初识Shell 脚本,shell基础练习以及shell中常见命令的使用
Shell
1.什么是Shell?
shell也是操作系统的一个软件,它包在linux内核外面,为用户提供和内核之间的交互提供了一个接口。
系统中的命令用shell去解释;shell接收系统回应的输出并显示其到屏幕中
bash =GUN Bourne-Again Shell
2.什么是Shell脚本?
>脚本是一种解释性语言
>用Shell 脚本保存执行动作
>用脚本判定命令的执行条件
>用脚本来实现动作的批量执行 #也是脚本的意义所在
2.1>shell和shell 脚本的区别:
shell script是利用shell的功能所写的一个程序,这个程序是使用纯文本文件,将一些shell的语法与指令写在里面,然后用正规表示法,管道命令以及数据流重导向等功能,以达到我们所想要的处理目的。
更明白地来说,shell script就像早期dos年代的 .bat,最简单的功能就是将许多指令汇整写一起,让使用者很容易地就能够一个操作执行多个命令,而shell script更是提供了 数组,循环,条件以及 逻辑判断等重要功能,让使用者可以直接以shell来写程序,而不必使用类似C程序语言等传统程序编写的语法。
Shell就是一个 命令行解释器,它的作用就是遵循一定的语法将输入的命令加以解释并传给系统。它为用户提供了一个向Linux发送请求以便运行程序的接口系统级程序,用户可以用Shell来启动、挂起、停止甚至是编写一些程序。 Shell本身是一个用C语言编写的程序,它是用户使用Linux的桥梁。Shell既是一种命令语言,又是一种 程序设计语言(就是你所说的shell脚本)。作为命令语言,它互动式地解释和执行用户输入的命令;作为程序设计语言,它定义了各种变量和参数,并提供了许多在高阶语言中才具有的控制结构,包括循环和分支。它虽然不是 Linux系统 内核的一部分,但它调用了系统内核的大部分功能来执行程序、创建文档并以并行的方式协调各个程序的运行
3.Shell和C JAVA 区别:
Shell 是解释性语言;执行速度慢
C JAVA 是程序类语言;执行速度快
3.1 实验操作:c 和 shell script区别:
1.1>c语言的建立和编译:
1 vim hello.c
#include #include 用来提供程序要求的信息
是在程序编译之前要处理的内容,称为编译预处理命令。编译预处理命令还有很多,它们都以“#”开头,并且不用分号结尾,所以是c语言的程序语句。
main () #主函数
{
printf ("hello world\n')
}
2 yum install gcc #安装c编译安装包
3 gcc hello.c
4 ls
5 ./a.out #生成文件
6 gcc hello.c -o hello
7 ls
8 ./hello
9 chmod +x hello.c
10./hello.c 1.2>shell的简单建立和执行:
1 cd /mnt/
2 ls
3 vim hello.sh
#!/bin/bash "#!" 是一个约定的标记,它告诉系统这个脚本需要什么解释器来执行,即使用哪一种Shell
echo hello world #echo命令用于向窗口输出文本。
4 sh hello.sh
5 chmod +x hello.sh
6 /mnt/hello.sh
7 cat hello.sh
8 vim hello.sh
9 /mnt/hello.sh #打入后台
10 ps -f
11 cat hello.sh 
1.3>脚本示例:
1 执行ip_show.sh 显示当前主机的ip地址
1>vim ip_show.sh
2>cat ip_show.sh
#!/bin/bash
ifconfig eth0 | awk -F " " '/inet\>/{print $2}'
3>sh ip_show.sh
172.25.254.132 1>vim clear_log.sh
2>sh clear_log.sh
3>cat clear_log.sh
4>cat /var/log/messages 4 建立.sh文件自动调用SetTitle函数
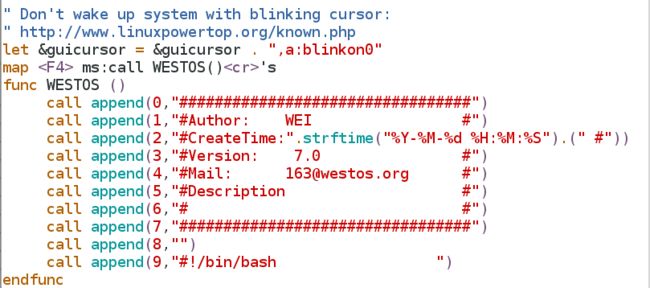
4.1 > 需要键入F4才能调用的SETTITLE
1 vim /etc/vimrc
map ms:call MEILI()'s #当按下"F4"会调用"MEILI"
func MEILI ()
call append(0,"#########################")
call append(1,"#Xiaoxiannu:yuhan".(" #"))
call append(2,"#Habby: manhua".(" #"))
call append(3,"#Charactor:changtuimeizi".("#"))
call append(4,"#Nicheng:guaiguai".(" #"))
call append(5,"#########################")
call append(6," ")
call append(7,"#!/bin/bash")
endfunc
2 vim yuhan.sh #当按下“F4”会调MEILI 4.1 vim /etc/vimrc
vim lala.sh +"F4"

4.2 >升级之后的SETTITLE
1 vim /etc/vimrc
"map ms:call MEILI()'s #注释
autocmd BufNewFile #.sh exec ":call MEILI()" #当文件格式为.sh时,自动调用"MEILI"
func MEILI ()
call append(0,"#########################")
call append(1,"#Xiaoxiannu:yuhan".(" #"))
call append(2,"#Habby: manhua".(" #"))
call append(3,"#Charactor:changtuimeizi".("#"))
call append(4,"#Nicheng:guaiguai".(" #"))
call append(5,"#########################")
call append(6," ")
call append(7,"#!/bin/bash")
endfunc
vim yuhanshengjiban.sh #自动调用MEILI 4.2 vim /etc/vimrc
5 shell 中的命令以及命令的灵活运用:
5.1 diff patch
diff以逐行的方式,比较文本文件的异同处,指定目录的话,如果指定的是目录,则比较目录中相同文件名的文件,但不会比较其中子目录。
diff 在比较文件过程中结果读取方式:
[num1,num2][a|c|d][num3,num4]
num1,num2表示在第一个文件中的行数
a 表示添加 ---add
c 表示修改 ---change
d 表示删除 ---delete
< 表示第一个文件的内容,>表示第二个文件的内容,---分割线;num3,num4表示在第二个文件中的行数
2,4c2,4 表示改变第一个文件中的第二行和第四行才能匹配第二个文件的第二行和第四行1 vim westos
2 vim westos1
3 cat westos
4 cat westos1
5 diff westos westos1 #比较两个文件的不同
6 diff -u westos westos1
7 diff -u westos westos1 > westos.path #比较不同,并生成布丁文件
8 cat westos.path
9 cat westos
10 yum install patch -y
11 patch westos westos.path #打补丁,即将不同的地方通过打补丁的方式将两文件内容相同
12 cat westos #查看测试,是否westos内容修改的和westos1相同
13 patch -b westos westos.path #生成原始westos文件,因为此时文件已经被打了补丁,所以生成rej文件,该文件说明了文件是怎么修改的
14 ls
15 cat westos.rej

1 vim westos
2 diff westos westos1
3 cat westos
4 cat westos1
5 diff -u westos westos1 > westos.path #生成补丁文件
6 patch -b westos westos.path #此时并没有打补丁,-b执行之后不仅打了补丁,还生成了westos原始文件,相当于文件的备份修改
7 ls
8 cat westos.orig
9 cat westos

5.2 cut命令多用于字符截取
cut -d 指定分隔符
cut -f 1,7|1-7 指定截取的列
cut -c 1,4|1-4 指定截取的字符位置用命令查看某机网络是否于本机畅通,如果畅通则输出ip is up;若不通则输出ip is down
1>ping -c1 -w1 172.25.254.64 &> /dev/null && echo 172.25.254.64 is up || 172.25.254.64 is down
2>ping -c1 -w1 172.25.254.232 &> /dev/null && echo 172.25.254.232 is up || 172.25.254.232 is down
用脚本实现其后所跟的第一串字符即ip所对应的主机网络是否与本机相通
1 vim check_ip.sh
2 sh check_ip.sh 172.25.254.64
#!/bin/bash
ping -c1 -w1 $1 &> /dev/null && echo $1 is up || echo $1 is down

5.3 sort,quid
sort 多用于字符排序
sort -n 纯数字排序
sort -r 倒序
sort -u 去掉重复数字
sort -o 输出到指定文件
sort -t 指定分隔符
sort -k 指定要排序的列
uniq 对重复字符作相应的处理
uniq -u 显示唯一的行
uniq -d 显示重复的行
uniq -c 每行显示一次并统计重复次数1 vim westos
2 sort -rn westos #倒序排列
3 sort -urn westos -o file #只排列不重复的unique,并输出到file文件中
4 sort -urn westos
5 cat file
#当文件中有多列字符时
6 vim westos
7 cat westos
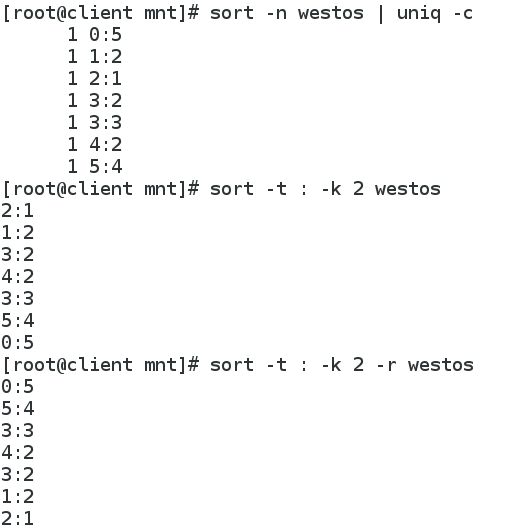
8 sort -n westos | uniq -c #每行显示一次并统计重复次数
9 sort -t : -k 2 westos #指定分隔符为":",即相隔一个":"为一列,这里比较第二列
10 sort -t : -k 2 -n westos #正向比较第二列
11 sort -t : -k 2 -r westos #反向比较第二列
12 cat westos | uniq -c
13 vim westos
14 cat westos
15 sort -n westos | uniq -c
16 sort -n westos | uniq -d #显示重复的行
17 sort -n westos | uniq -u #显示唯一的行
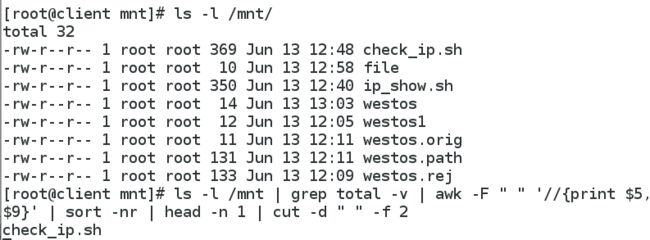
查看/mnt中最大的文件名称
1 ls -l /mnt/
2 ls -l /mnt | grep total -v | awk -F " " '//{print $5}'
3 ls -l /mnt | grep total -v | awk -F " " '//{print $5,$9}' | sort -nr
4 ls -l /mnt | grep total -v | awk -F " " '//{print $5,$9}' | sort -nr | head -n 1
5 ls -l /mnt | grep total -v | awk -F " " '//{print $5,$9}' | sort -nr | head -n 1 | cut -d " " -f 2
7 ls -Sl /mnt/
8 ls -Sl /mnt/ | grep -v total
9 ls -Sl /mnt/ | grep -v total | awk -F " " 'NR==1{prinf $9}'
5.5 test命令
test命令和[]等同
test "$A"=="$B" 等同于["$A"=="$B"]
["$A"="$B"] #判断A=B
["$A"!="$B"] #A!=B
["$A"-eq "$B"] #A=B
["$A"-ne "$B"] #!=
["$A"-le "$B"] #小于等于
["$A"-lt "$B"] #小于
["$A"-ge "$B"] #大于等于
["$A"-gt "$B"] #大于
["$A"-ne "$B"-a "$A"-gt "$B"] #-a 表示与操作即都要满足,A!=B且A大于B
["$A"-ne "$B"-o "$A"-gt "$B"] #-a 表示或操作即只用满足其中之一,A!=B或A大于B
[-z "$A"] #为空
[-n "$A"] #不为空
[-e "file"] #文件是否存在
[-f "file"] #是否为普通文件
[-L "file"] #是否为软链接
[-S "file"] #是否为套接字
[-b "file"] #是否为块链接
[-d "file"] #是否为目录
[-c "file"] #是否为字符设备
test 通常和&& || 连用;
当满足test条件时执行&&之后的命令
当不满足test条件时执行||之后的命令1 a=1
2 b=2
3 test "$a" = "$b" && echo yes || echo no
4 a=1
5 b=3
6 test "$a" = "$b" && echo yes || echo no
7 a=3
8 test "$a" = "$b" && echo yes || echo no
9 [ "$a" = "$b" ] && echo yes || echo no
10 echo $c
11 [ -z "$c" ] && echo yes || echo no
12 [ -n "$c" ] && echo yes || echo no
13 c=1
14 [ -z "$c" ] && echo yes || echo no
15 [ -n "$c" ] && echo yes || echo no 判断一个文件的文件类型并输出
1 vim file.sh
#!/bin/bash
[ -z "&1" ]&& {
echo please input a file !!
exit 1 #当没有需要判断的文件
}
[ "-e" "$1" ] || {
echo File is not exist !!
} #存在
[ "-f" "$1" ]&& {
echo "Common"
} #常规
[ "-S" "$1" ]&& {
echo "Socket"
} #套接字
[ "-L" "$1" ]&& {
echo "link"
} #链接
[ "-b" "$1" ]&& {
echo "Block"
} #块设备
[ "-s" "$1" ]|| {
echo "Empty"
} #空
[ "-c" "$1" ]&& {
echo "Zifu"
} #字符
2 sh file.sh lala5.6 tr 转换
tr转换
#!/bin/bash
WORD=$(echo $1 |tr 'A-Z' 'a-z') #该命令和WORD=$`echo $1 |tr 'A-Z' 'a-z'`;表先执行该转换操作,当输入有大写字母时,会将其先转换为小写,并将该转换赋给WORD输出
[ "$WORD" = "woshixiaokeai" ]&& { #当输入"woshixiaokeai"或者"WOSHIXIAOKEAI"就会执行&&之后的命令;当输入其他的,则执行||之后的命令
echo nizhenshigexiaokeai
} ||{
echo error
}
1 vim test.sh
2 sh test.sh
3 sh test.sh HELLO
4 sh test.sh hello
5 cat test.sh 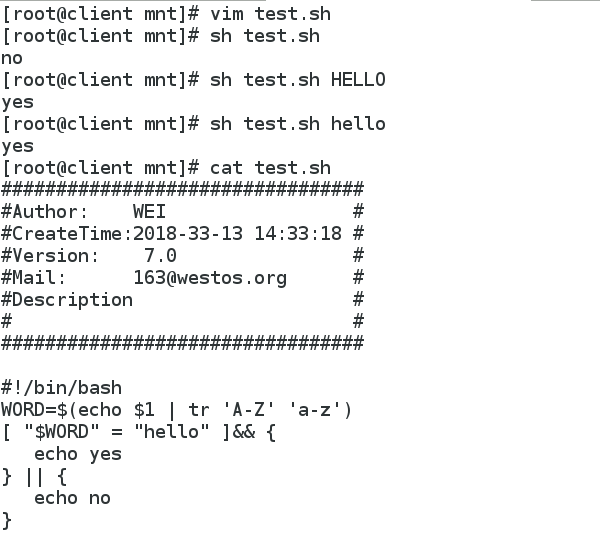
接下来要进行一波实验操作啦 !!!
1 检测网络是否畅通:
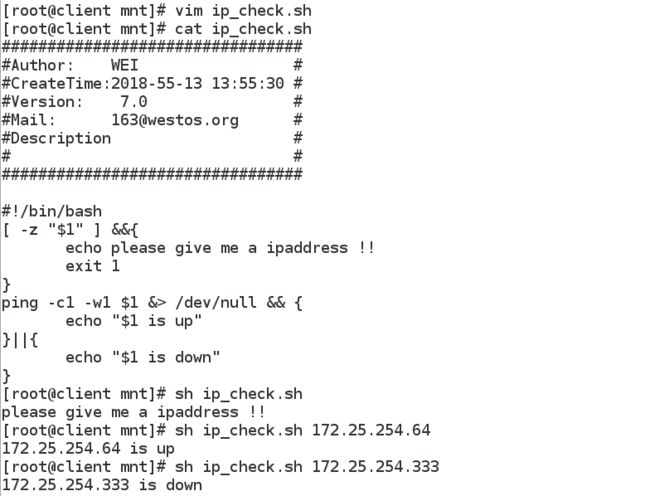
1 vim ip_check.sh
#!/bin/bash
[ -z "$1" ] &&{
echo please give me a ipaddress !!
exit 1
}
ping -c1 -w1 $1 &> /dev/null && {
echo "$1 is up"
}||{
echo "$1 is down"
}
2 cat ip_check.sh
3 sh ip_check.sh
4 sh ip_check.sh 172.25.254.64
5 sh ip_check.sh 172.25.254.3332 脚本测试输入数字是十以内的:
1 vim num_check.sh
2 cat num_check.sh
#测试
3 sh num_check.sh
4 sh num_check.sh 1
5 sh num_check.sh -1
6 sh num_check.sh 32
3 检测/mnt/lala文件类型
1 vim file.sh
2 [ "$1" "/mnt/lala" ]&& echo yes || echo no
3 sh file.sh -e #lala是否存在
4 touch lala
5 sh file.sh -f
6 sh file.sh -L
7 rm -f lala
8 ln -s /mnt/file.sh /mnt/lala
9 sh file.sh -L
-l 链接
ef 表示互为硬链接,两个文件指向一个文件的inode
nt 表示新的文件,即出现时间晚
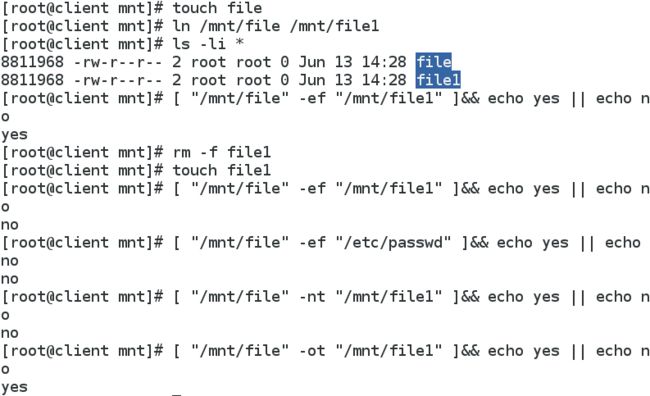
ot 表示旧的文件,即出现时间早1 touch file
2 ln /mnt/file /mnt/file1
3 ls -li *
4 [ "/mnt/file" -ef "/mnt/file1" ]&& echo yes || echo no
5 rm -f file1
6 touch file1
7 [ "/mnt/file" -ef "/mnt/file1" ]&& echo yes || echo no
8 [ "/mnt/file" -ef "/etc/passwd" ]&& echo yes || echo no
9 [ "/mnt/file" -nt "/mnt/file1" ]&& echo yes || echo no
10 [ "/mnt/file" -ot "/mnt/file1" ]&& echo yes || echo no-S套接字
TCP用主机的IP地址加上主机上的端口号作为TCP连接的端点,这种端点就叫做套接字(socket)或插口。
套接字用(IP地址:端口号)表示。
它是网络通信过程中端点的抽象表示,包含进行网络通信必需的五种信息:连接使用的协议,本地主机的IP地址,本地进程的协议端
口,远地主机的IP地址,远地进程的协议端口。流式套接字 双向字节流
口,远地主机的IP地址,远地进程的协议端口。流式套接字 双向字节流
1 sh file.sh -S
2 yum install mariadb-server
3 systemctl start mariadb
4 cd /var/lib/mysql/
5 ll
6 cp mysql.sock /mnt/lala
4 写一个脚本;当输入一个用户时,当该用户存在,则提示用户已存在,当该用户不存在时,则建立该用户,并设置该用户密码为自己的输入
方法一:
1 vim user_create.sh
#!/bin/bash
[ -e "/home/$1" ] &&{
echo The User is already exist!!
} ||{
useradd $1
password $2 | stdin $1
}
2 sh user_create.sh westos 123方法二:
1 vim user_create.sh
#!/bin/bash
[ "$#" -eq "2" ] || {
echo "Please input username and password after script !!"
exit 1
} #判断脚本后面是否有两串字符
Check_User=`getent passwd $1` #先执行``里面的内容,判断用户是否存在
[ -n "$Check_User" ]&&{
echo $1 is exist!!
exit 1
}
useradd $1 #用户不存在则建立该用户,并将脚本后的第二串字符设置为新建用户的密码
echo $2 | passwd --stdin $1
1 vim user_check.sh
2 getent passwd root
3 getent passwd westos
4 grep root /etc/passwd
测试:
5 sh user_check.sh westos 111
6 getent passwd westos
7 grep westos /etc/passwd
8 sh user_check.sh hello
9 sh user_check.sh root
10 sh user_check.sh root redhat
11 sh user_check.sh vim user_check.sh