Java文件输入流和输出流实战分析(适合小白)
Java API中,可以从其中读入一个字节序列的对象称为输入流,而可以从其中写入一个字节序列的对象称为输出流,这两个流我们涉及最多的是InputStream和OutputStream两个抽象类。本文是我阅读《Java核心技术第二卷》的心得体会,代码都是我结合具体的场景编写,相信初学输入流输出流的读者看完一定能准确区分两种流。最后,创作不易,点赞、收藏、关注三连,蟹蟹~
一、输入流和文件输入流
1、初探read方法
首先,InputStream类有一个抽象方法:abstract int read()
这个方法将读入一个字节,并返回读入的字节,或者到输入末尾时返回-1。注意:由于InputStream实际中很少直接使用,我们大多用的是InputStream的子类,其中最常用的是FileInputStream,其中FileInputStream类重写了InputStream类的read方法。
此处搬上JDK源码作为参照:
InputStream的read()源码:
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
ensureOpen();
return -1;
}下图中注释部分说道:从这个输入流中读取一个字节的数据。如果没有输入可用于读,这个方法会阻塞。返回下一个字节。如果到文件末尾则返回-1。
/**
* Reads a byte of data from this input stream. This method blocks
* if no input is yet available.
*
* @return the next byte of data, or {@code -1} if the end of the
* file is reached.
* @throws IOException if an I/O error occurs.
*/
public int read() throws IOException {
return read0();
}下面具体举例。
打开IDEA(千万不要再用万恶的Eclipse了,这东西压根不好使),创建一个文本文件Test.txt,文件内容为:Hello!
建立Test.java文件,首先得创建文件对象:File file = new File("E:\\喷涂问题\\Test.txt");
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("E:\\喷涂问题\\Test.txt");
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(file);
int read = in.read();
System.out.println(read);
}
}输出:72。
或许有人好奇为什么输出了一个数字呢?其实这就是H字母对应的ASCII码!
经过查表得出H,e,l,l,o,!对应的ASCII码分别为72 101 108 108 111 33,所以我们只需要将整型转化为字符型即可。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("E:\\喷涂问题\\Test.txt");
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(file);
int read = in.read();
char text=(char)read;
System.out.println(text);
}
}这样就可以输出:H
2、readAllBytes方法
如果单单用read方法,比如上例中则要一个一个读取'H','E','L'...,显然太慢了,而且不方便。因此从Java9开始,提供了一个readAllBytes()方法,这个方法直接将输入流中的所有字符读入到一个字节数组中。那么再通过转换就可以一次性输出文本信息了!
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("E:\\喷涂问题\\Test.txt");
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = in.readAllBytes();
for (byte Byte : bytes) {
char c=(char)Byte;
System.out.print(c);
}
}
}
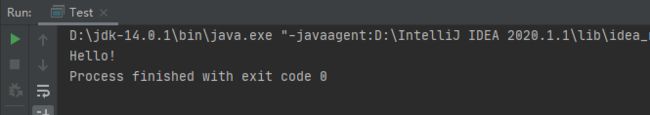
控制台输出:
二、文件输出流
现在承上启下地阐释一下之前输入流整体步骤:
1、创建一个文本文件并输入一段文本Hello!
2、将文本信息通过输入流读取到字节数组byte[]中。
---------------------------------------------分割线------------------------------------------------
那么输出流呢?
当然是反过来了!!即将字节数组中已经有的数据输出到一个空的文本文件中。
在前面的基础上举例吧:
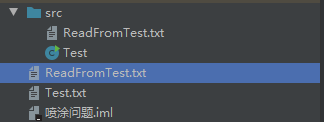
1、先创建一个空的文本文件ReadFromTest.txt。
2、创建一个代表空文件的对象file2,调用out.write()方法即可,可以理解为输出流已经和新文件绑定,将字节数组写入输出流就相当于写入了新文件中。
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file1 = new File("E:\\喷涂问题\\Test.txt");
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(file1);
byte[] bytes = in.readAllBytes();
//以上部分的代码将原来Test.txt中的hello!转移到字符数组bytes中了
File file2 = new File("E:\\喷涂问题\\ReadFromTest.txt");
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file2);
out.write(bytes);
}
}3、运行以上代码会发现新文件ReadFromTest.txt中出现了Hello!文本信息。
不知道为什么后面有个乱码,知道怎么消去的朋友可以留言区评论!