K8s之持久化卷(PV和PVC)
1. Persistent Volumes简介
PersistentVolume(持久卷,简称PV)是集群内,由管理员提供的网络存储的一部分。就像集群中的节点一样,PV也是集群中的一种资源。它也像Volume一样,是一种volume插件,但是它的生命周期却是和使用它的Pod相互独立的。PV这个API对象,捕获了诸如NFS、ISCSI、或其他云存储系统的实现细节。
PersistentVolumeClaim(持久卷声明,简称PVC)是用户的一种存储请求。它和Pod类似,Pod消耗Node资源,而PVC消耗PV资源。Pod能够请求特定的资源(如CPU和内存)。PVC能够请求指定的大小和访问的模式(可以被映射为一次读写或者多次只读)。
两种PV提供的方式:静态和动态
静态PV:集群管理员创建多个PV,它们携带着真实存储的详细信息,这些存储对于集群用户是可用的。它们存在于Kubernetes API中,并可用于存储使用。
动态PV:当管理员创建的静态PV都不匹配用户的PVC时,集群可能会尝试专门地供给volume给PVC。这种供给基于StorageClass。
PVC与PV的绑定是一对一的映射。没找到匹配的PV,那么PVC会无限期得处于unbound未绑定状态。
2. PV和PVC的生命周期
使用
Pod使用PVC就像使用volume一样。集群检查PVC,查找绑定的PV,并映射PV给Pod。对于支持多种访问模式的PV,用户可以指定想用的模式。一旦用户拥有了一个PVC,并且PVC被绑定,那么只要用户还需要,PV就一直属于这个用户。用户调度Pod,通过在Pod的volume块中包含PVC来访问PV。
释放
当用户使用PV完毕后,他们可以通过API来删除PVC对象。当PVC被删除后,对应的PV就被认为是已经是“released”了,但还不能再给另外一个PVC使用。前一个PVC的属于还存在于该PV中,必须根据策略来处理掉。
回收
PV的回收策略告诉集群,在PV被释放之后集群应该如何处理该PV。当前,PV可以被Retained(保留)、 Recycled(再利用)或者Deleted(删除)。保留允许手动地再次声明资源。对于支持删除操作的PV卷,删除操作会从Kubernetes中移除PV对象,还有对应的外部存储(如AWS EBS,GCE PD,Azure Disk,或者Cinder volume)。动态供给的卷总是会被删除。
3. NFS PV 示例
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: pv1
spec:
capacity:
storage: 1Gi
volumeMode: Filesystem
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Recycle
storageClassName: slow
mountOptions:
- hard
- nfsvers=4.1
nfs:
path: /nfsdata
server: 172.25.254.4
几点说明:
访问模式
ReadWriteOnce – 该volume只能被单个节点以读写的方式映射
ReadOnlyMany – 该volume可以被多个节点以只读方式映射
ReadWriteMany – 该volume可以被多个节点以读写的方式映射
在命令行中,访问模式可以简写为:
RWO - ReadWriteOnce
ROX - ReadOnlyMany
RWX - ReadWriteMany
回收策略
Retain:保留,需要手动回收
Recycle:回收,自动删除卷中数据
Delete:删除,相关联的存储资产,如AWS EBS,GCE PD,Azure Disk,or OpenStack Cinder卷都会被删除
当前,只有NFS和HostPath支持回收利用,AWS EBS,GCE PD,Azure Disk,or OpenStack Cinder卷支持删除操作。
状态:
Available:空闲的资源,未绑定给PVC
Bound:绑定给了某个PVC
Released:PVC已经删除了,但是PV还没有被集群回收
Failed:PV在自动回收中失败了
命令行可以显示PV绑定的PVC名称。
4. NFS持久化存储实战(静态PV)
(1)安装配置NFS服务
# yum install -y nfs-utils
# mkdir -m 777 /nfsdata
# vim /etc/exports
/nfsdata *(rw,sync,no_root_squash)
# systemctl enable --now rpcbind
# systemctl enbale --now nfs
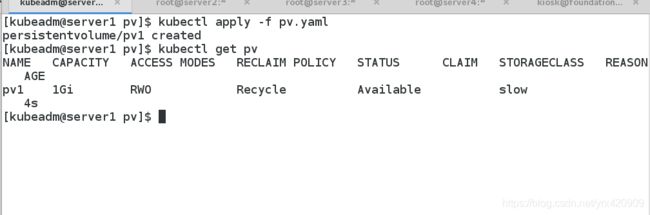
(2) 创建NFS PV卷
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: nfs-pv1
spec:
capacity:
storage: 1Gi
volumeMode: Filesystem
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Recycle
storageClassName: nfs
nfs:
path: /nfsdata
server: 172.25.254.4
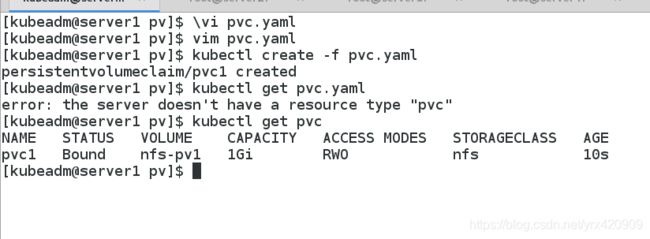
vim pvc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: pvc1
spec:
storageClassName: nfs
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
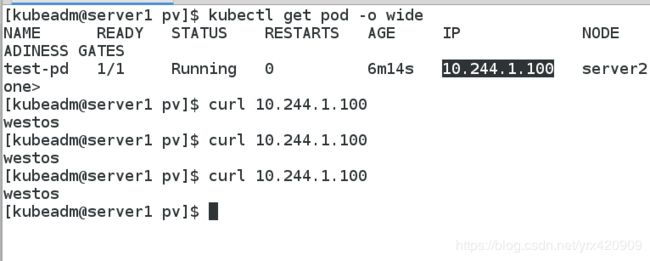
vim pod.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-pd
spec:
containers:
- image: reg.westos.org/k8s/nginx
name: nginx
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
name: pv1
volumes:
- name: pv1
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: pvc1
上述我们学习了 PV 和 PVC 的使用方法,但是前面的 PV 都是静态的,什么意思?就是我要使用的一个 PVC 的话就必须手动去创建一个 PV,我们也说过这种方式在很大程度上并不能满足我们的需求,比如我们有一个应用需要对存储的并发度要求比较高,而另外一个应用对读写速度又要求比较高,特别是对于 StatefulSet 类型的应用简单的来使用静态的 PV 就很不合适了,这种情况下我们就需要用到动态 PV,也就是我们接下来要讲解的 StorageClass。
5. StorageClass简介
StorageClass提供了一种描述存储类(class)的方法,不同的class可能会映射到不同的服务质量等级和备份策略或其他策略等。
每个 StorageClass 都包含 provisioner、parameters 和 reclaimPolicy 字段, 这些字段会在StorageClass需要动态分配 PersistentVolume 时会使用到。
StorageClass的属性
Provisioner(存储分配器):用来决定使用哪个卷插件分配 PV,该字段必须指定。可以指定内部分配器,也可以指定外部分配器。外部分配器的代码地址为: kubernetes-incubator/external-storage,其中包括NFS和Ceph等。
Reclaim Policy(回收策略):通过reclaimPolicy字段指定创建的Persistent Volume的回收策略,回收策略包括:Delete 或者 Retain,没有指定默认为Delete。
更多属性查看:https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/concepts/storage/storage-classes/
要使用 StorageClass,我们就得安装对应的自动配置程序,比如我们这里存储后端使用的是 nfs,那么我们就需要使用到一个 nfs-client 的自动配置程序,我们也叫它 Provisioner,这个程序使用我们已经配置好的 nfs 服务器,来自动创建持久卷,也就是自动帮我们创建 PV。
NFS Client Provisioner是一个automatic provisioner,
使用NFS作为存储,自动创建PV和对应的PVC,本身不提供NFS存储,
需要外部先有一套NFS存储服务。
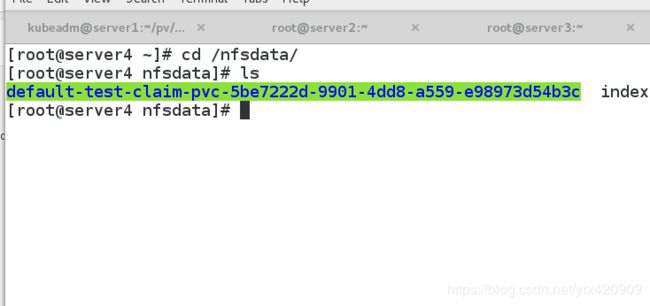
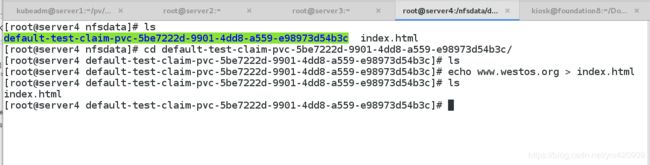
PV以 ${namespace}-${pvcName}-${pvName}的命名格式提供
(在NFS服务器上)
PV回收的时候以 archieved-${namespace}-${pvcName}-${pvName}
的命名格式(在NFS服务器上)
nfs-client-provisioner源码地址:
https://github.com/kubernetes-incubator/external-storage/tree/master/nfs-client
6. NFS动态分配PV示例
外部分配器链接
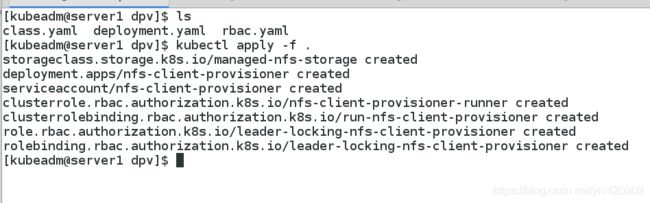
(1)配置授权
vim rbac.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumes"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "delete"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["persistentvolumeclaims"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "update"]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["storageclasses"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: run-nfs-client-provisioner
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: nfs-client-provisioner-runner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["endpoints"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch"]
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: leader-locking-nfs-client-provisioner
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
(2)部署NFS Client Provisioner
vim deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nfs-client-provisioner
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
# replace with namespace where provisioner is deployed
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
strategy:
type: Recreate
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nfs-client-provisioner
spec:
serviceAccountName: nfs-client-provisioner
containers:
- name: nfs-client-provisioner
image: reg.westos.org/k8s/nfs-client-provisioner:latest
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-client-root
mountPath: /persistentvolumes
env:
- name: PROVISIONER_NAME
value: westos/nfs
- name: NFS_SERVER
value: 172.25.254.4
- name: NFS_PATH
value: /nfsdata
volumes:
- name: nfs-client-root
nfs:
server: 172.25.254.4
path: /nfsdata
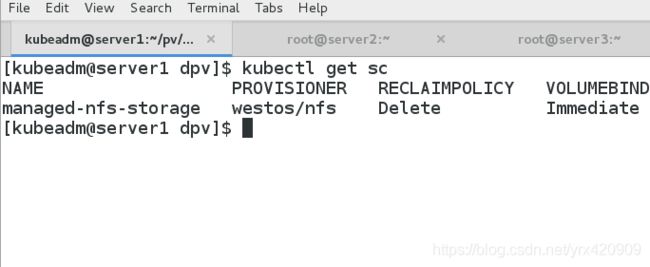
(3)创建 NFS SotageClass
vim class.yaml
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: managed-nfs-storage
provisioner: westos/nfs # or choose another name, must match deployment's env PROVISIONER_NAME'
parameters:
archiveOnDelete: "false"
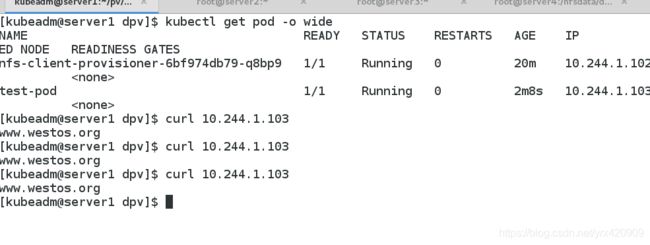
[kubeadm@server1 dpv]$ kubectl get all
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nfs-client-provisioner-6bf974db79-q8bp9 1/1 Running 0 59s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 443/TCP 12d
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/nfs-client-provisioner 1/1 1 1 60s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/nfs-client-provisioner-6bf974db79 1 1 1 60s
[kubeadm@server1 dpv]$
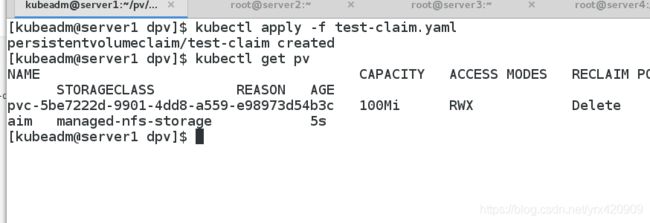
(4)创建PVC
vim test-claim.yaml
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: test-claim
annotations:
volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-class: "managed-nfs-storage"
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 100Mi
按需自动分配pv
删除pvc后pv也将不复存在
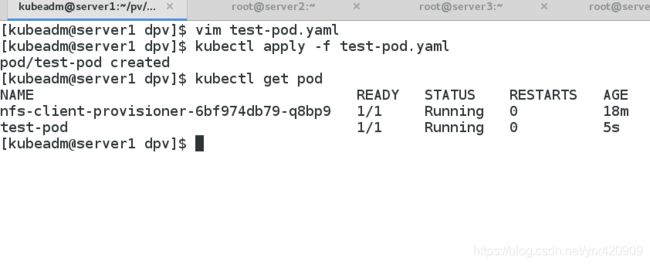
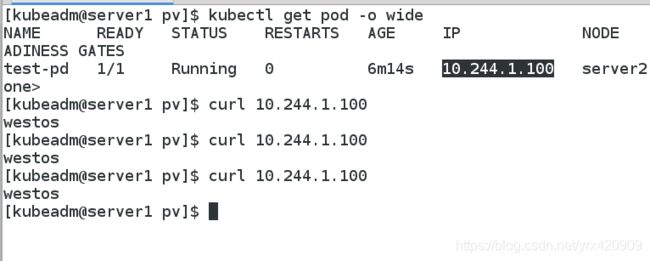
(5)创建测试Pod
vim test-pod.yaml
kind: Pod
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: test-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: test-pod
image: reg.westos.org/k8s/nginx
volumeMounts:
- name: nfs-pvc
mountPath: "/usr/share/nginx/html"
volumes:
- name: nfs-pvc
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: test-claim