【二叉搜索树】1305. 两棵二叉搜索树中的所有元素(非递归中序遍历)
题目
给你 root1 和 root2 这两棵二叉搜索树。
请你返回一个列表,其中包含 两棵树 中的所有整数并按 升序 排序。.
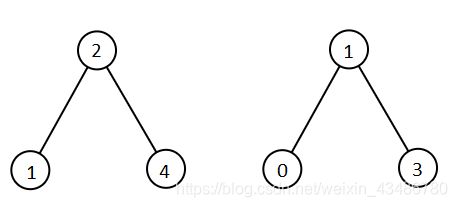
输入:root1 = [2,1,4], root2 = [1,0,3]
输出:[0,1,1,2,3,4]
示例 2:
输入:root1 = [0,-10,10], root2 = [5,1,7,0,2]
输出:[-10,0,0,1,2,5,7,10]
示例 3:
输入:root1 = [], root2 = [5,1,7,0,2]
输出:[0,1,2,5,7]
示例 4:
输入:root1 = [0,-10,10], root2 = []
输出:[-10,0,10]
输入:root1 = [1,null,8], root2 = [8,1]
输出:[1,1,8,8]
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/all-elements-in-two-binary-search-trees
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
最简单的思路是遍历两棵树,将所有元素放到一个数组里,然后对数组排序。
由于二叉搜索树本来就是有序的,因此本文采用的是同时中序遍历两颗二叉搜索树,这里需要采用非递归的方式中序遍历二叉树,代码如下
public void InOrder(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode curNode = root;
while (curNode != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (curNode != null) {
// 将所有左孩子入队
stack.push(curNode);
curNode = curNode.left;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode tmpNode = stack.pop();
System.out.print(tmpNode.val + " ");
curNode = tmpNode.right; // 移动到右孩子处(可能为null)
}
}
}
基于上述代码,同时中序遍历两颗二叉树,在遍历时,分别比较栈顶元素的大小,把小的元素添加到结果列表中,然后移动小元素所在的二叉树(即访问下一个节点),而另一颗二叉树不动,直到他的栈顶元素比另一颗树的小时才访问其它节点。
需要注意当有一个栈为空时,则表明其中一颗二叉树已经访问完了,此时只需中序遍历另一颗树即可。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> getAllElements(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<>(), stack2 = new Stack<>();
TreeNode curNode1 = root1, curNode2 = root2;
List<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
while (curNode1 != null || !stack1.isEmpty() || curNode2 != null || !stack2.isEmpty()) {
while (curNode1 != null) {
stack1.push(curNode1);
curNode1 = curNode1.left;
}
while (curNode2 != null) {
stack2.push(curNode2);
curNode2 = curNode2.left;
}
if (stack1.isEmpty()) {
// 中序遍历stack2
TreeNode topNode2 = stack2.pop();
res.add(topNode2.val);
curNode2 = topNode2.right;
} else if (stack2.isEmpty()) {
// 中序遍历stack1
TreeNode topNode1 = stack1.pop();
res.add(topNode1.val);
curNode1 = topNode1.right;
} else {
TreeNode topNode1 = stack1.peek();
TreeNode topNode2 = stack2.peek();
if (topNode1.val <= topNode2.val) {
stack1.pop();
res.add(topNode1.val);
curNode1 = topNode1.right;
} else {
stack2.pop();
res.add(topNode2.val);
curNode2 = topNode2.right;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}