Kafka Consumer如何实现exactly once/at least once
目录
- 消费端幂等性
- 消费时出现几种异常情况
- 自动提交
- 手动提交
- 精确一次消费实现
- 总结
- 至少消费一次
消费端幂等性
kafka具有两种提交offset(消费偏移量)方式,在Kafka每个分区具备一offset记录消费位置,如果消费者一直处于正常的运行转态,那么offset将没有什么用处,因为正常消费时,consumer记录了本次消费的offset和下一次将要进行poll数据的offset起始位置,但是如果消费者发生崩溃或者有新的消费者加入消费者组,就会触发再均衡Rebalance,Rebalance之后,每个消费者将会分配到新的分区,而消费者对于新的分区应该从哪里进行起始消费,这时候提交的offset信息就起作用了,提交的offset信息包括消费者组所有分区的消费进度,这时候消费者可以根据消费进度继续消费,offset自动提交是最不具确定性的,所以要使用手动提交来控制offset
消费时出现几种异常情况
自动提交
- 重复消费:当数据已经被处理,然后自动提交offset时消费者出现故障或者有新消费者加入组导致再均衡,这时候offset提交失败,导致这批已经处理的数据的信息没有记录,后续会重复消费一次
- 丢失数据:如果业务处理时间较长一点,这时候数据处理业务还未完成,offset信息已经提交了,但是在后续处理数据过程中程序发生了崩溃,导致这批数据未正常消费,这时候offset已经提交,消费者后续将不在消费这批数据,导致这批数据将会丢失
手动提交
- 重复消费(最少一次消费语义实现):消费数据处理业务完成后进行offset提交,可以保证数据最少一次消费,因为在提交offset的过程中可能出现提交失败的情况,导致数据重复消费
- 丢失数据(最多一次消费语义实现):在消费数据业务处理前进行offset提交,可以保证最多一次消费,在后续数据业务处理程序出现故障,将导致数据丢失
精确一次消费实现
offset手动提交,业务逻辑成功处理后,提交offset
解决方案:
- 对于流程中的消息,每条消息中包含唯一id,比如业务id,在数据库中将业务id作为Unique key,插入重复时会报duplicate key异常,不会导致数据库中出现脏数据
- Redis中使用set存储业务id,天然幂等性
- 如果不是上面两个场景,需要让生产者发送每条数据的时候,里面加一个全局唯一的 id,然后你这里消费到了之后,先根据这个 id 去比如 Redis 里查一下消费过吗?如果没有消费过,就处理,然后这个 id 写 Redis。如果消费过了,那就别处理了,保证不重复处理相同的消息即可
自行控制offset的准确性,这里数据不具备状态,存储使用关系型数据库,比如MySQL。这里简单说明一下实现思路:
1)利用consumer api的seek方法可以指定offset进行消费,在启动消费者时查询数据库中记录的offset信息,如果是第一次启动,那么数据库中将没有offset信息,需要进行消费的元数据插入,然后从offset=0开始消费
2)关系型数据库具备事务的特性,当数据入库时,同时也将offset信息更新,借用关系型数据库事务的特性保证数据入库和修改offset记录这两个操作是在同一个事务中进行
3)使用ConsumerRebalanceListener来完成在分配分区时和Relalance时作出相应的处理逻辑
记录kafka信息表设计
create table kafka_info(
topic_group_partition varchar(32) primary key, //主题+组名+分区号 这里冗余设计方便通过这个主键进行更新提升效率
topic_group varchar(30), //主题和组名
partition_num tinyint,//分区号
offsets bigint default 0 //offset信息
);
代码实现
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.*;
import org.apache.kafka.common.PartitionInfo;
import org.apache.kafka.common.TopicPartition;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.*;
public class AccurateConsumer {
private static final Properties props = new Properties();
private static final String GROUP_ID = "Test";
static {
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "192.168.142.139:9092");
props.put("group.id", GROUP_ID);
props.put("enable.auto.commit", false);//注意这里设置为手动提交方式
props.put("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
props.put("value.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
}
final KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer;
//用于记录每次消费时每个partition的最新offset
private Map<TopicPartition, Long> partitionOffsetMap;
//用于缓存接受消息,然后进行批量入库
private List<Message> list;
private volatile boolean isRunning = true;
private final String topicName;
private final String topicNameAndGroupId;
public AccurateConsumer(String topicName) {
this.topicName = topicName;
topicNameAndGroupId = topicName + "_" + GROUP_ID;
consumer = new KafkaConsumer<>(props);
consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList(topicName), new HandleRebalance());
list = new ArrayList<>(100);
partitionOffsetMap = new HashMap<>();
}
//这里使用异步提交和同步提交的组合方式
public void receiveMsg() {
try {
while (isRunning) {
ConsumerRecords<String, String> consumerRecords = consumer.poll(Duration.ofSeconds(1));
if (!consumerRecords.isEmpty()) {
for (TopicPartition topicPartition : consumerRecords.partitions()) {
List<ConsumerRecord<String, String>> records = consumerRecords.records(topicPartition);
for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records) {
//使用fastjson将记录中的值转换为Message对象,并添加到list中
list.addAll(JSON.parseArray(record.value(), Message.class));
}
//将partition对应的offset信息添加到map中,入库时将offset-partition信息一起进行入库
partitionOffsetMap.put(topicPartition, records.get(records.size() - 1)
.offset() + 1);//记住这里一定要加1,因为下次消费的位置就是从+1的位置开始
}
}
//如果list中存在有数据,则进行入库操作
if (list.size() > 0) {
boolean isSuccess = insertIntoDB(list, partitionOffsetMap);
if (isSuccess) {
//将缓存数据清空,并将offset信息清空
list.clear();
partitionOffsetMap.clear();
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
//处理异常
} finally {
//offset信息由我们自己保存,提交offset其实没有什么必要
//consumer.commitSync();
close();
}
}
private boolean insertIntoDB(List<Message> list, Map<TopicPartition, Long> partitionOffsetMap) {
Connection connection = getConnection();//获取数据库连接 自行实现
boolean flag = false;
try {
//设置手动提交,让插入数据和更新offset信息在一个事务中完成
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
insertMessage(list);//将数据进行入库 自行实现
updateOffset(partitionOffsetMap);//更新offset信息 自行实现
connection.commit();
flag = true;
} catch (SQLException e) {
try {
//出现异常则回滚事务
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
//处理异常
}
}
return flag;
}
//获取数据库连接 自行实现
private Connection getConnection() {
return null;
}
public void close() {
isRunning = false;
if (consumer != null) {
consumer.close();
}
}
private class HandleRebalance implements ConsumerRebalanceListener {
@Override
public void onPartitionsRevoked(Collection<TopicPartition> partitions) {
//发生Rebalance时,只需要将list中数据和记录offset信息清空即可
//这里为什么要清除数据,应为在Rebalance的时候有可能还有一批缓存数据在内存中没有进行入库,
//并且offset信息也没有更新,如果不清除,那么下一次还会重新poll一次这些数据,将会导致数据重复
list.clear();
partitionOffsetMap.clear();
}
@Override
public void onPartitionsAssigned(Collection<TopicPartition> partitions) {
//获取对应Topic的分区数
List<PartitionInfo> partitionInfos = consumer.partitionsFor(topicName);
Map<TopicPartition, Long> partitionOffsetMapFromDB = getPartitionOffsetMapFromDB
(partitionInfos.size());
//在分配分区时指定消费位置
for (TopicPartition partition : partitions) {
//如果在数据库中有对应partition的信息则使用,否则将默认从offset=0开始消费
if (partitionOffsetMapFromDB.get(partition) != null) {
consumer.seek(partition, partitionOffsetMapFromDB.get(partition));
} else {
consumer.seek(partition, 0L);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 从数据库中查询分区和offset信息
* @param size 分区数量
* @return 分区号和offset信息
*/
private Map<TopicPartition, Long> getPartitionOffsetMapFromDB(int size) {
Map<TopicPartition, Long> partitionOffsetMapFromDB = new HashMap<>();
//从数据库中查询出对应信息
Connection connection = getConnection();//获取数据库连接 自行实现
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
String querySql = "SELECT partition_num,offsets from kafka_info WHERE topic_group = ?";
try {
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(querySql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, topicNameAndGroupId);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()) {
partitionOffsetMapFromDB.put(new TopicPartition(topicName, resultSet.getInt(1)),
resultSet.getLong(2));
}
//判断数据库是否存在所有的分区的信息,如果没有,则需要进行初始化
if (partitionOffsetMapFromDB.size() < size) {
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
StringBuilder sqlBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//partition分区号是从0开始,如果有10个分区,那么分区号就是0-9
/*这里拼接插入数据 格式 INSERT INTO kafka_info(topic_group_partition,topic_group,partition_num) VALUES
(topicNameAndGroupId_0,topicNameAndGroupId,0),(topicNameAndGroupId_1, topicNameAndGroupId,1)....*/
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
sqlBuilder.append("(").append
(topicNameAndGroupId).append("_").append(i).append(",").append
(topicNameAndGroupId).append(",").append(i).append("),");
}
//将最后一个逗号去掉加上分号结束
sqlBuilder.deleteCharAt(sqlBuilder.length() - 1).append(";");
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO kafa_info" +
"(topic_group_partition,topic_group,partition_num) VALUES " + sqlBuilder.toString());
preparedStatement.execute();
connection.commit();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
//处理异常 回滚事务 这里应该结束程序 排查错误
try {
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
//打印日志 排查错误信息
}
} finally {
try {
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (preparedStatement != null) {
preparedStatement.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
//处理异常 打印日志即可 关闭资源失败
}
}
return partitionOffsetMapFromDB;
}
}
数据对象
public class Message {
private String id;
private String name;
private Syring desc;
private Date time;
//get set toString 方法省略
}
这种实现方式对于以下故障场景测试通过,虽然不能说所有故障场景均可以保证精确一次消费,但目前基本覆盖大部分故障场景
- 一个消费者组中的某个消费者频繁加入组或离开组
- 直接kill消费应用程序
- 故障kafka集群中某个节点
- 故障客户端网络,使其不能连接kafka server端
- 直接重启应用程序所在虚拟机
总结
这里主要使用自己管理offset的方式来确保数据和offset信息是同时变化的,通过数据库事务的特性来保证一致性和原子性。
至少消费一次
Kafka中由Consumer维护消费状态,当Consumer消费消息时,支持2种模式commit消费状态,分别为立即commit和周期commit。前者会导致性能低下,做到消息投递恰好一次;后者性能高,通常用于实际应用,但极端条件下无法保证消息不丢失。
问题分析
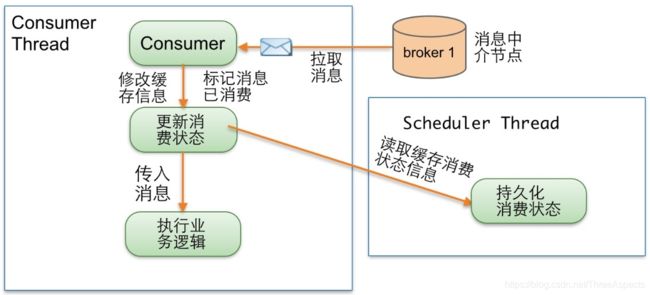
Consumer Thread读取一条消息,更新缓存消费状态,传入消息执行业务逻辑,同时有另外一个调度线程异步周期执行,从缓存中读取消费状态信息,持久化消费状态。假设Consumer Thread更新了缓存消费状态,Scheduler Thread在“执行业务逻辑”完成前就持久化消费状态,正在此时,Consumer失效或宕机了,这条消息就丢失了。
解决思路

等待“执行业务逻辑”成功完成后更新缓存消费状态,就可以保证消息不会丢失。具体做法:新增一个消费机制策略开关,此开关启动执行图2策略,关闭启动执行图1策略
import kafka.utils.{IteratorTemplate, Logging, Utils}
import java.util.concurrent.{TimeUnit, BlockingQueue}
import kafka.serializer.Decoder
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference
import kafka.message.{MessageAndOffset, MessageAndMetadata}
import kafka.common.{KafkaException, MessageSizeTooLargeException}
class ConsumerIterator[K, V](private val channel: BlockingQueue[FetchedDataChunk],
consumerTimeoutMs: Int,
private val keyDecoder: Decoder[K],
private val valueDecoder: Decoder[V],
val clientId: String, val consumerAtLeastOnceMessageEnabled: Boolean)
extends IteratorTemplate[MessageAndMetadata[K, V]] with Logging {
private var current: AtomicReference[Iterator[MessageAndOffset]] = new AtomicReference(null)
private var currentTopicInfo: PartitionTopicInfo = null
private var consumedOffset: Long = -1L
private val consumerTopicStats = ConsumerTopicStatsRegistry.getConsumerTopicStat(clientId)
override def next(): MessageAndMetadata[K, V] = {
val item = super.next()
if(consumedOffset < 0)
throw new KafkaException("Offset returned by the message set is invalid %d".format(consumedOffset))
if (consumerAtLeastOnceMessageEnabled)
currentTopicInfo.resetConsumeOffset(consumedOffset)
val topic = currentTopicInfo.topic
trace("Setting %s consumed offset to %d".format(topic, consumedOffset))
consumerTopicStats.getConsumerTopicStats(topic).messageRate.mark()
consumerTopicStats.getConsumerAllTopicStats().messageRate.mark()
item
}
protected def makeNext(): MessageAndMetadata[K, V] = {
var currentDataChunk: FetchedDataChunk = null
// if we don't have an iterator, get one
var localCurrent = current.get()
if(localCurrent == null || !localCurrent.hasNext) {
if (consumerTimeoutMs < 0)
currentDataChunk = channel.take
else {
currentDataChunk = channel.poll(consumerTimeoutMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
if (currentDataChunk == null) {
// reset state to make the iterator re-iterable
resetState()
throw new ConsumerTimeoutException
}
}
if(currentDataChunk eq ZookeeperConsumerConnector.shutdownCommand) {
debug("Received the shutdown command")
return allDone
} else {
currentTopicInfo = currentDataChunk.topicInfo
val cdcFetchOffset = currentDataChunk.fetchOffset
val ctiConsumeOffset = currentTopicInfo.getConsumeOffset
if (ctiConsumeOffset < cdcFetchOffset) {
error("consumed offset: %d doesn't match fetch offset: %d for %s;\n Consumer may lose data"
.format(ctiConsumeOffset, cdcFetchOffset, currentTopicInfo))
currentTopicInfo.resetConsumeOffset(cdcFetchOffset)
}
localCurrent = currentDataChunk.messages.iterator
current.set(localCurrent)
}
// if we just updated the current chunk and it is empty that means the fetch size is too small!
if(currentDataChunk.messages.validBytes == 0)
throw new MessageSizeTooLargeException("Found a message larger than the maximum fetch size of this consumer on topic " +
"%s partition %d at fetch offset %d. Increase the fetch size, or decrease the maximum message size the broker will allow."
.format(currentDataChunk.topicInfo.topic, currentDataChunk.topicInfo.partitionId, currentDataChunk.fetchOffset))
}
var item = localCurrent.next()
// reject the messages that have already been consumed
while (item.offset < currentTopicInfo.getConsumeOffset && localCurrent.hasNext) {
item = localCurrent.next()
}
consumedOffset = item.nextOffset
item.message.ensureValid() // validate checksum of message to ensure it is valid
new MessageAndMetadata(currentTopicInfo.topic, currentTopicInfo.partitionId, item.message, item.offset, keyDecoder, valueDecoder)
}
def clearCurrentChunk() {
try {
debug("Clearing the current data chunk for this consumer iterator")
current.set(null)
}
}
def resetConsumeOffset() {
if (!consumerAtLeastOnceMessageEnabled)
currentTopicInfo.resetConsumeOffset(consumedOffset)
}
}
class ConsumerTimeoutException() extends RuntimeException()