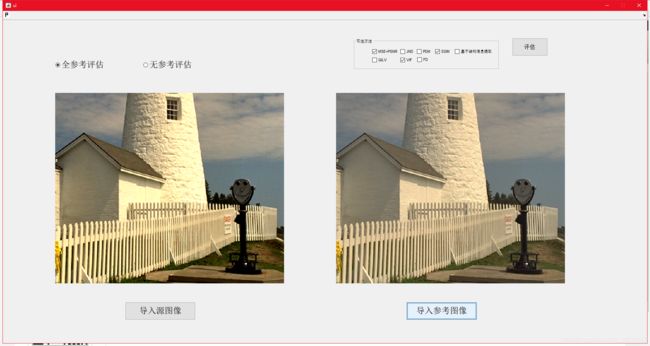
基于结构信息提取的图像质量评价的matlab实现
基于结构信息提取的图像质量评价(Structural Information Extraction),隶属于全参考的图像质量评估方法,是基于已提出的SSIM(structural similarity index),对图像进行离散余弦变换后,根据频率域的系数,将图像分为若干个部分后,对每个部分反变换(IDCT)到空间域,比较两个图像每个还原后部分的SSIM,并乘以对应部门的权重相加得到最后的综合SSIM即是两个图像基于结构信息提取的图像质量评价。原文:《基于结构信息提取的图像质量评价,叶盛楠,2008,电子学报》
使用原图像与参考图像如下:
主要步骤:设I1、I2分别为原图像和参考图像(最好先转为灰度图像),对两个图像依次进行如下处理:
1.对于图像I(I1或I2),先对图像I进行离散余弦变换(dct2),得到频率域图像I_dct;
[m,n]=size(I);
I_dct=dct2(I,[m n]);
2.设D(i,j)为点(i,j)到左上角的距离(欧式距离),A(i,j)为频率域图像I_dct在(1:i,1:j)的幅值(即这块区域的最大值减最小值);
D(i,j)=sqrt((i-1)^2+(j-1)^2);
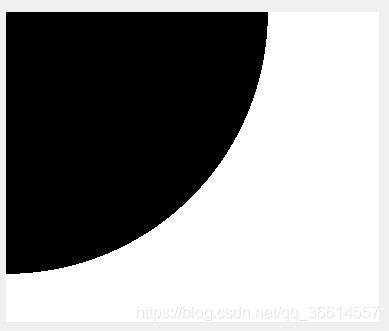
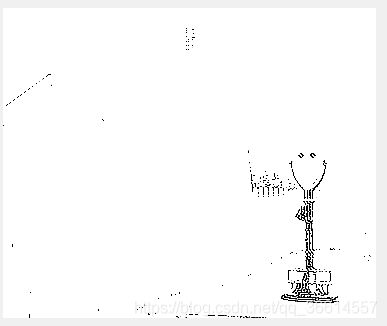
A(i,j)=max(max(I_dct(1:i,1:j)))-min(min(I_dct(1:i,1:j))); 3.根据频率阈值tf和能量阈值te将频率域图像I_dct分为以下三类:
如果D(i,j) 如果D(i,j)>tf 且A (i,j) >te那么该点属于第二类(结构信息类,I_dct_s) 如果D(i,j)>tf 且A (i,j) [通过一个和图像等大的矩阵,对不同点的对应位置标记上不同的数值实现,tf取D的均值,te取A的均值] (由于当时疏忽部分中间过程图像未转uint8格式,导致无法显示正常图像,其中IDCT后的低频图像应与原图像近似) (次要信息在边缘,只有一行一列,显示为灰色) 4.根据分类结果,提取出分类的每一个部分,(剩下的取0),分别对每个部分进行还原(idct2): 5.对两个输入图像还原的每个部分的图像进行计算ssim,最后根据不同的权值计算最后得到的综合ssim,即要求的SIExt值。 计算图像DCT分类后还原的函数:(返回三个还原后的图像,即上面的三个截图) 对两个图像求SIExt的代码:(根据原文章,结构信息的权值较大,另外两个较小) 附:求两个图像SSIM的函数: function [I_l,I_s,I_n]=getSI(I)%返回对DCT解构后再进行IDCT的图像
[m,n]=size(I);
I_dct=dct2(I,[m n]);
D=zeros(m,n);%D(i,j) :点(i,j) 到左上角距离
A=zeros(m,n);%A(i,j)为I_dct(i,j)的幅值(max-min)
map=zeros(m,n);%map: I_dct(i,j)对应的分类结果 0=低频系数 100-结构信息系数 200-次要信息系数
for i=1:m
for j=1:n %计算D\A
D(i,j)=sqrt((i-1)^2+(j-1)^2);
A(i,j)=max(max(I_dct(1:i,1:j)))-min(min(I_dct(1:i,1:j)));
end
end
tf=mean(mean(D));%频率阈值
te=mean(mean(A));%能量阈值
for i=1:m
for j=1:n
if(D(i,j)function[siext]= SIExt(I1,I2) %I1复原图像 I2 参考图像
I1=double(rgb2gray(I1));
I2=double(rgb2gray(I2));
if size(I1)~=size(I2)
siext=-Inf;
return
end
[I1_l,I1_s,I1_n]=getSI(I1);
[I2_l,I2_s,I2_n]=getSI(I2);
[sl,map]=ssim(I1_l,I2_l);
[ss,map]=ssim(I1_s,I2_s);
[sn,map]=ssim(I1_n,I2_n);
wl=0.1;%权值
ws=0.8;
wn=0.1;
siext=wl*sl+ws*ss+wn*sn;
endfunction [mssim, ssim_map] = ssim(img1, img2, K, window, L)
% ========================================================================
% SSIM Index with automatic downsampling, Version 1.0
% Copyright(c) 2009 Zhou Wang
% All Rights Reserved.
%
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------
% Permission to use, copy, or modify this software and its documentation
% for educational and research purposes only and without fee is hereby
% granted, provided that this copyright notice and the original authors'
% names appear on all copies and supporting documentation. This program
% shall not be used, rewritten, or adapted as the basis of a commercial
% software or hardware product without first obtaining permission of the
% authors. The authors make no representations about the suitability of
% this software for any purpose. It is provided "as is" without express
% or implied warranty.
%----------------------------------------------------------------------
%
% This is an implementation of the algorithm for calculating the
% Structural SIMilarity (SSIM) index between two images
%
% Please refer to the following paper and the website with suggested usage
%
% Z. Wang, A. C. Bovik, H. R. Sheikh, and E. P. Simoncelli, "Image
% quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity,"
% IEEE Transactios on Image Processing, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 600-612,
% Apr. 2004.
%
% http://www.ece.uwaterloo.ca/~z70wang/research/ssim/
%
% Note: This program is different from ssim_index.m, where no automatic
% downsampling is performed. (downsampling was done in the above paper
% and was described as suggested usage in the above website.)
%
% Kindly report any suggestions or corrections to [email protected]
%
%----------------------------------------------------------------------
%
%Input : (1) img1: the first image being compared
% (2) img2: the second image being compared
% (3) K: constants in the SSIM index formula (see the above
% reference). defualt value: K = [0.01 0.03]
% (4) window: local window for statistics (see the above
% reference). default widnow is Gaussian given by
% window = fspecial('gaussian', 11, 1.5);
% (5) L: dynamic range of the images. default: L = 255
%
%Output: (1) mssim: the mean SSIM index value between 2 images.
% If one of the images being compared is regarded as
% perfect quality, then mssim can be considered as the
% quality measure of the other image.
% If img1 = img2, then mssim = 1.
% (2) ssim_map: the SSIM index map of the test image. The map
% has a smaller size than the input images. The actual size
% depends on the window size and the downsampling factor.
%
%Basic Usage:
% Given 2 test images img1 and img2, whose dynamic range is 0-255
%
% [mssim, ssim_map] = ssim(img1, img2);
%
%Advanced Usage:
% User defined parameters. For example
%
% K = [0.05 0.05];
% window = ones(8);
% L = 100;
% [mssim, ssim_map] = ssim(img1, img2, K, window, L);
%
%Visualize the results:
%
% mssim %Gives the mssim value
% imshow(max(0, ssim_map).^4) %Shows the SSIM index map
%========================================================================
if (nargin < 2 | nargin > 5)
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
if (size(img1) ~= size(img2))
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
[M N] = size(img1);
if (nargin == 2)
if ((M < 11) | (N < 11))
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
window = fspecial('gaussian', 11, 1.5); %
K(1) = 0.01; % default settings
K(2) = 0.03; %
L = 255; %
end
if (nargin == 3)
if ((M < 11) | (N < 11))
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
window = fspecial('gaussian', 11, 1.5);
L = 255;
if (length(K) == 2)
if (K(1) < 0 | K(2) < 0)
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
else
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
end
if (nargin == 4)
[H W] = size(window);
if ((H*W) < 4 | (H > M) | (W > N))
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
L = 255;
if (length(K) == 2)
if (K(1) < 0 | K(2) < 0)
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
else
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
end
if (nargin == 5)
[H W] = size(window);
if ((H*W) < 4 | (H > M) | (W > N))
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
if (length(K) == 2)
if (K(1) < 0 | K(2) < 0)
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
else
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
end
img1 = double(img1);
img2 = double(img2);
% automatic downsampling
f = max(1,round(min(M,N)/256));
%downsampling by f
%use a simple low-pass filter
if(f>1)
lpf = ones(f,f);
lpf = lpf/sum(lpf(:));
img1 = imfilter(img1,lpf,'symmetric','same');
img2 = imfilter(img2,lpf,'symmetric','same');
img1 = img1(1:f:end,1:f:end);
img2 = img2(1:f:end,1:f:end);
end
C1 = (K(1)*L)^2;
C2 = (K(2)*L)^2;
window = window/sum(sum(window));
mu1 = filter2(window, img1, 'valid');
mu2 = filter2(window, img2, 'valid');
mu1_sq = mu1.*mu1;
mu2_sq = mu2.*mu2;
mu1_mu2 = mu1.*mu2;
sigma1_sq = filter2(window, img1.*img1, 'valid') - mu1_sq;
sigma2_sq = filter2(window, img2.*img2, 'valid') - mu2_sq;
sigma12 = filter2(window, img1.*img2, 'valid') - mu1_mu2;
if (C1 > 0 & C2 > 0)
ssim_map = ((2*mu1_mu2 + C1).*(2*sigma12 + C2))./((mu1_sq + mu2_sq + C1).*(sigma1_sq + sigma2_sq + C2));
else
numerator1 = 2*mu1_mu2 + C1;
numerator2 = 2*sigma12 + C2;
denominator1 = mu1_sq + mu2_sq + C1;
denominator2 = sigma1_sq + sigma2_sq + C2;
ssim_map = ones(size(mu1));
index = (denominator1.*denominator2 > 0);
ssim_map(index) = (numerator1(index).*numerator2(index))./(denominator1(index).*denominator2(index));
index = (denominator1 ~= 0) & (denominator2 == 0);
ssim_map(index) = numerator1(index)./denominator1(index);
end
mssim = mean2(ssim_map);
return