ElasticSearch基本操作
作者:dominating
本文将介绍使用ElasticSearch提供的REST API来对ElasticSearch进行基础的操作。
###安装curl
安装curl(https://curl.haxx.se/download.html)下载安装包,或者直接下载
wget http://curl.haxx.se/download/curl-7.20.0.tar.gz
解压到指定目录
tar -zxf curl-7.20.0.tar.gz
进入解压后的目录,配置,指定安装的目录
cd curl-7.17.1
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/curl
make
make install
将curl命令加入到环境变量
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/curl/bin
执行source /etc/profile
###索引
一个索引就是一个拥有几分相似特征的文档的集合。比如说,你可以有一个客户数据的索引,另一个产品目录的索引,还有一个订单数据的索引。一个索引由一个名字来标识(必须全部是小写字母的),并且当我们要对对应于这个索引中的文档进行索引、搜索、更新和删除的时候,都要使用到这个名字。
查看索引
curl 'http://192.168.255.143:9200/_cat/indices?v'
curl -XPUT 'http://192.168.255.143:9200/customer'
再次查看索引
![]()
现在有一个叫做customer的索引,并且它有5个主分片和1份复制(都是默认值),其中包含0个文档
删除索引
curl -X DELETE 'localhost:9200/ customer'
###文档
一个文档是一个可被索引的基础信息单元。比如,你可以拥有某一个客户的文档,某一个产品的一个文档,当然,也可以拥有某个订单的一个文档。文档以 JSON(Javascript Object Notation)格式来表示。
添加文档
为了索引一个文档,我们必须告诉Elasticsearch这个文档要到这个索引的哪个类型(type)下
将一个简单的客户文档索引到customer索引、“external”类型中,这个文档的ID是1,操作如下:
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPUT 'http://192.168.255.143:9200/customer/external/1' -d '{"name": "John Doe"}'
![]()
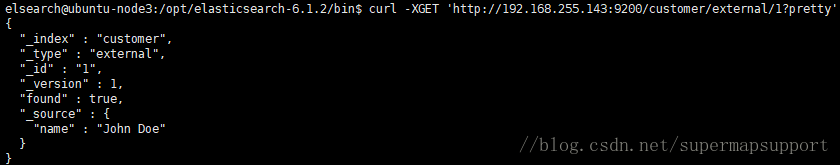
查询刚才添加的文档
curl -XGET ‘http://192.168.255.143:9200/customer/external/1?pretty’
新增记录的时候,也可以不用指定id,但是得改成POST请求,生成的id为一个随机字符串
![]()
删除文档
curl -XDELETE ‘http://192.168.255.143:9200/customer/external/1’
更新文档
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPOST 'http://192.168.255.143:9200/customer/external/1/_update?pretty' -d '
{
"doc":{"name":"lisi"}
}'

批处理
使用_bulk API实现,这个功能之所以重要,在于它提供了非常高效的机制来尽可能快的完成多个操作,与此同时使用尽可能少的网络往返
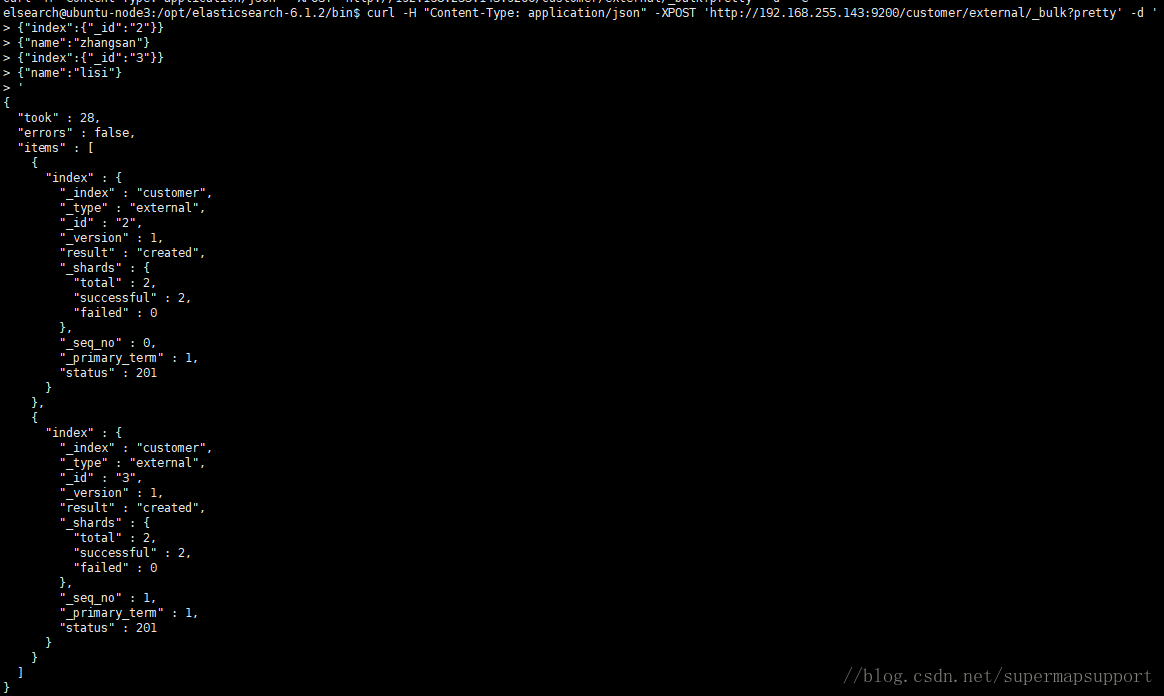
以下调用在一次bulk操作中索引了两个文档(ID 2 - zhangsan 和ID 3 - lisi):
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPOST 'http://192.168.255.143:9200/customer/external/_bulk?pretty' -d '{"index":{"_id":"2"}} {"name":"zhangsan"}{"index":{"_id":"3"}} {"name":"lisi"} '
###搜索数据
1、返回所有记录
用GET方法,直接请求/Index/Type/_search,就能返回所有结果
curl -XGET 'http://192.168.255.143:9200/customer/external/_search?pretty'
- took —— Elasticsearch执行这个搜索的耗时,以毫秒为单位
- timed_out —— 指明这个搜索是否超时
- _shards —— 指出多少个分片被搜索了,同时也指出了成功/失败的被搜索的shards的数量
- hits —— 搜索结果
- hits.total —— 能够匹配我们查询标准的文档的总数目
- hits.hits —— 真正的搜索结果数据(默认只显示前10个文档)
执行搜索,Elasticsearch提供一种JSON风格的特定领域语言,查询DSL,利用它可以执行查询
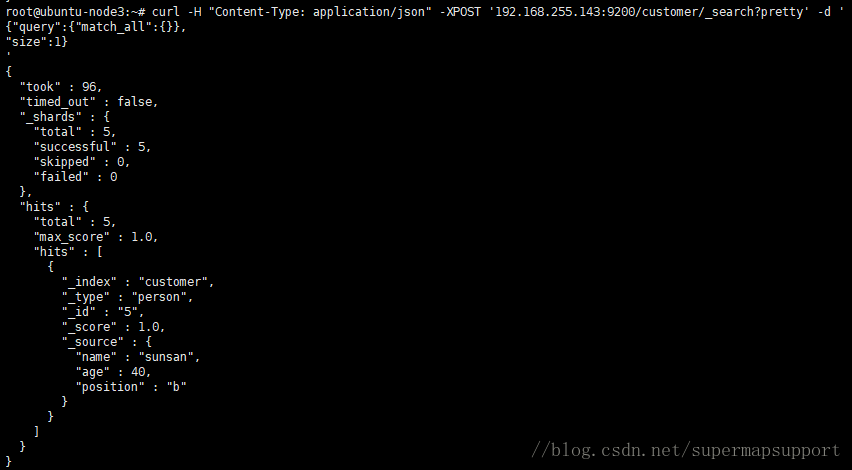
curl -XPOST 192.168.255.143:9200/customer/_search?pretty' -d '
{
"query": { "match_all": {} },
"size": 1
}'
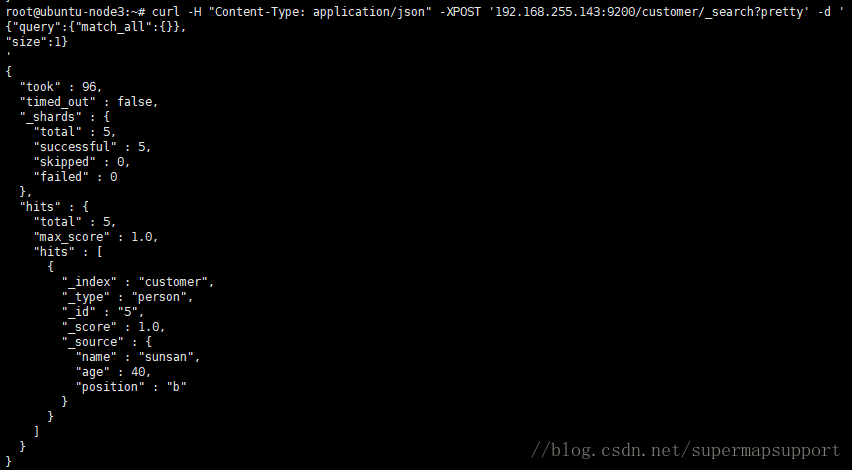
使用match_all进行查询,并且只返回第一个文档。如果没有指定size的值,则默认返回前10个文档
也可以指定返回从哪个文档开始,返回多少文档
curl -XPOST ‘192.168.255.143:9200/bank/_search?pretty' -d '
{
"query": { "match_all": {} },
“from”:10,
"size": 20
}'
以上做了一次match_all查询并且返回第11个到第20个文档
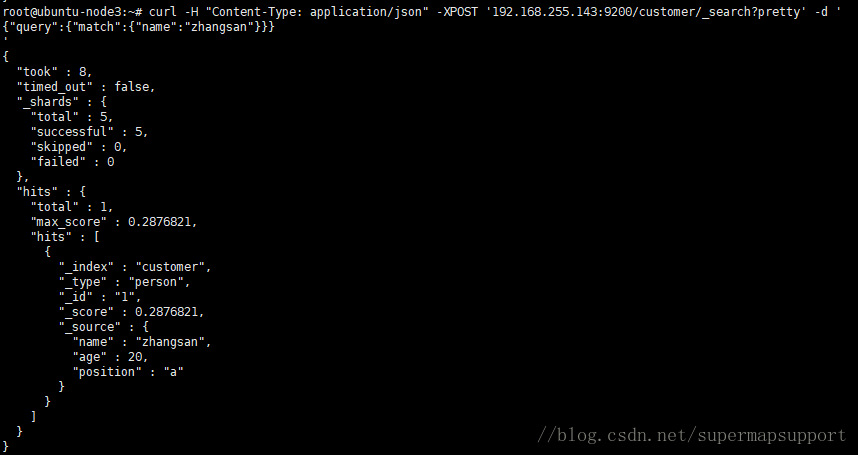
查询姓名为”zhangsan”的记录
curl -XPOST ‘192.168.255.143:9200/customer/_search?pretty' -d '
{
"query": { "match": { "name ": “zhangsan” } }
}'
逻辑运算
查询姓名为”zhangsan”或者”lisi”的记录
curl -XPOST 192.168.255.143:9200/customer/_search?pretty' -d '
{
"query": { "match": { "name ": “zhangsan lisi” } }
}'
curl -XPOST 192.168.255.143:9200/ customer /_search?pretty' -d '
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "name": "zhangsan" } },
{ "match": { "age": "20" } }
]
}
}
}'
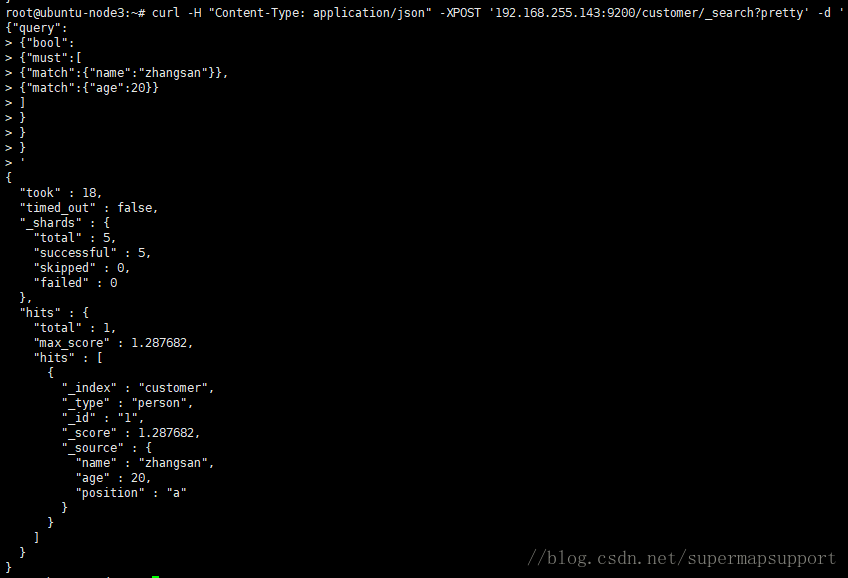
也可以修改bool参数, 除了must,还有should(或),must_not(不包括)
过滤查询
查询年龄在20-30岁的记录,使用filter进行过滤,嵌套在bool查询内部使用
curl -XPOST ‘192.168.255.143:9200/customer/_search?pretty' -d '
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": { "match_all": {} },
"filter": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 20,
"lte": 30
}
}
}
}
}
}'
聚合
聚合提供了用户进行分组和数理统计的能力,可以把聚合理解成SQL中的GROUP BY和分组函数。在ES中,你可以在一次搜索查询的时间内,即完成搜索操作也完成聚合操作,这样就降低了多次使用REST API造成的网络开销
一个简单的terms聚合例子,查询所有的文档,并且按照岗位分组统计:
curl -XPOST ‘192.168.255.143:9200:9200/ customer/_search?pretty' -d '
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_position": {
"terms": {
"field": "position"
}
}
}
}'
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPUT '192.168.255.143:9200/customer/_mapping/person' -d '
{
"properties":{
"position":{
"type":"text",
"fielddata":true
}
}
}
它类似于SQL中的下面的语句:
SELECT state, COUNT() FROM customer GROUP BY position ORDER BY COUNT() DESC
聚合嵌套
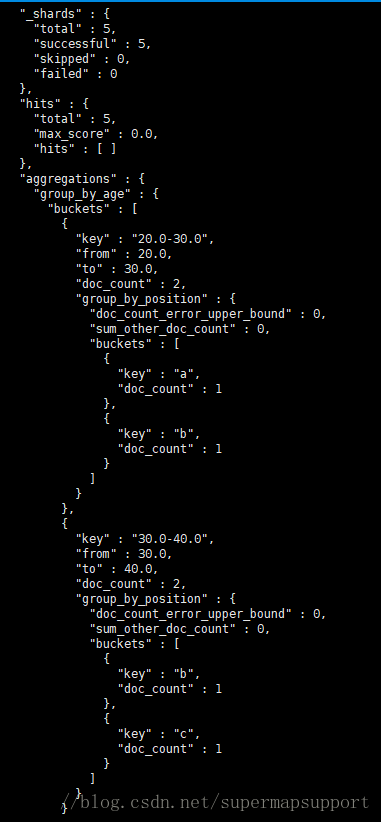
先按年龄分组,再统计岗位
curl -XPOST ‘192.168.255.143:9200:9200/bank/_search?pretty' -d '
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_age": {
"range": {
"field": "age",
"ranges": [
{
"from": 20,
"to": 30
},
{
"from": 30,
"to": 40
},
]
},
"aggs": {
"group_by_position": {
"terms": {
"field": " position"
}
}
}
}
}
}'
以上的话就是ElasticSearch中的一些基本操作,要了解更多的ElasticSearch的操作可以参考ElasticSearch的官方文档
https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/elasticsearch/guide/current/index.html