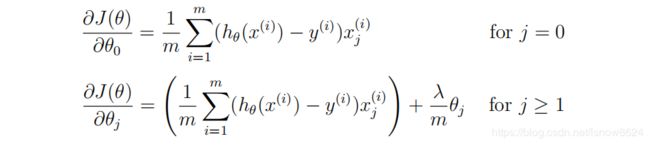吴恩达机器学习 EX5 作业 正则化线性回归 偏差 VS 方差 学习曲线
1、偏差、方差、学习曲线
1.1 偏差、方差
从下图可以看出
a、线性回归存在欠拟合,高偏差问题,如左图
b、多项式或者很多特征存在过拟合、高方差问题,如右图

训练集误差和交叉验证集误差近似时:偏差/欠拟合
交叉验证集误差远大于训练集误差时:方差/过拟合

1.2 正则化和方差、偏差
和多项式模型次数问题类似
当lambda很大时,高偏差/欠拟合,如左图
当lambda很小时,高方差/过拟合,如右图
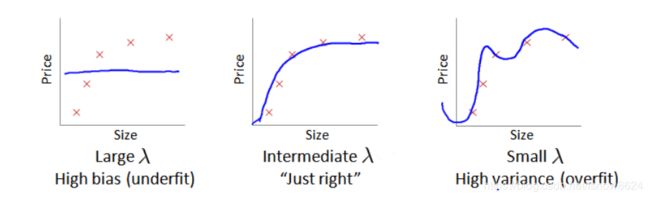
当lamdba较小时,训练集误差较小(过拟合)而交叉验证集误差较大
随着lambda的增加,训练集误差不断增加(欠拟合),而交叉验证集误差则是先减小后增加

1.3 学习曲线
学习曲线就是一种很好的工具,使用学习曲线可以判断某一个学习算法是否处于偏差、方差问题。学习曲线是学习算法的一个很好的合理检验(sanity check)。学习曲线是将训练集误差和交叉验证集误差作为训练集实例数量(m)的函数绘制的图表。
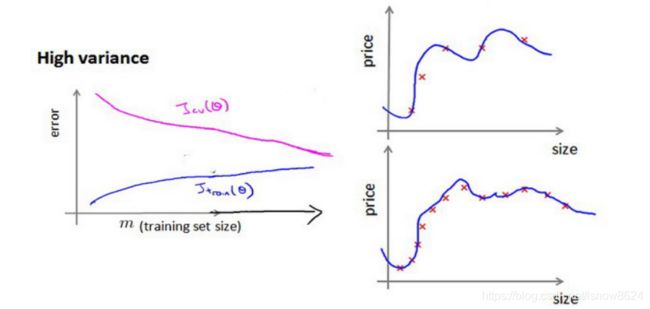
如下图,高偏差/欠拟合的情况下,增加数据到训练集不一定能有帮助

如下图,高方差/过拟合情况下,增加更多数据到训练集可能可以提高算法效果
2、导入模块和数据
导入模块
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import scipy.io as scio
import linearRegCostFunction as lrcf
import trainLinearReg as tlr
import learningCurve as lc
import polyFeatures as pf
import featureNormalize as fn
import plotFit as plotft
import validationCurve as vc
导入数据
plt.ion()
np.set_printoptions(formatter={'float': '{: 0.6f}'.format})
# Load from ex5data1:
data = scio.loadmat('ex5data1.mat')
X = data['X']
y = data['y'].flatten()
Xval = data['Xval']
yval = data['yval'].flatten()
Xtest = data['Xtest']
ytest = data['ytest'].flatten()
m = y.size
print('X.shape: ', X.shape, '\ny.shape: ', y.shape)
X.shape: (12, 1)
y.shape: (12,)
print('Xval.shape: ', Xval.shape, '\nyval.shape: ', yval.shape)
Xval.shape: (21, 1)
yval.shape: (21,)
print('Xtest.shape: ', Xtest.shape, '\nytest.shape: ', ytest.shape)
Xtest.shape: (21, 1)
ytest.shape: (21,)
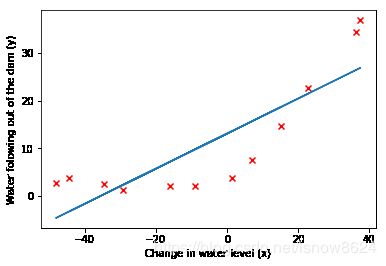
绘制训练集数据散点图
# Plot training data
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(X, y, c='r', marker="x")
plt.xlabel('Change in water level (x)')
plt.ylabel('Water folowing out of the dam (y)')
3、正则化线性回归代价函数(linearRegCostFunction.py)
def linear_reg_cost_function(theta, x, y, lmd):
# Initialize some useful values
m = y.size
# You need to return the following variables correctly
cost = 0
grad = np.zeros(theta.shape)
X = np.c_[np.ones(m), x] # 增加偏置单元bias 12 x 2
reg_theta = theta[1:] # 正则化梯度时不包含theta0
hythesis = np.dot(X, theta) # 假设函数 12
# 代价函数
cost = np.sum((hythesis - y ) ** 2) / (2 * m) + (lmd / (2 * m)) * np.sum(reg_theta * reg_theta )
# 梯度
theta_grad = np.sum(X * (hythesis - y)[:, np.newaxis], 0) / m
# 正则化梯度不包含theta0
theta_grad[1:] += (lmd / m) * reg_theta
grad = theta_grad
return cost, grad
测试,验证损失值
theta = np.ones(2)
cost, _ = linear_reg_cost_function(theta, X, y, 1)
print('Cost at theta = [1 1]: {:0.6f}\n(this value should be about 303.993192'.format(cost))
Cost at theta = [1 1]: 303.993192
(this value should be about 303.993192
测试,验证梯度
theta = np.ones(2)
cost, grad = linear_reg_cost_function(theta, X, y, 1)
print('Gradient at theta = [1 1]: {}\n(this value should be about [-15.303016 598.250744]'.format(grad))
Gradient at theta = [1 1]: [-15.303016 598.250744]
(this value should be about [-15.303016 598.250744]
4、高级优化,训练正则化线性回归函数(trainLinearReg.py)
import scipy.optimize as opt
def train_linear_reg(x, y, lmd):
initial_theta = np.ones(x.shape[1]+1)
def cost_func(t):
return linear_reg_cost_function(t, x, y, lmd)[0]
def grad_func(t):
return linear_reg_cost_function(t, x, y, lmd)[1]
theta, *unused = opt.fmin_cg(cost_func, initial_theta, grad_func, maxiter=200, disp=False,
full_output=True)
return theta
5、非正则化,lamdba=0
lambda=0时训练,此时高偏差/欠拟合
lmd = 0
theta = train_linear_reg(X, y, lmd)
显示训练的结果参数theta
theta
array([ 13.087907, 0.367779])
绘制非正则化训练图形
# Plot fit over the data
plt.scatter(X, y, c='r', marker="x")
plt.xlabel('Change in water level (x)')
plt.ylabel('Water folowing out of the dam (y)')
plt.plot(X, np.dot(np.c_[np.ones(m), X], theta))
6、学习曲线函数(learningCurve.py)
import trainLinearReg
import linearRegCostFunction
def learning_curve(X, y, Xval, yval, lmd):
# Number of training examples
m = X.shape[0]
# You need to return these values correctly
error_train = np.zeros(m)
error_val = np.zeros(m)
# 从一个训练样本开始逐个增加训练训练集
for i in range(m):
x_i = X[:i+1]
y_i = y[:i+1]
theta = train_linear_reg(x_i, y_i, lmd)
error_train[i] = linear_reg_cost_function(theta, x_i, y_i, lmd)[0]
error_val[i] = linear_reg_cost_function(theta, Xval, yval, lmd)[0]
return error_train, error_val
非正则化调用学习曲线函数训练
lmd = 0
error_train, error_val = learning_curve(X, y, Xval, yval, lmd)
打印非正则化训练误差和交叉验证误差
print('error_train:\n', error_train)
print('error_val:\n', error_val)
error_train:
[ 0.000000 0.000000 3.286595 2.842678 13.154049 19.443963 20.098522
18.172859 22.609405 23.261462 24.317250 22.373906]
error_val:
[ 169.870708 110.300366 45.010231 48.368921 35.865165 33.829962
31.970986 30.862446 31.135997 28.936207 29.551432 29.433813]
绘制非正则化学习曲线图,随着训练样本数量的增加,训练误差和交叉验证逐渐接近,但误差较大,高偏差、欠拟合
plt.figure()
plt.plot(np.arange(m), error_train, np.arange(m), error_val)
plt.title('Learning Curve for Linear Regression')
plt.legend(['Train', 'Cross Validation'])
plt.xlabel('Number of Training Examples')
plt.ylabel('Error')
plt.axis([0, 12, 0, 150])
7、多项式函数(polyFeatures.py)
线性回归存在高偏差/前拟合问题,通过多项式函数增加更多特征
def poly_features(X, p):
# You need to return the following variable correctly.
X_poly = np.zeros((X.size, p))
#X_poly[:, 0] = X.flatten()
#for i in range(1, 5):
# X_poly[:, i] = np.power(X_poly[:, 0], i+1)
p = np.arange(1, p+1)
X_poly = X ** p
return X_poly
设置dgree为8
p = 8
# Map X onto Polynomial Features and Normalize
X_poly = poly_features(X, p)
显示经多项式函数处理后的训练样本维度
X_poly.shape
(12, 8)
8、规范化处理函数(featureNormalize.py)
由于样本增加了多项式维度,需要将样本做规范化处理,否则样本特征之间数据大小差异过大,不利于训练
import numpy as np
def feature_normalize(X):
mu = np.mean(X, 0)
sigma = np.std(X, 0, ddof=1)
X_norm = (X - mu) / sigma
return X_norm, mu, sigma
多项式训练样本做规范化处理
X_poly, mu, sigma = fn.feature_normalize(X_poly)
# X_poly = np.c_[np.ones(m), X_poly]
print('X_poly:\n', X_poly)
print('mu:\n', mu)
print('sigma:\n', sigma)
X_poly:
[[-0.362141 -0.755087 0.182226 -0.706190 0.306618 -0.590878 0.344516
-0.508481]
[-0.803205 0.001258 -0.247937 -0.327023 0.093396 -0.435818 0.255416
-0.448912]
[ 1.377467 0.584827 1.249769 0.245312 0.978360 -0.012156 0.756568
-0.170352]
[ 1.420940 0.706647 1.359846 0.395534 1.106162 0.125637 0.871929
-0.059638]
[-1.434149 1.854000 -2.037163 2.331431 -2.411536 2.602212 -2.645675
2.766085]
[-0.128687 -0.975969 0.251385 -0.739687 0.316953 -0.594997 0.345812
-0.508955]
[ 0.680582 -0.780029 0.340656 -0.711721 0.326509 -0.591790 0.346830
-0.508613]
[-0.988534 0.451358 -0.601282 0.092917 -0.218473 -0.141608 0.039403
-0.266693]
[ 0.216076 -1.074993 0.266275 -0.743369 0.317561 -0.595129 0.345835
-0.508960]
[-1.311501 1.422806 -1.548121 1.493396 -1.515908 1.388655 -1.368307
1.224144]
[ 0.403777 -1.015010 0.273379 -0.741977 0.317742 -0.595098 0.345839
-0.508959]
[ 0.929375 -0.419808 0.510968 -0.588624 0.382616 -0.559030 0.361832
-0.500665]]
mu:
[-5.085426 848.904834 -12829.017311 1289677.885732 -29831459.159615
2293303013.788949 -68452728425.890808 4422337592290.961914]
sigma:
[ 29.964402 787.889103 48189.617840 1734904.307556 93939204.010417
3853453725.497600 197934704929.754150 8688967999573.497070]
交叉验证样本做多项式和规范化处理
# Map X_poly_val and normalize (using mu and sigma)
X_poly_val = poly_features(Xval, p)
# X_poly_val, _, _ = fn.feature_normalize(X_poly_val)
X_poly_val -= mu
X_poly_val /= sigma
测试样本做多项式和规范化处理
# Map X_poly_test and normalize (using mu and sigma)
X_poly_test = poly_features(Xtest, p)
# X_poly_test, _, _ = fn.feature_normalize(X_poly_test)
X_poly_test -= mu
X_poly_test /= sigma
打印一个多项式训练样本示例,值均在-1和1之间
print('Normalized Training Example 1 : \n{}'.format(X_poly[0]))
Normalized Training Example 1 :
[-0.362141 -0.755087 0.182226 -0.706190 0.306618 -0.590878 0.344516
-0.508481]
9、规范化处理后多项式样本学习曲线
9.1 lambda=0,非正则化
训练训练样本梯度参数
lmd = 0
theta = train_linear_reg(X_poly, y, lmd)
打印参数
theta
array([ 11.221939, 9.863868, 19.615335, 27.002894, -32.236403,
-69.304040, 15.484336, 56.625713, 15.138545])
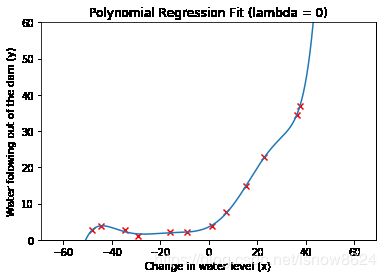
显示非正则化、规划范多项式训练学习曲线
# Plot trainint data and fit
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(X, y, c='r', marker="x")
plotft.plot_fit(np.min(X), np.max(X), mu, sigma, theta, p)
plt.xlabel('Change in water level (x)')
plt.ylabel('Water folowing out of the dam (y)')
plt.ylim([0, 60])
plt.title('Polynomial Regression Fit (lambda = {})'.format(lmd))
图形上看拟合蛮好,过拟合不明显。作业上给出图形明显过拟合,不知何故,有知道原因的请留言或消息告知,谢谢!!!
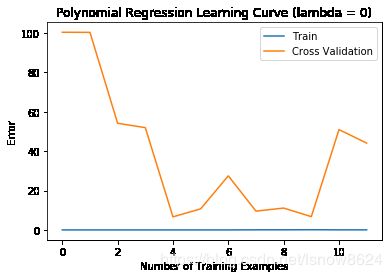
error_train, error_val = learning_curve(X_poly, y, X_poly_val, yval, 0)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(np.arange(m), error_train, np.arange(m), error_val)
plt.title('Polynomial Regression Learning Curve (lambda = {})'.format(0))
plt.legend(['Train', 'Cross Validation'])
plt.xlabel('Number of Training Examples')
plt.ylabel('Error')
# plt.axis([0, 12, 0, 120])
非正则化时,规范化多项式训练学习曲线
打印非正则化、规范化处理的多项式训练过程损失值
print('Polynomial Regression (lambda = {})'.format(lmd))
print('# Training Examples\tTrain Error\t\tCross Validation Error')
for i in range(m):
print(' \t{}\t\t{}\t{}'.format(i, error_train[i], error_val[i]))
Polynomial Regression (lambda = 0)
# Training Examples Train Error Cross Validation Error
0 9.860761315262648e-32 100.37625186942519
1 1.5506047168250513e-28 100.32002110040524
2 3.077881824176015e-11 54.14375688073054
3 3.813636997990325e-09 51.9415467951801
4 1.4279233789539115e-08 6.638188709159506
5 3.9536921002667376e-08 10.687615575308106
6 1.7575669209078703e-05 27.45634781574713
7 0.04964313836295177 9.543428777568863
8 0.050643257981608056 11.097991482520138
9 0.10237302642296423 6.739524626803059
10 0.03121892340099548 50.927902274709304
11 0.029911407557440928 44.081719243979315
9.1 lambda=1,正则化学习曲线
训练规范会处理的多项式训练样本,并绘图
# Train linear regression with lambda = 0
lmd = 1
theta = train_linear_reg(X_poly, y, lmd)
# Plot trainint data and fit
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(X, y, c='r', marker="x")
plotft.plot_fit(np.min(X), np.max(X), mu, sigma, theta, p)
plt.xlabel('Change in water level (x)')
plt.ylabel('Water folowing out of the dam (y)')
plt.ylim([0, 120])
plt.title('Polynomial Regression Fit (lambda = {})'.format(lmd))
lambda=1时,训练拟合效果较好,lambda=0时左侧有过拟合嫌疑

lambda=1时规范化处理的多项式学习曲线,5个训练样本后拟合效果较好
error_train, error_val = learning_curve(X_poly, y, X_poly_val, yval, lmd)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(np.arange(m), error_train, error_val)
plt.title('Polynomial Regression Learning Curve (lambda = {})'.format(lmd))
plt.legend(['Train', 'Cross Validation'])
plt.xlabel('Number of Training Examples')
plt.ylabel('Error')
plt.axis([0, 13, 0, 150])
print('Polynomial Regression (lambda = {})'.format(lmd))
print('# Training Examples\tTrain Error\t\tCross Validation Error')
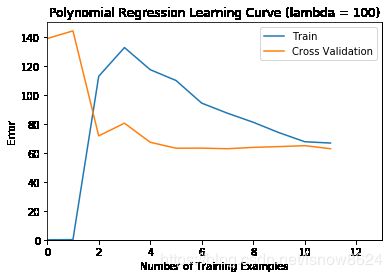
lambda=100 时规范化处理的多项式训练效果,拟合效果较差
# Train linear regression with lambda = 0
lmd = 100
theta = train_linear_reg(X_poly, y, lmd)
# Plot trainint data and fit
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(X, y, c='r', marker="x")
plotft.plot_fit(np.min(X), np.max(X), mu, sigma, theta, p)
plt.xlabel('Change in water level (x)')
plt.ylabel('Water folowing out of the dam (y)')
plt.ylim([0, 60])
plt.title('Polynomial Regression Fit (lambda = {})'.format(lmd))
lambda=100 时规范化处理的多项式学习曲线,损失值较大,拟合效果较差
error_train, error_val = learning_curve(X_poly, y, X_poly_val, yval, lmd)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(np.arange(m), error_train, np.arange(m), error_val)
plt.title('Polynomial Regression Learning Curve (lambda = {})'.format(lmd))
plt.legend(['Train', 'Cross Validation'])
plt.xlabel('Number of Training Examples')
plt.ylabel('Error')
plt.axis([0, 13, 0, 150])
10、不同lambda,交叉验证
def validation_curve(X, y, Xval, yval):
# Selected values of lambda (don't change this)
lambda_vec = np.array([0, 0.0001, 0.0003, 0.001, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10])
# You need to return these variables correctly.
error_train = np.zeros(lambda_vec.size)
error_val = np.zeros(lambda_vec.size)
for i in range(lambda_vec.size):
theta = train_linear_reg(X, y, lambda_vec[i])
error_train[i] = linear_reg_cost_function(theta, X, y, lambda_vec[i])[0]
error_val[i] = linear_reg_cost_function(theta, Xval, yval, lambda_vec[i])[0]
return lambda_vec, error_train, error_val
调用交叉验证,返回交叉验证结果(训练集误差和交叉验证误差)
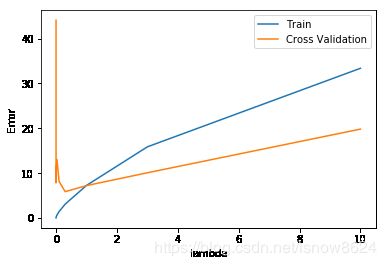
lambda_vec, error_train, error_val = validation_curve(X_poly, y, X_poly_val, yval)
绘制交叉验证曲线,和作业介绍结果不一致,不知何故,有知道原因的请留言或消息告知,谢谢!!!
plt.figure()
plt.plot(lambda_vec, error_train, lambda_vec, error_val)
plt.legend(['Train', 'Cross Validation'])
plt.xlabel('lambda')
plt.ylabel('Error')
# plt.axis([0, 10, 0, 40])
for i in range(len(lambda_vec)):
print(lambda_vec[i], error_train[i], error_val[i], error_train[i] - error_val[i])
0.0 0.029911407557440928 44.081719243979315 -44.05180783642187
0.0001 0.080787158736208 7.8396650477755605 -7.758877889039352
0.0003 0.1076058102169635 8.831025193699851 -8.723419383482888
0.001 0.1747948583975907 9.907398598157725 -9.732603739760133
0.03 0.6692749154166904 13.05577148575913 -12.386496570342441
0.1 1.4434703781683387 8.148901399325872 -6.705431021157533
0.3 3.1015910692352286 5.882452259461671 -2.780861190226442
1.0 7.26814810400188 7.2274754492151 0.04067265478678017
3.0 15.86768820311661 10.089388597666556 5.778299605450055
10.0 33.372202903680176 19.81978848368485 13.552414419995326
前一篇 吴恩达机器学习 EX4 作业 神经网络反向传播 手写数字
后一篇 吴恩达机器学习 EX6 作业 第一部分 了解支持向量机 高斯核函数