【题目大意】
有一棵树,m次操作。对于一次操作:x y z,意思是对于点x到点y的路径上,每个点都添加种类为z的一个食物。操作完成后,每个点都有若干种食物,每种食物有一定的数量。对于每个点,输出该点数量最多的那种食物,如果有多种,输出种类编号最小的,如果没有,输出0。
【思路】
拿到这种题,想到树链剖分是不难的。
如果直接维护的话,因为食物的种类太多,复杂度显然过高。但是注意到,树链剖分,剖分后,实际上是类似于线段树的维护。我们把操作定在线段的树的节点上,每个点的最后情况,就是线段树的根到对应叶子节点的所有操作和。
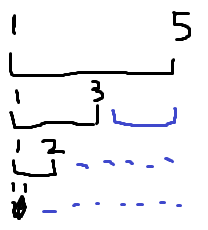
举个例子吧。树链剖分后,操作的实质就是对某个区间添加一种食物z,数量为1。最后的答案就是每个点数目最多的食物。我们将操作定在线段树节点上(不做任何下传),如果有5个点,最后点1的的食物情况,就是下图中,黑色线段中所有操作的和。
那么,如果在外部,用另外一个线段树维护食物的情况,扫一下原来的那个线段树,这题就能做了。
但是,很遗憾,这样会T。。。原来一个操作,最多能分成log(n)个连续线段,一个线段,在线段树上最多能分成log(n)个节点。那么,最开始的那个线段树上最多有log(n)^2个操作,外部又用线段树维护,总复杂度最坏为n*log(n)^3。
我们回到,“原题中的一个操作,树剖后,就是对log(n)个线段进行操作”这点。突然想到,如果我们在线段首部添加这个操作,然后在线段末部删掉这种操作,最后扫一下这个整个线段不就好了!这样的话,总操作数会下降到n*log(n)*2。最坏复杂度为n*log(n)^2。
P.S. 赛后发现,这题居然是原题,顿时觉得世界满满的恶意。。。
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000")
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
