPY_HW_I2C1_SCL (pin_B6)
#define MICROPY_HW_I2C1_SDA (pin_B7)
#define MICROPY_HW_I2C2_SCL (pin_B10)
#define MICROPY_HW_I2C2_SDA (pin_B11)
I2C bus
Hardware I2C is available on the X and Y halves of the pyboard via I2C('X') and I2C('Y'). Alternatively pass in the integer identifier of the peripheral, eg I2C(1). Software I2C is also available by explicitly specifying the scl and sda pins instead of the bus name. For more details see machine.I2C.
from machine import I2C
i2c = I2C('X', freq=400000) # create hardware I2c object
i2c = I2C(scl='X1', sda='X2', freq=100000) # create software I2C object
i2c.scan() # returns list of slave addresses
i2c.writeto(0x42, 'hello') # write 5 bytes to slave with address 0x42
i2c.readfrom(0x42, 5) # read 5 bytes from slave
i2c.readfrom_mem(0x42, 0x10, 2) # read 2 bytes from slave 0x42, slave memory 0x10
i2c.writeto_mem(0x42, 0x10, 'xy') # write 2 bytes to slave 0x42, slave memory 0x10Note: for legacy I2C support see pyb.I2C.
from machine import I2C
i2c = I2C(freq=400000) # create I2C peripheral at frequency of 400kHz
# depending on the port, extra parameters may be required
# to select the peripheral and/or pins to use
i2c.scan() # scan for slaves, returning a list of 7-bit addresses
i2c.writeto(42, b'123') # write 3 bytes to slave with 7-bit address 42
i2c.readfrom(42, 4) # read 4 bytes from slave with 7-bit address 42
i2c.readfrom_mem(42, 8, 3) # read 3 bytes from memory of slave 42,
# starting at memory-address 8 in the slave
i2c.writeto_mem(42, 2, b'\x10') # write 1 byte to memory of slave 42
# starting at address 2 in the slave
使用样例:
import pyb
from pyb import I2C
import time;
import binascii;
#https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python-convert-bytearray-to-hexadecimal-string/
from pyb import CAN
import pyb
can1 = CAN(1, CAN.NORMAL)
can2 = CAN(2, CAN.NORMAL)
msg=b'\x00\x20\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00'
CAN2_ID = 0x634 #0x621 0x634
CAN1_ID = 0x500 #0x621 0x634
#CAN2_ID = 0x521 # 0x521
can2.send(msg, CAN2_ID)
can1.send(msg, CAN1_ID)
print("CAN2 transmit DATA to",CAN2_ID)
print("CAN1 transmit DATA to",CAN1_ID)
# Catch all filter
can2.setfilter(0, CAN.MASK16, 0, (0, 0, 0, 0));
can2.setfilter(1, CAN.MASK16, 0, (0, 0, 0, 0));
can1.setfilter(0, CAN.MASK16, 0, (0, 0, 0, 0));
can1.setfilter(1, CAN.MASK16, 0, (0, 0, 0, 0));
tim = pyb.Timer(4, freq=8) #freq>=4,can work
def tick(timer):
# can1.send(msg, CAN1_ID)
can2.send(msg, CAN2_ID)
def tick2(timer):
print(can2.recv(0))
#print(can2.any(0), can.info())
#click three times “Enter” Key
tim.callback(tick)
#tim.callback(None)
#// I2C busses
#define MICROPY_HW_I2C1_SCL (pin_B6)
#define MICROPY_HW_I2C1_SDA (pin_B7)
#define MICROPY_HW_I2C2_SCL (pin_B10)
#define MICROPY_HW_I2C2_SDA (pin_B11)
#i2c = I2C(1)
i2c = I2C(2)
#i2c.writeto(0x11, b'123') # write 3 bytes to slave with 7-bit address 42
i2c.init(I2C.MASTER, baudrate=400000)
#print(i2c.scan())
#i2c.is_ready(0x03)
#print(i2c.mem_read(4,0x03, 0))
i2c.send(0x00, 0x01) #
R_data = i2c.recv(16, 0x01)
print(type(R_data))
res = binascii.hexlify(bytearray(R_data))
print(str(res))
#https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/python-convert-string-to-n-chunks-tuple/?ref=rp
N = 2
res = tuple(res[ i : i + N] for i in range(0, len(res), N))
print("Chunked String into tuple : " + str(res))
for i in range( 0, 17):
print("Addr: " ,hex(i), str(res[i]))
#print("The string after conversion : " + str(res))
for i in range (0, 17):
print("%#04x" % i,'=', "%#04x" % R_data_1[i])
#>>> "0x%#x" %a
#'0x0xa'
#>>> "0x%#04x" %a
#'0x0x0a'
#>>> "0x%04x" %a
#'0x000a'
#>>> "%#04x" %a
#'0x0a'
i2c.deinit()
结果:
$ python3.6 pyboard.py My_test-i2c.py
CAN2 transmit DATA to 1588
CAN1 transmit DATA to 1280
b'749c550990ff03f311a7000060021a20'
Chunked String into tuple : (b'74', b'9c', b'55', b'09', b'90', b'ff', b'03', b'f3', b'11', b'a7', b'00', b'00', b'60', b'02', b'1a', b'20')
Addr: 0x0 b'74'
Addr: 0x1 b'9c'
Addr: 0x2 b'55'
Addr: 0x3 b'09'
Addr: 0x4 b'90'
Addr: 0x5 b'ff'
Addr: 0x6 b'03'
Addr: 0x7 b'f3'
Addr: 0x8 b'11'
Addr: 0x9 b'a7'
Addr: 0xa b'00'
Addr: 0xb b'00'
Addr: 0xc b'60'
Addr: 0xd b'02'
Addr: 0xe b'0a'
Addr: 0xf b'20'
Addr: 0x10 b'01'
0x00 = 0x74
0x01 = 0x9c
0x02 = 0x55
0x03 = 0x09
0x04 = 0x90
0x05 = 0xff
0x06 = 0x03
0x07 = 0xf3
0x08 = 0x11
0x09 = 0xa7
0x0a = 0x00
0x0b = 0x00
0x0c = 0x60
0x0d = 0x02
0x0e = 0x1a
0x0f = 0x20
0x10 = 0x01
I2c线连接有问题的话会报错:
$ python3.6 pyboard.py My_test-i2c.py
CAN2 transmit DATA to 1588
CAN1 transmit DATA to 1280
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 55, in
OSError: 16