Programming Exercise 7:K-means Clustering and Principal Component Analysis 第一部分
大家好,我是Mac Jiang,今天和大家分享Coursera-Stanford University-Machine Learning-Programming Exercise 7:K-means Clustering and Principal Principal Component Analysis的第一部分的编码。第一部分讲的是K-means Clustering,即K均值算法的实现过程,虽然我写的代码是正确的,但不一定是最好的,如果有更好的实现方法,请留言指正。当然,欢迎大家转载我的博客,不过在转载之前请标明出处,谢谢。第二部分的地址为:http://blog.csdn.net/a1015553840/article/details/50879343
好的,我们开始讲解第一部分K-means Clustering的具体实现过程。
这部分的主要有两大块内容:
(1)主要是训练PCA算法,并在OpenGL上绘制出K均值算法的具体计算过程,绘制出每次分类情况和中心变换情况。
(2)利用K均值算法对一幅图像进行压缩,此图像为128*128,每个像素由RGB三种颜色标识,而每种颜色用1BYTE(8bit)表示,范围为0-255。如果不采取压缩,那么图像所占存储空间大小为128*128*3BYTE=128*128*24bits = 393,216bits。我们要进行的是利用K均值算法聚类出最常用的16中颜色,这16中颜色只要用4bit标识,加上这十六种颜色与RGB的映射关系共128*128*4 + 16*24 = 65,920bit。可以看到,压缩后存储只占压缩前存储量的1/6左右。
数据集:ex7data2.mat---用于训练K均值算法的训练样本
bird_small.png---用于做压缩测试的图像
函数:displayData.m---把训练样本X的数据可视化
drawLine.m---画出2D降为1D的直线 plotDataPoints.m---k均值算法的点,当属于不同中心时用不同颜色画出
plotProgresskMeans.m---做出k均值算法的中心 runMeans.m---运行k均值算法
ex7.m---K均值算法的主控制函数,控制算法的进行过程
kMeansInitCentroid.m---初始化k均值算法的中心,需要完善代码!
findClosestCentroids.m---将每个样本归为离他最近的中心的那一类,需要完善代码!
computeCentroids.m---将上面求得的类,计算每一类的新的中心,需要完善代码!
这部分作业共三个文件需要完善代码
K均值算法的计算为:
初始化中心;(kMeansInitCentroids.m实现)
Repeat{
from 1 to m:计算每个样本离各类中心的距离,将每个样本分别归类(findClosestCentroids.m实现)
from 1 to K:z在归类后,计算各类的中心(compureCentroids.m实现)
}
这我们需要完成的任务就是编写初始化,样本分类,求新分类中心三个操作
1.ex7的控制过程
%% Machine Learning Online Class
% Exercise 7 | Principle Component Analysis and K-Means Clustering
%
% Instructions
% ------------
%
% This file contains code that helps you get started on the
% exercise. You will need to complete the following functions:
%
% pca.m
% projectData.m
% recoverData.m
% computeCentroids.m
% findClosestCentroids.m
% kMeansInitCentroids.m
%
% For this exercise, you will not need to change any code in this file,
% or any other files other than those mentioned above.
%
%% Initialization
clear ; close all; clc
%% ================= Part 1: Find Closest Centroids ====================
% To help you implement K-Means, we have divided the learning algorithm
% into two functions -- findClosestCentroids and computeCentroids. In this
% part, you shoudl complete the code in the findClosestCentroids function.
%
fprintf('Finding closest centroids.\n\n');
% Load an example dataset that we will be using
load('ex7data2.mat');
% Select an initial set of centroids
K = 3; % 3 Centroids
initial_centroids = [3 3; 6 2; 8 5];
% Find the closest centroids for the examples using the
% initial_centroids
idx = findClosestCentroids(X, initial_centroids);
fprintf('Closest centroids for the first 3 examples: \n')
fprintf(' %d', idx(1:3));
fprintf('\n(the closest centroids should be 1, 3, 2 respectively)\n');
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ===================== Part 2: Compute Means =========================
% After implementing the closest centroids function, you should now
% complete the computeCentroids function.
%
fprintf('\nComputing centroids means.\n\n');
% Compute means based on the closest centroids found in the previous part.
centroids = computeCentroids(X, idx, K);
fprintf('Centroids computed after initial finding of closest centroids: \n')
fprintf(' %f %f \n' , centroids');
fprintf('\n(the centroids should be\n');
fprintf(' [ 2.428301 3.157924 ]\n');
fprintf(' [ 5.813503 2.633656 ]\n');
fprintf(' [ 7.119387 3.616684 ]\n\n');
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% =================== Part 3: K-Means Clustering ======================
% After you have completed the two functions computeCentroids and
% findClosestCentroids, you have all the necessary pieces to run the
% kMeans algorithm. In this part, you will run the K-Means algorithm on
% the example dataset we have provided.
%
fprintf('\nRunning K-Means clustering on example dataset.\n\n');
% Load an example dataset
load('ex7data2.mat');
% Settings for running K-Means
K = 3;
max_iters = 10;
% For consistency, here we set centroids to specific values
% but in practice you want to generate them automatically, such as by
% settings them to be random examples (as can be seen in
% kMeansInitCentroids).
initial_centroids = [3 3; 6 2; 8 5];
% Run K-Means algorithm. The 'true' at the end tells our function to plot
% the progress of K-Means
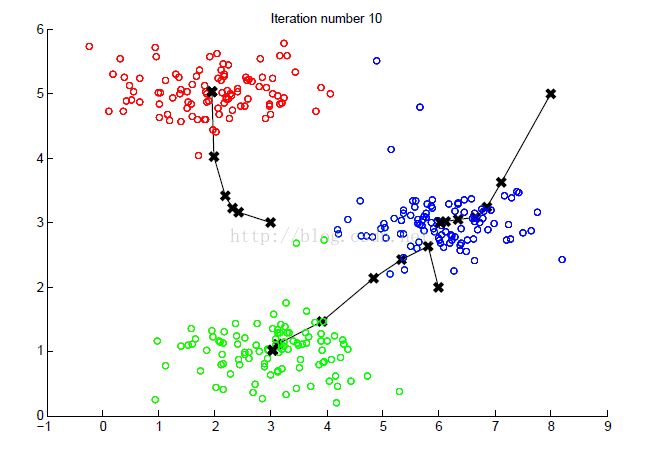
[centroids, idx] = runkMeans(X, initial_centroids, max_iters, true);
fprintf('\nK-Means Done.\n\n');
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ============= Part 4: K-Means Clustering on Pixels ===============
fprintf('\nRunning K-Means clustering on pixels from an image.\n\n');
% Load an image of a bird
A = double(imread('bird_small.png'));
A = A / 255; % Divide by 255 so that all values are in the range 0 - 1
% 图片为128行,128列,每个像素RGB三种颜色,每个颜色1Byte = 8bit,共128*128*24bits
img_size = size(A);
%原图A为img_size(1)行,img_size(2)列,每个像素点的颜色由RGB三种表示,每种8bit共3字节,故为img_size(1)*img_size(2)*3
%由于我们要使用K-means,所以我们要把行和列铺平,成为一个响亮,成为一个长度为img_size(1)*img_size(2)的向量,每个元素有RGB三种共3字节
%把图像铺平,这样每个元素即为一个输入x,他有RGB三个维度
X = reshape(A, img_size(1) * img_size(2), 3);
%我们的目的是把RGB共256*256*256种颜色压缩成16种颜色,这16种颜色是通过K均值算法计算出来的
%假如不压缩,原图为128*128*3Byte = 128*128*24bit = 393216bits;
%如果压缩成16种颜色,那么只要4bit表示颜色的种类,然后再记录用到的这16种颜色的RGB表示16*24bits...
%共16*24 +%128*128*4 = 65920bit8,图像压缩了将近6倍
K = 16;
max_iters = 10;
%初始化中心
initial_centroids = kMeansInitCentroids(X, K);
%运行K均值算法
[centroids, idx] = runkMeans(X, initial_centroids, max_iters);
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ================= Part 5: Image Compression ======================
fprintf('\nApplying K-Means to compress an image.\n\n');
% Find closest cluster members
idx = findClosestCentroids(X, centroids);
% Essentially, now we have represented the image X as in terms of the
% indices in idx.
% We can now recover the image from the indices (idx) by mapping each pixel
% (specified by it's index in idx) to the centroid value
X_recovered = centroids(idx,:);
% Reshape the recovered image into proper dimensions
%本实验本身并未压图片,最后只是把各点颜色用那16种代替了而已,但是提供的是一种压缩图片的思想
X_recovered = reshape(X_recovered, img_size(1), img_size(2), 3);
% Display the original image
subplot(1, 2, 1);
imagesc(A);
title('Original');
% Display compressed image side by side
subplot(1, 2, 2);
imagesc(X_recovered)
title(sprintf('Compressed, with %d colors.', K));
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
Part1:Find Closest Centroids---利用ex7data2.mat和当前中心,计算的每个样本离每个中心的距离,将他们分为最近的中心的类别中
Part2:Compute Means---利用第一部分的到的新的分类,计算每个新的分类的中心
Part3:K-Means Clustering---利用K均值算法进行聚类,并画出每次聚类的类别变化过程和新中心的转变过程
Part4:K-Means Clustering Pixels---利用K均值算法对图像进行聚类分析,找到16中使用最多的颜色】
Park5:Image Compressing---在part4得到的16种颜色的基础上,对图像进行压缩。这里实际上并未对图像进行压缩,而是把图片各颜色换成16中颜色内与之相近的颜色。这里只是给我们提供这种图片压缩的方法,并未最终实现
2.kMeansInitCentroids.m的实现
function centroids = kMeansInitCentroids(X, K)
%KMEANSINITCENTROIDS This function initializes K centroids that are to be
%used in K-Means on the dataset X
% centroids = KMEANSINITCENTROIDS(X, K) returns K initial centroids to be
% used with the K-Means on the dataset X
%
% You should return this values correctly
centroids = zeros(K, size(X, 2));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: You should set centroids to randomly chosen examples from
% the dataset X
%
%初始化中心centroids,从X中随机取K行作为初始化中心
randidx = randperm(size(X,1)); %打乱X的行,列不变
centroids = X(randidx(1:K),:); %从打乱的X中取前K个作为初始化中心
% =============================================================
end
初始化中心时,是随机选取训练样本X中的K个作为初始化中心,所以先打乱X,然后取前K个即可。
3.findcloestCentroids.m的实现
function idx = findClosestCentroids(X, centroids)
%FINDCLOSESTCENTROIDS computes the centroid memberships for every example
% idx = FINDCLOSESTCENTROIDS (X, centroids) returns the closest centroids
% in idx for a dataset X where each row is a single example. idx = m x 1
% vector of centroid assignments (i.e. each entry in range [1..K])
%
% Set K
K = size(centroids, 1);
% You need to return the following variables correctly.
idx = zeros(size(X,1), 1);
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Go over every example, find its closest centroid, and store
% the index inside idx at the appropriate location.
% Concretely, idx(i) should contain the index of the centroid
% closest to example i. Hence, it should be a value in the
% range 1..K
%
% Note: You can use a for-loop over the examples to compute this.
%
temp = zeros(K,1); %存储样本x离各个中心距离的距离,方便求解该x离哪个点最近
for i = 1:size(X,1), %对X的每个样本进行遍历
for j = 1:K, %在进行x(i)时候,计算他离每个中心的距离,存储在temp中
temp(j) = sum((X(i,:) - centroids(j,:)).^2);
[value,idx(i)] = min(temp,[],1); %计算temp中最小值的行号,就是x(i)距离最近的中心标号
end
end
% =============================================================
end
4.computeCentroids.m的实现
function centroids = computeCentroids(X, idx, K)
%COMPUTECENTROIDS returs the new centroids by computing the means of the
%data points assigned to each centroid.
% centroids = COMPUTECENTROIDS(X, idx, K) returns the new centroids by
% computing the means of the data points assigned to each centroid. It is
% given a dataset X where each row is a single data point, a vector
% idx of centroid assignments (i.e. each entry in range [1..K]) for each
% example, and K, the number of centroids. You should return a matrix
% centroids, where each row of centroids is the mean of the data points
% assigned to it.
%
% Useful variables
[m n] = size(X);
% You need to return the following variables correctly.
centroids = zeros(K, n);
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Go over every centroid and compute mean of all points that
% belong to it. Concretely, the row vector centroids(i, :)
% should contain the mean of the data points assigned to
% centroid i.
%
% Note: You can use a for-loop over the centroids to compute this.
%
for i = 1:K, %对每个中心遍历,一个一个计算
centroids(i,:) = (X' * (idx == i)) / sum(idx == i); %矩阵的方法,idx == i的意思是是idx向量的元素为i的位置置1,不为i的置0;
%然后乘以X’就是把对应中心i的X值加起来,最后除以sum及求平均
%这里实际上可以再采用一个for循环计算centroids,但是向量的方法更快,故采取向量的方法
end
% =============================================================
end
这里对每个类别进行遍历(共K类),然后对每类计算他的中心。对每个类别进行遍历时候需要一个FOR循环;在计算每个类别的中心时也可以采取一个for循环,但是这样太慢,可以采取向量的方法加快计算速度。
向量的方法即利用(idx==i)得到一个m*1的向量,当idx对应的位置为i时,此向量对应位置为1,否则为0。
FROM:http://blog.csdn.net/a1015553840/article/details/50877623