高通linux-reboot 分析
reboot 分析
1 版本
平台:高通8009
busybox:1.24
linux kernel:3.18.48
2 流程
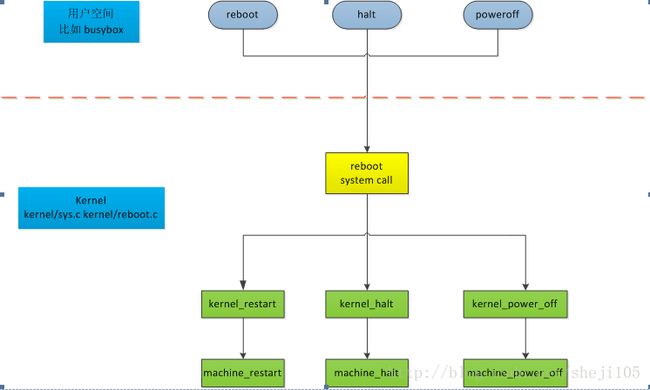
可以通过reboot、halt、poweroff等命令,对linux操作系统进行控制,具体的操作流程如下:
3 分析
在arm 板上,可知:
# ls /sbin/reboot -la
lrwxrwxrwx 1 1000 1000 14 Jun 21 2017 /sbin/reboot -> ../bin/busybox
常规reboot是以busybox为入口,然后进入halt_main函数。
reboot不带参数执行,会给init进程发送SIGTERM信号,init进程接收到信号后给其他进程发送终止信号,最后调用C库函数reboot,reboot通过系统调用sys_reboot进入内核,系统重启。
reboot -f 带参数执行,则通过halt_main直接调用C函数reboot,不经过init进程。
函数实现如下:
int halt_main(int argc, char **argv) MAIN_EXTERNALLY_VISIBLE;
int halt_main(int argc UNUSED_PARAM, char **argv)
{
static const int magic[] = {
RB_HALT_SYSTEM,
RB_POWER_OFF,
RB_AUTOBOOT
};
static const smallintsignals[] = { SIGUSR1, SIGUSR2, SIGTERM };
int delay = 0;
int which, flags, rc;
/* Figure out which appletwe're running */
for (which = 0;"hpr"[which] != applet_name[0]; which++)
continue;
/* Parse and handlearguments */
opt_complementary ="d+"; /* -d N */
/* We support -w even if!ENABLE_FEATURE_WTMP,
* in order to not break scripts.
* -i (shut down network interfaces) isignored.
*/
flags = getopt32(argv,"d:nfwi", &delay);
sleep(delay);
write_wtmp();
if (flags & 8) /* -w */
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
if (!(flags & 2)) /* no-n */
sync();
/* Perform action. */
rc = 1;
if (!(flags & 4)) { /*no -f */
//TODO: I tend to think that signalling linuxrc is wrong
// pity original author didn't comment on it...
if (ENABLE_FEATURE_INITRD){
/* talk tolinuxrc */
/* bboxinit/linuxrc assumed */
pid_t *pidlist= find_pid_by_name("linuxrc");
if (pidlist[0]> 0)
rc =kill(pidlist[0], signals[which]);
if(ENABLE_FEATURE_CLEAN_UP)
free(pidlist);
}
if (rc) {
/* talk toinit */
if(!ENABLE_FEATURE_CALL_TELINIT) {
/* bboxinit assumed */
rc =kill(1, signals[which]);
} else {
/* SysVstyle init assumed */
/*runlevels:
* 0 == shutdown
* 6 == reboot */
execlp(CONFIG_TELINIT_PATH,
CONFIG_TELINIT_PATH,
which== 2 ? "6" : "0",
(char*)NULL
);
bb_perror_msg_and_die("can'texecute '%s'",
CONFIG_TELINIT_PATH);
}
}
} else {
rc =reboot(magic[which]);
}
if (rc)
bb_perror_nomsg_and_die();
return rc;
}
进入linux内核后,实现位于kernel/reboot.c, 函数原型如下:
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(reboot,int, magic1, int, magic2, unsigned int, cmd,
void __user *, arg)
该函数的参数解释如下:
magic1、magic2:两个int类型的magic,用于防止误操作。
cmd: reboot方式。
arg:其它的额外参数。
magic1、magic2、cmd具体在 include/uapi/linux/reboot.h 中定义。
reboot 方式:
位于: include/uapi/linux/reboot.h
/*
* Commands accepted by the _reboot() systemcall.
*
* RESTART Restart system using default command and mode.
* HALT Stop OS and give system control to ROM monitor, if any.
* CAD_ON Ctrl-Alt-Del sequence causes RESTART command.
* CAD_OFF Ctrl-Alt-Del sequence sends SIGINT to init task.
* POWER_OFF Stop OS and remove all power from system, if possible.
* RESTART2 Restart system using given command string.
* SW_SUSPEND Suspend system using software suspend if compiled in.
* KEXEC Restart system using a previously loaded Linux kernel
*/
#define LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_RESTART 0x01234567
#define LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_HALT 0xCDEF0123
#define LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_CAD_ON 0x89ABCDEF
#define LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_CAD_OFF 0x00000000
#define LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_POWER_OFF 0x4321FEDC
#define LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_RESTART2 0xA1B2C3D4
#define LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_SW_SUSPEND 0xD000FCE2
#define LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_KEXEC 0x45584543
kernel_restart 函数实现
/**
* kernel_restart- reboot the system
* @cmd:pointer to buffer containing command to execute for restart
* or%NULL
*
* Shutdowneverything and perform a clean reboot.
* Thisis not safe to call in interrupt context.
*/
voidkernel_restart(char *cmd)
{
kernel_restart_prepare(cmd);
migrate_to_reboot_cpu();
syscore_shutdown();
if (!cmd)
pr_emerg("Restartingsystem\n");
else
pr_emerg("Restarting system withcommand '%s'\n", cmd);
kmsg_dump(KMSG_DUMP_RESTART);
machine_restart(cmd);
}
说明:
Ø 调用kernel_restart_prepare,前期准备工作
Ø 调用migrate_to_reboot_cpu(); 将当前的进程(task)移到一个CPU上; 对于多CPU的机器,无论哪个CPU触发了当前的系统调用,代码都可以运行在任意的CPU上。这个接口将代码分派到一个特定的CPU上,并禁止调度器分派代码到其它CPU上。也就是说,这个接口被执行后,只有一个CPU在运行,用于完成后续的reboot动作。
Ø 调用syscore_shutdown接口,将系统核心器件关闭(例如中断等);
Ø 调用printk以及kmsg_dump,打印日志;
Ø 最后,machine_restart。
machine_restart是属于Architecture相关的处理函数,如ARM。ARM在“arch/arm/kernel/process.c”中实现,具体如下:
/*
* Restart requires that the secondary CPUsstop performing any activity
* while the primary CPU resets the system.Systems with a single CPU can
* use soft_restart() as their machinedescriptor's .restart hook, since that
* will cause the only available CPU to reset.Systems with multiple CPUs must
* provide a HW restart implementation, toensure that all CPUs reset at once.
* This is required so that any code runningafter reset on the primary CPU
* doesn't have to co-ordinate with other CPUsto ensure they aren't still
* executing pre-reset code, and using RAM thatthe primary CPU's code wishes
* to use. Implementing such co-ordinationwould be essentially impossible.
*/
voidmachine_restart(char *cmd)
{
local_irq_disable();
smp_send_stop();
/* Flush the console to make sure all therelevant messages make it
* outto the console drivers */
arm_machine_flush_console();
if (arm_pm_restart)
arm_pm_restart(reboot_mode, cmd);
else
do_kernel_restart(cmd);
/* Give a grace period for failure torestart of 1s */
mdelay(1000);
/* Whoops - the platform was unable toreboot. Tell the user! */
printk("Reboot failed -- Systemhalted\n");
local_irq_disable();
while (1);
}
接口注释, 大意如下:
1)单CPU系统时,可以直接用soft_restart 实现reboot。
2)多CPU系统时,当主CPU重置系统时,重启要求辅助CPU停止执行任何活动。
系统的多个CPU必须提供一个硬件启动实施,确保所有的CPU复位一次。以保证所有CPU同步重启。
函数实现:
1)调用smp_send_stop接口,确保其它CPU处于非活动状态;
2)arm_pm_restart,实现真正的restart。在“arch/arm/kernel/process.c”声明。
void (*arm_pm_restart)(enum reboot_mode reboot_mode,const char *cmd);
3)等待1s;
4)如果没有返回,则restart成功,否则失败,打印错误信息。
arm_pm_restart 在arch/arm 中对应平台restart函数,执行复位动作。
高通平台arch/arm/mach-msm 目前代码无restart函数,
那么就执行do_kernel_restart(cmd);
其它平台例子:
arch/arm/mach-omap2/board-omap3logic.c
MACHINE_START(OMAP3_TORPEDO, "LogicOMAP3 Torpedo board")
.atag_offset = 0x100,
.reserve = omap_reserve,
.map_io = omap3_map_io,
.init_early = omap35xx_init_early,
.init_irq = omap3_init_irq,
.init_machine = omap3logic_init,
.init_late = omap35xx_init_late,
.init_time = omap3_sync32k_timer_init,
.restart = omap3xxx_restart,
MACHINE_END
omap3xxx_restart 开始触发硬件复位
/**
*omap3xxx_restart - trigger a software restart of the SoC
*@mode: the "reboot mode", see arch/arm/kernel/{setup,process}.c
*@cmd: passed from the userspace program rebooting the system (if provided)
*
*Resets the SoC. For @cmd, see the'reboot' syscall in
*kernel/sys.c. No return value.
*/
void omap3xxx_restart(enum reboot_modemode, const char *cmd)
{
omap3_ctrl_write_boot_mode((cmd? (u8)*cmd : 0));
omap3xxx_prm_dpll3_reset();/* never returns */
while(1);
}
参数cmd,每个平台可以自已定义,比如bootloader,recovery。
例子,应用层到驱动的流程:
androidrecovery模式启动进入流程
http://blog.csdn.net/yzhang8703/article/details/7166593