网络安全学习第4篇-使用特征码和MD5对勒索病毒进行专杀,并对加密文件进行解密
请使用IDA或其它分析工具分析本次的样本文件,写一个简要的行为分析报告,并编写一个针对于这次样本的专杀(恢复)程序。
要求:
1、样本分析只要说明主要行为即可。提示:sub_401320主要用于文件加密操作;sub_401470主要用于查找docx文件;sub_4017D0主要用于创建自删除脚本文件;sub_4019B0主要用于创建readme说明文件。
2、专杀工具需要能够识别本次的样本文件,可采用课堂上说过的两种取特征码的方法(也可以采用你自己的方法)进行样本识别与查杀。
3、专杀工具需要有文件恢复功能,需要采用逆运算的方式解密文件,同时还需要修改文件后缀,改回docx的扩展名。专杀工具采用的编程语言不限。
4、本次实验需要提交实验报告以及专杀程序的源代码。
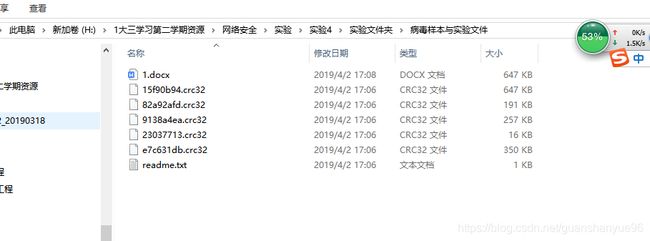
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/10YhRSY40GgWXKln8BE1F3Q
提取码:1yto
实验开始准备阶段:
首先从网络教学平台下载资源,然后把自己电脑的杀毒软件关掉,因为样本有可能会被杀毒软件认为是病毒。所以要把杀毒软件关掉。
注意:这个实验期末考试会选出一段进行考试,所以要注意
病毒样本分析
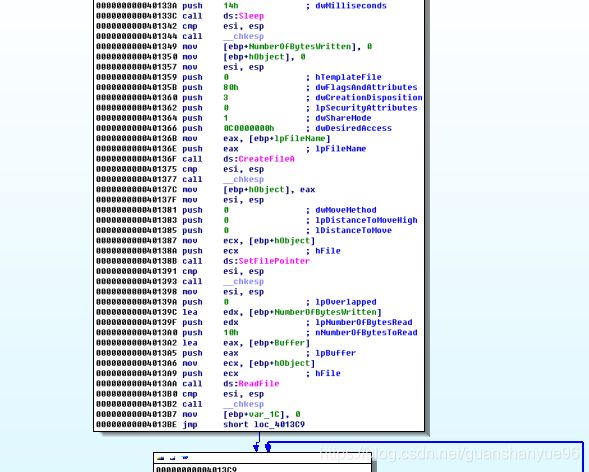
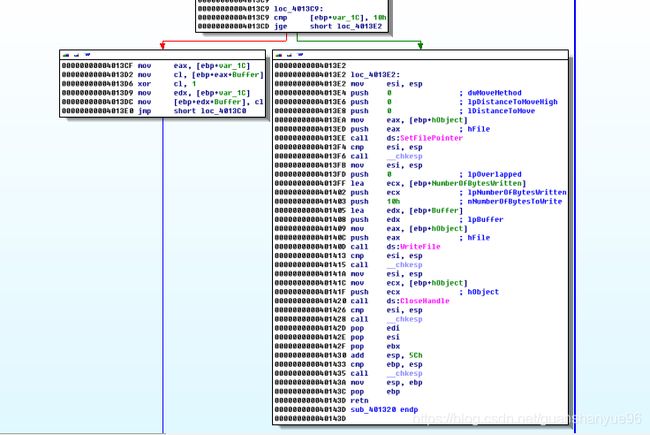
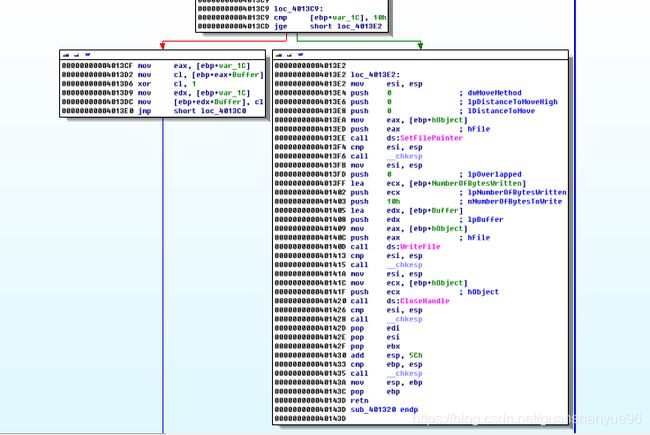
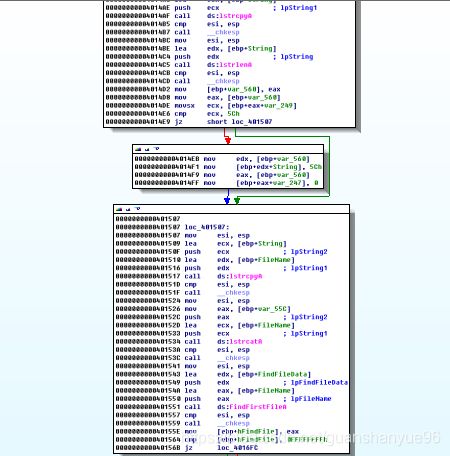
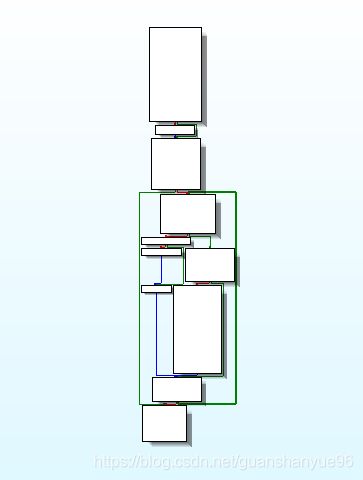
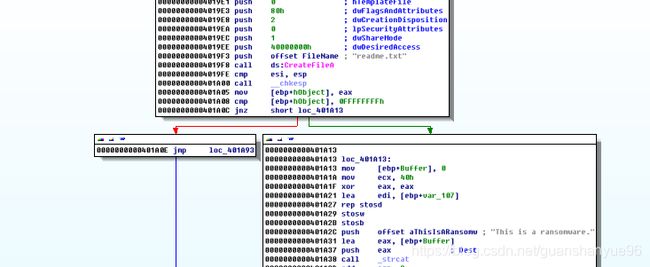
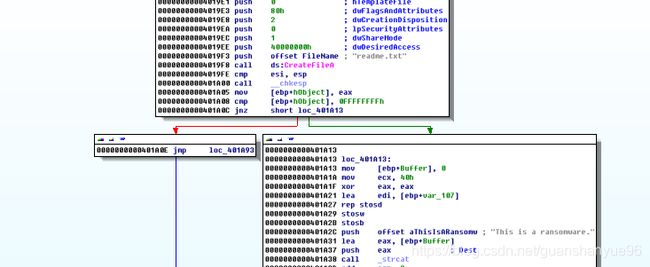
(1)对sub_401320文件加密操作分析
分析:
- sleep - 程序休眠一点时间
- CreateFileA - 创建一个新的文件
- 移动文件指针到头部
- 读取同一个文件夹下的一个文件
分析:
- sleep - 程序休眠一点时间
- CreateFileA - 创建一个新的文件
- 移动文件指针到头部
- 读取同一个文件夹下的一个文件
(1)* 00000000004013C9 cmp [ebp+var_1C], 10h 比较,如果文件还未加密完(前16个字节),跳转00000000004013CF,
* xor c1,1 - 按位或1将获取的值加密
* 反之跳转00000000004013E2
* setFilePointer - 对文件指针偏移到最开始
* writeFile - 把前16个字节加密后的数据流写入之前创建的新文件
* Closehandle - 关闭文件句柄
具体流程图:
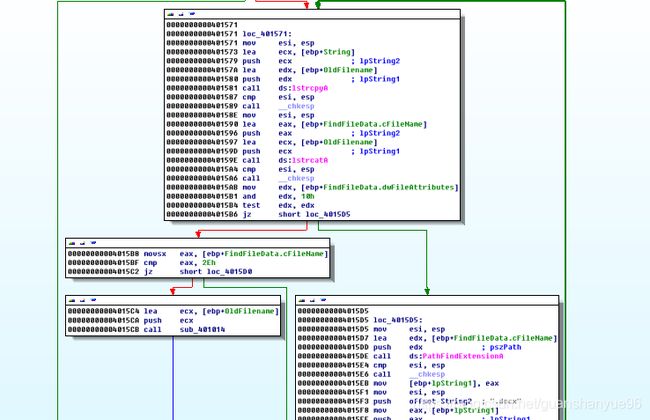
(2)sub_401470主要用于查找docx文件
分析:
LstrcpyA 、LstrlenA、lstrcatA - 主要获取文件夹里的路径,文件名,并对之进行处理
FindFirstFileEx - 根据文件名查找文件。该函数到一个文件夹(包括子文件夹)去搜索指定文件 如果要使用附加属性去搜索文件的话 可以使用FindFirstFileEx函数。
如果没有这些文件,跳转 loc_4016FC
有,则跳转0000000000401571
链接:
https://baike.baidu.com/item/FindFirstFile/9621776 - FindFirstFile
分析:
lstrcpyA - 复制字符串
LstrcatA - 连接字符串
总之就是一系列字符串的复制拼接
然后判断是否为空,不为空(!0),则跳转00000000004016FC
反之,为空(0)则跳转00000000004015D5
注:
test eax,eax 基本上和 And eax,eax 是一样的,不同的是test 不改变eax的结果,只是改变FLAG寄存器的状态,也就是改变进位标志,零标志,溢出标志等 等。举一个例子,如果eax=01h,test eax,eax 就是两个01h 作与操作,所以结果还是01h,不是0的话,就不会跳转 je xxxx。所以要跳转je xxxx,只有一种可能就是eax=0h.所以现在eax=0a 则不会跳转 je xxxx
链接:
https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/106832847.html - test eax,eax 如何解释?
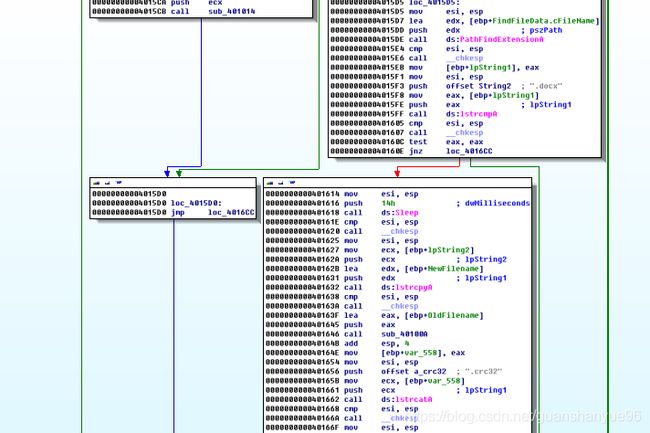
分析:
PathFindExtension - 获得文件后缀名
Lstrcmp - 比较文件后缀名,如果是.docx 跳转0000000000401614,如果不是.docx,跳转00000000004016CC
注:PathFindExtension函数的功能是获取绝对路径或文件名中的文件扩展名。
链接:https://baike.baidu.com/item/PathFindExtension/2910474?noadapt=1 - PathFindExtension
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
分析:
上面一系列函数主要是用于装换.crc32后缀名,拼接文件名和路径
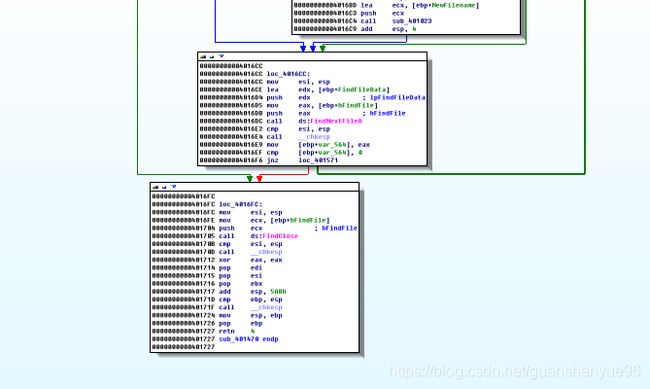
解释:
findNextFileA - 查找下一个文件
.text:004016EF cmp [ebp+var_564], 0 - 比较是否查找到最后,查找到最后,跳转00000000004016FC
.text:004016F6 jnz loc_401571 反之,跳转loc_401571
findClose - 查找停止
总的逻辑图
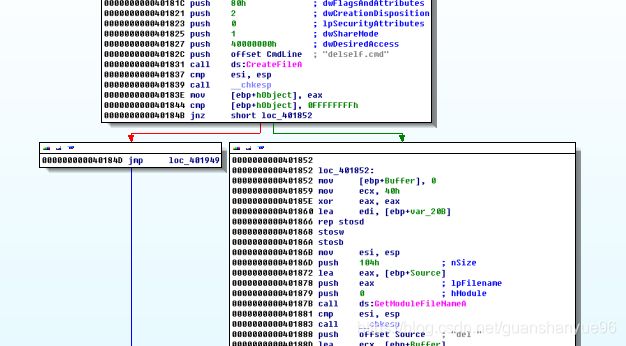
(3)对sub_4017D0主要用于创建自删除脚本文件分析
分析:
createFileA - 打开一个文件
.text:00401844 cmp [ebp+hObject], 0FFFFFFFFh
.text:0040184B jnz short loc_401852 - 如果文件打开成功,跳转到0000000000401852
反之,跳转到000000000040184D
GetModuleFileName -
获取当前进程已加载模块的文件的完整路径,该模块必须由当前进程加载。
如果想要获取另一个已加载模块的文件路径,可以使用GetModuleFileNameEx函数。
注:
(1)mov si,offset BUFFER 汇编后是mov si, xxxx,这里的xxxx指的是一个相对偏移量,是BUFFER在内存中的相对地址,是一串数字。
汇编器知道BUFFER相对于DS的地址,因为在做汇编的时候,告诉了汇编程序DS的值(ASSUME),然后汇编器通过计算BUFFER之前的东西要多少字节,就能知道BUFFER相对于DS的地址。
(2)Delself.cmd - 删除自身
(3)CreateFile
这个函数的功能是创建或者打开一个文件或者I/O设备,通常使用的I/O形式有文件、文件流、目录、物理磁盘、卷、终端流等。如执行成功,则返回文件句柄。 INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE 表示出错,会设置 GetLastError 。
链接:
https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/30115564 - offset到底是起什么作用?
http://www.bkjia.com/sdfd/967246.html - 反病毒攻防研究:自我复制与自删除
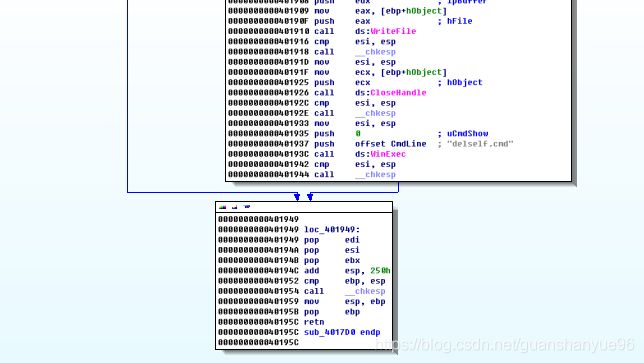
分析:
Writefile - 写一个勒索文件
CloseHandle - 关闭句柄
winExec - 运行删除程序
注:WinAPI: WinExec - 运行外部程序
完整逻辑图:
-
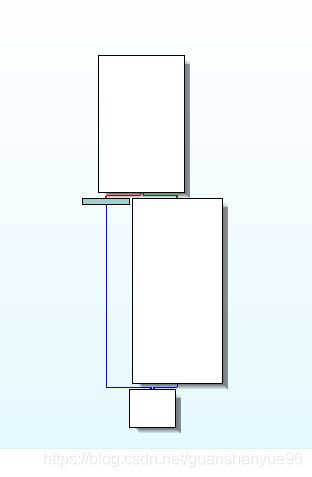
(4)sub_4019B0主要用于创建readme说明文件。
分析:
createFileA - 创建readme.txt文件
分析:
WriteFile - 给文件写入内容
closeHandle - 关闭句柄
具体流程图:
第二部分:专杀工具编写思路
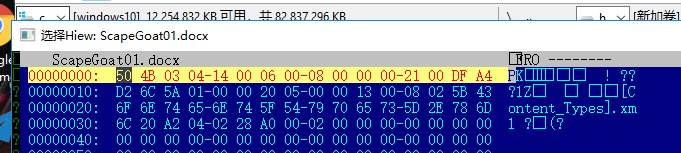
- 用total command打开ScapeGoat01.docx
- 再点击运行病毒,用total command查看加密后的病毒,结合病毒分析,可以知道是
病毒分析:
该病毒virus.exe_是把word文件加密,怎么加密呢?是把word文件的文件前16个字节(好像是前16个字节)加密,word是一个压缩文件,打开它就是一个解密的过程,而对它的前16个字节加密,就是对word文件头进行加密(包含PE)。解压的原理是看被解压文件的文件头,看这个文件是什么类型,再依靠此信息进行解压。如果改变了文件头,就不能知道这个文件是什么文件,所以就不能打开被病毒加密的文件。所以我们要对文件解密,就要把被修改的文件头进行还原。病毒virus.exe_是通过什么方式进行进行加密的,就是把前16个字节的每一个字节xor(按位异或)1,怎么把它解密呢?
方法如下:
解密是把前16个字节再xor(按位异或)1
如原来的值为:11011101
加密:
11011101
^00000001
__________
11011100
解密:
11011100
^ 00000001
-----------------
11011101
注:
按位异或^
运算符^
1^1=0;0^0=0; //相同则为0
0^1=1;1^0=1; //不相同为1
专杀方法(两种):
提特征码
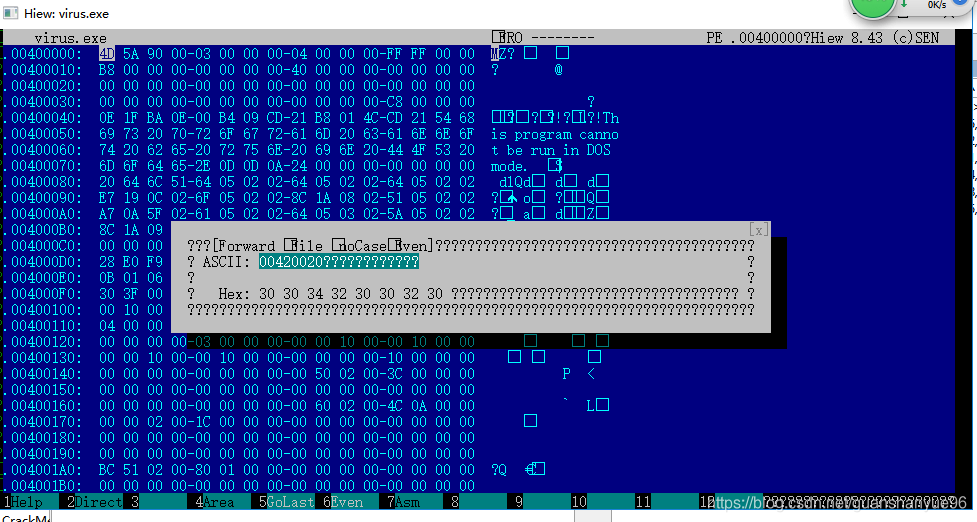
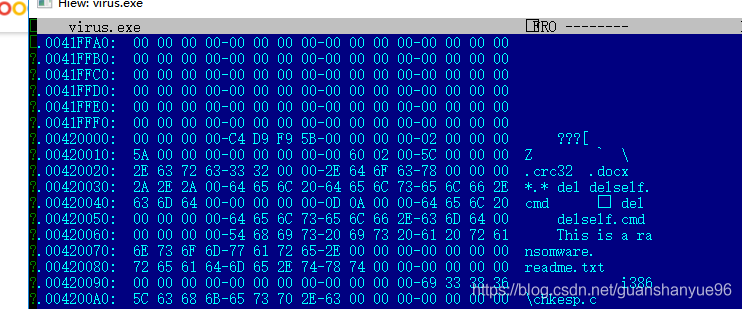
跳转oX00420020:
修改:此处有问题,就是通过地址跳转要使用F5(Goto)- 注意:输入的是偏移量,通过特征码跳转要使用F7(Search),上面这个图是错的,大家参考时知道就行
提取特征值:00420020 - 2E 63 72 63 33 32 00 00 2E 64 6F 63 78 00 00 00
提字符串:delself.cmd,或者是那句话(勒索的话),crc32
- 找偏移(地址:要减去前面的基地值),提取特征码,进行专杀
hash值MD5
(1)c语言查看程序MD5的值
https://www.jb51.net/article/37428.htm - 用c获取文件MD5的值
(2)以特征码查杀
https://blog.csdn.net/ioio_jy/article/details/51198544 - 病毒特征码查杀之基本原理
(3)https://blog.csdn.net/xibeichengf/article/details/48750315 - Windows下查看文件MD5值
(4)Java查看程序的MD5值:
代码:
virus病毒专杀工具.cpp
pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "md5.h"
using namespace std;
char *MD5_file(char *path, int md5_len);
boolean my_decrypt(char* fd); //读数据函数//读数据函数
boolean signature_code_killing(char* fd);
/**
作者:
时间:2019.4.1
功能:写一个关于virus.exe的专杀工具
方法:可以使用virus.exe 的 md5 值,或者特征值
virus.exe的MD5值:
16 : 89a075c3651a37e6
32 : defc08e589a075c3651a37e6117e638c
特征码:.00420020: 2E 63 72 63-33 32 00 00-2E 64 6F 63-78 00 00 00 .crc32 .docx
*/
char md5_16[30] = { "89a075c3651a37e6\0" }; //md5值16进制
char md5_32[40] = { "defc08e589a075c3651a37e6117e638c\0" }; //md5值32进制
char signature_code[16] = { 0x2E,0x63,0x72,0x63,0x33,0x32,0x00,0x00,0x2E,0x64,0x6F,0x63,0x78,0x00,0x00,0x00 }; //特征值
int main()
{
while (true)
{
cout << "-----------------------菜单----------------------" << endl;
cout << "\t1.获得程序md5值" << endl;
cout << "\t2.查杀 virus 病毒" << endl;
cout << "\t3.解密 virus 加密文件" << endl;
cout << "\t4.退出程序" << endl;
cout << "-----------------------选择----------------------" << endl;
int option;
cin >> option;
if (option == 1) //获得程序md5值
{
cout << "请输入文件的路径:";
char filePath[200] = { 0 };
cin >> filePath;
//md5
char *md5;
md5 = MD5_file(filePath , 16);
cout << "16:" << md5 << endl;
free(md5);
md5 = MD5_file(filePath, 32);
cout << "32:" << md5 << endl;
free(md5);
}
else if (option == 2) //查杀 virus 病毒
{
while (1)
{
cout << "-----------------------查杀virus.exe----------------------" << endl;
cout << "\t\t1.md5查杀" << endl;
cout << "\t\t2.特征值查杀" << endl;
cout << "\t\t3.返回" << endl;
cout << "----------------------------选择--------------------------" << endl;
cout << ">>:";
int option2;
cin >> option2;
if (option2 == 1) //使用MD5查杀
{
cout << "--当前正使用md5查杀--" << endl;
cout << "请输入要查杀文件的路径:";
char filePath[200] = { 0 };
cin >> filePath;
//md5
char *md5;
md5 = MD5_file(filePath, 16);
cout << "要查杀的文件MD5值的16进制为:" << md5 << endl;
if (strcmp(md5, md5_16) == 0)
{
cout << "--此目标程序是病毒库中的病毒,请选择是否查杀(y/n)--" << endl;
cout << ">>:";
char option3;
cin >> option3;
if (option3 == 'y' || option3 == 'Y')
{
//查杀
if (remove(filePath) == 0)
{
cout << "--查杀成功!!!--" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "警告:遇到未知错误,查杀失败!" << endl;
}
break;
}
else if(option3 == 'n' || option3 == 'N')
{
cout << "--已放弃查杀--" << endl;
break;
}
else
{
cout << "--你的输入有误!请重新输入--" << endl;
break;
}
}
}
else if(option2 == 2) //使用特征码查杀
{
cout << "--当前你正使用特征值查杀--" << endl;
cout << "请输入要查杀文件的路径:";
char filePath[200] = { 0 };
cin >> filePath;
boolean yOrN = signature_code_killing(filePath);
if (yOrN == true)
{
if (remove(filePath) == 0)
{
cout << "--查杀成功!!!--" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "警告:遇到未知错误,查杀失败!" << endl;
}
}
}
else if(option == 3)
{
break;
}
else
{
cout << "你的输入有误,请重新输入!" << endl;
break;
}
}
}
else if (option == 3) //解密 virus 加密文件
{
cout << "--当前正进行virus解密--" << endl;
cout << "请输入要解密文件的路径:";
char filePath[200] = { 0 };
cin >> filePath;
boolean sOrN = my_decrypt(filePath); //对文件解密
break;
}
else
{
cout << "--没有此选择!你的输入有误,请重新输入--" << endl;
break;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//使用特征码查杀
boolean signature_code_killing(char* fd)
{
fstream file;
file.open(fd, ios::binary | ios::in | ios::ate); //打开时指针在文件尾
if (!file)
{
cout << "--错误:不能打开输入文件!--" << endl;
return 1;
}
long length = file.tellg();
cout << "读取的文件长度:" << length << endl;
char* imgData = new char[length];
//seekg()是对输入文件定位,它有两个参数:第一个参数是偏移量,第二个参数是基地址。
long offset = 0x00020020; //偏移量
long base_address = 0x00400000; //基地址
cout << "测试101:指针指向的偏移量为:" << offset << endl;
cout << "测试102:指针指向的基地址为:" << base_address << endl;
assert(file);
file.seekg(0x00020020, ios::beg); //指向文件0x00420020
file.read(imgData, 16); //二进制只能用这个读,读取文件0x00420020前16个字节
int flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
//long currentI = (i + offset + base_address)/8;
cout << "--0x00420020文件第" << i << "个字节为:"<< hex << imgData[i] << "--" << endl; //把int转为16进制输出
cout << "--特征码第" << i << "个字节值为:" << hex << signature_code[i] << "--" << endl;
if (imgData[i] == signature_code[i])
{
cout << "特征码第" << i << "个字符匹配" << endl;
}
else
{
flag = 1;
cout << "特征码第" << i << "个字符不匹配" << endl;
}
}
file.close();
if (flag == 0) //flag==0,进行查杀
{
cout << "--当前文件是" << fd << "--" << endl;
cout << "--此目标程序是病毒库中的病毒,请选择是否查杀(y/n)--" << endl;
cout << ">>:";
char option3;
cin >> option3;
if (option3 == 'y' || option3 == 'Y')
{
//查杀
return true;
}
else if (option3 == 'n' || option3 == 'N')
{
cout << "--已放弃查杀--" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "--你的输入有误!请重新输入--" << endl;
}
return false;
}
else
{
cout << "此程序不是病毒库中的病毒!!" << endl;
return false;
}
}
//获得文件md5的值
char *MD5_file(char *path, int md5_len)
{
FILE *fp = fopen(path, "rb");
MD5_CTX mdContext;
int bytes;
unsigned char data[1024];
char *file_md5;
int i;
if (fp == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "fopen %s failed\n", path);
return NULL;
}
MD5Init(&mdContext);
while ((bytes = fread(data, 1, 1024, fp)) != 0)
{
MD5Update(&mdContext, data, bytes);
}
MD5Final(&mdContext);
file_md5 = (char *)malloc((md5_len + 1) * sizeof(char));
if (file_md5 == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "malloc failed.\n");
return NULL;
}
memset(file_md5, 0, (md5_len + 1));
if (md5_len == 16)
{
for (i = 4; i < 12; i++)
{
sprintf(&file_md5[(i - 4) * 2], "%02x", mdContext.digest[i]);
}
}
else if (md5_len == 32)
{
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
sprintf(&file_md5[i * 2], "%02x", mdContext.digest[i]);
}
}
else
{
fclose(fp);
free(file_md5);
return NULL;
}
fclose(fp);
return file_md5;
}
//读写文件出现的错误
void my_err(const char *err_string, int line)
{
fprintf(stderr, "line:%d ", line); //fprintf()函数根据指定的格式(format)向输出流(stream)写入数据,把后面的写到前面
perror(err_string);//先输出err_string ,再输出错误原因
exit(1);
}
//对文件解密
//参考:https://blog.csdn.net/hankai1024/article/details/8014757 - c++文件处理
//参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u013749051/article/details/83308710 - c++用文件流实现文件拷贝
boolean my_decrypt(char* fd) //解密函数
{
fstream file;
file.open(fd, ios::binary | ios::in | ios::ate); //打开时指针在文件尾
if (!file)
{
cout << "--错误:不能打开输入文件!--" << endl;
return 1;
}
int length = file.tellg();
char* imgData = new char[length];
file.seekg(0); //指向文件头
file.read(imgData, length); //二进制只能用这个读,读取文件前16个字节
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++)
{
cout << "--未解密前文件第" << i << "个字节为:" << hex << int(imgData[i])<< "--" << endl; //把int转为16进制输出
imgData[i] = imgData[i] ^ 1;
cout << "--解密后文件第" << i << "个字节为:" << hex << int(imgData[i]) << "--" << endl; //把int转为16进制输出
}
cout << "--请输入解密后的文件路径(包含文件名--)" << endl;
char fileName[100] = { 0 };
cin >> fileName;
fstream file2;
file2.open(fileName, ios::binary|ios::out);
file2.write(imgData, length); //二进制只能用这个写
file2.close();
file.close();
if (file2)
{
cout << "--解密成功,新的文件已创建,请查看" << fileName << "文件!!!--" << endl;
return true;
}
else
{
cout << "--错误:解密失败!请检查操作是否正确!--" << endl;
return false;
}
}
md5.h
#pragma once
/*
**********************************************************************
** md5.h -- Header file for implementation of MD5 **
** RSA Data Security, Inc. MD5 Message Digest Algorithm **
** Created: 2/17/90 RLR **
** Revised: 12/27/90 SRD,AJ,BSK,JT Reference C version **
** Revised (for MD5): RLR 4/27/91 **
** -- G modified to have y&~z instead of y&z **
** -- FF, GG, HH modified to add in last register done **
** -- Access pattern: round 2 works mod 5, round 3 works mod 3 **
** -- distinct additive constant for each step **
** -- round 4 added, working mod 7 **
**********************************************************************
*/
/*
**********************************************************************
** Copyright (C) 1990, RSA Data Security, Inc. All rights reserved. **
** **
** License to copy and use this software is granted provided that **
** it is identified as the "RSA Data Security, Inc. MD5 Message **
** Digest Algorithm" in all material mentioning or referencing this **
** software or this function. **
** **
** License is also granted to make and use derivative works **
** provided that such works are identified as "derived from the RSA **
** Data Security, Inc. MD5 Message Digest Algorithm" in all **
** material mentioning or referencing the derived work. **
** **
** RSA Data Security, Inc. makes no representations concerning **
** either the merchantability of this software or the suitability **
** of this software for any particular purpose. It is provided "as **
** is" without express or implied warranty of any kind. **
** **
** These notices must be retained in any copies of any part of this **
** documentation and/or software. **
**********************************************************************
*/
/* typedef a 32 bit type */
typedef unsigned long int UINT4;
/* Data structure for MD5 (Message Digest) computation */
typedef struct {
UINT4 i[2]; /* number of _bits_ handled mod 2^64 */
UINT4 buf[4]; /* scratch buffer */
unsigned char in[64]; /* input buffer */
unsigned char digest[16]; /* actual digest after MD5Final call */
} MD5_CTX;
//void MD5Init(MD5_CTX *mdContext);
//void MD5Update(MD5_CTX *mdContext, unsigned char *inBuf, unsigned int inLen);
//void MD5Final(MD5_CTX *mdContext);
static void Transform(UINT4 *buf, UINT4 *in);
static unsigned char PADDING[64] = {
0x80, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00
};
/* F, G and H are basic MD5 functions: selection, majority, parity */
#define F(x, y, z) (((x) & (y)) | ((~x) & (z)))
#define G(x, y, z) (((x) & (z)) | ((y) & (~z)))
#define H(x, y, z) ((x) ^ (y) ^ (z))
#define I(x, y, z) ((y) ^ ((x) | (~z)))
/* ROTATE_LEFT rotates x left n bits */
#define ROTATE_LEFT(x, n) (((x) << (n)) | ((x) >> (32-(n))))
/* FF, GG, HH, and II transformations for rounds 1, 2, 3, and 4 */
/* Rotation is separate from addition to prevent recomputation */
#define FF(a, b, c, d, x, s, ac) \
{(a) += F ((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (UINT4)(ac); \
(a) = ROTATE_LEFT ((a), (s)); \
(a) += (b); \
}
#define GG(a, b, c, d, x, s, ac) \
{(a) += G ((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (UINT4)(ac); \
(a) = ROTATE_LEFT ((a), (s)); \
(a) += (b); \
}
#define HH(a, b, c, d, x, s, ac) \
{(a) += H ((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (UINT4)(ac); \
(a) = ROTATE_LEFT ((a), (s)); \
(a) += (b); \
}
#define II(a, b, c, d, x, s, ac) \
{(a) += I ((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (UINT4)(ac); \
(a) = ROTATE_LEFT ((a), (s)); \
(a) += (b); \
}
void MD5Init(MD5_CTX *mdContext)
{
mdContext->i[0] = mdContext->i[1] = (UINT4)0;
/* Load magic initialization constants.
*/
mdContext->buf[0] = (UINT4)0x67452301;
mdContext->buf[1] = (UINT4)0xefcdab89;
mdContext->buf[2] = (UINT4)0x98badcfe;
mdContext->buf[3] = (UINT4)0x10325476;
}
void MD5Update(MD5_CTX *mdContext, unsigned char *inBuf, unsigned int inLen)
{
UINT4 in[16];
int mdi;
unsigned int i, ii;
/* compute number of bytes mod 64 */
mdi = (int)((mdContext->i[0] >> 3) & 0x3F);
/* update number of bits */
if ((mdContext->i[0] + ((UINT4)inLen << 3)) < mdContext->i[0])
mdContext->i[1]++;
mdContext->i[0] += ((UINT4)inLen << 3);
mdContext->i[1] += ((UINT4)inLen >> 29);
while (inLen--) {
/* add new character to buffer, increment mdi */
mdContext->in[mdi++] = *inBuf++;
/* transform if necessary */
if (mdi == 0x40) {
for (i = 0, ii = 0; i < 16; i++, ii += 4)
in[i] = (((UINT4)mdContext->in[ii + 3]) << 24) |
(((UINT4)mdContext->in[ii + 2]) << 16) |
(((UINT4)mdContext->in[ii + 1]) << 8) |
((UINT4)mdContext->in[ii]);
Transform(mdContext->buf, in);
mdi = 0;
}
}
}
void MD5Final(MD5_CTX *mdContext)
{
UINT4 in[16];
int mdi;
unsigned int i, ii;
unsigned int padLen;
/* save number of bits */
in[14] = mdContext->i[0];
in[15] = mdContext->i[1];
/* compute number of bytes mod 64 */
mdi = (int)((mdContext->i[0] >> 3) & 0x3F);
/* pad out to 56 mod 64 */
padLen = (mdi < 56) ? (56 - mdi) : (120 - mdi);
MD5Update(mdContext, PADDING, padLen);
/* append length in bits and transform */
for (i = 0, ii = 0; i < 14; i++, ii += 4)
in[i] = (((UINT4)mdContext->in[ii + 3]) << 24) |
(((UINT4)mdContext->in[ii + 2]) << 16) |
(((UINT4)mdContext->in[ii + 1]) << 8) |
((UINT4)mdContext->in[ii]);
Transform(mdContext->buf, in);
/* store buffer in digest */
for (i = 0, ii = 0; i < 4; i++, ii += 4) {
mdContext->digest[ii] = (unsigned char)(mdContext->buf[i] & 0xFF);
mdContext->digest[ii + 1] =
(unsigned char)((mdContext->buf[i] >> 8) & 0xFF);
mdContext->digest[ii + 2] =
(unsigned char)((mdContext->buf[i] >> 16) & 0xFF);
mdContext->digest[ii + 3] =
(unsigned char)((mdContext->buf[i] >> 24) & 0xFF);
}
}
/* Basic MD5 step. Transform buf based on in.
*/
static void Transform(UINT4 *buf, UINT4 *in)
{
UINT4 a = buf[0], b = buf[1], c = buf[2], d = buf[3];
/* Round 1 */
#define S11 7
#define S12 12
#define S13 17
#define S14 22
FF(a, b, c, d, in[0], S11, 3614090360); /* 1 */
FF(d, a, b, c, in[1], S12, 3905402710); /* 2 */
FF(c, d, a, b, in[2], S13, 606105819); /* 3 */
FF(b, c, d, a, in[3], S14, 3250441966); /* 4 */
FF(a, b, c, d, in[4], S11, 4118548399); /* 5 */
FF(d, a, b, c, in[5], S12, 1200080426); /* 6 */
FF(c, d, a, b, in[6], S13, 2821735955); /* 7 */
FF(b, c, d, a, in[7], S14, 4249261313); /* 8 */
FF(a, b, c, d, in[8], S11, 1770035416); /* 9 */
FF(d, a, b, c, in[9], S12, 2336552879); /* 10 */
FF(c, d, a, b, in[10], S13, 4294925233); /* 11 */
FF(b, c, d, a, in[11], S14, 2304563134); /* 12 */
FF(a, b, c, d, in[12], S11, 1804603682); /* 13 */
FF(d, a, b, c, in[13], S12, 4254626195); /* 14 */
FF(c, d, a, b, in[14], S13, 2792965006); /* 15 */
FF(b, c, d, a, in[15], S14, 1236535329); /* 16 */
/* Round 2 */
#define S21 5
#define S22 9
#define S23 14
#define S24 20
GG(a, b, c, d, in[1], S21, 4129170786); /* 17 */
GG(d, a, b, c, in[6], S22, 3225465664); /* 18 */
GG(c, d, a, b, in[11], S23, 643717713); /* 19 */
GG(b, c, d, a, in[0], S24, 3921069994); /* 20 */
GG(a, b, c, d, in[5], S21, 3593408605); /* 21 */
GG(d, a, b, c, in[10], S22, 38016083); /* 22 */
GG(c, d, a, b, in[15], S23, 3634488961); /* 23 */
GG(b, c, d, a, in[4], S24, 3889429448); /* 24 */
GG(a, b, c, d, in[9], S21, 568446438); /* 25 */
GG(d, a, b, c, in[14], S22, 3275163606); /* 26 */
GG(c, d, a, b, in[3], S23, 4107603335); /* 27 */
GG(b, c, d, a, in[8], S24, 1163531501); /* 28 */
GG(a, b, c, d, in[13], S21, 2850285829); /* 29 */
GG(d, a, b, c, in[2], S22, 4243563512); /* 30 */
GG(c, d, a, b, in[7], S23, 1735328473); /* 31 */
GG(b, c, d, a, in[12], S24, 2368359562); /* 32 */
/* Round 3 */
#define S31 4
#define S32 11
#define S33 16
#define S34 23
HH(a, b, c, d, in[5], S31, 4294588738); /* 33 */
HH(d, a, b, c, in[8], S32, 2272392833); /* 34 */
HH(c, d, a, b, in[11], S33, 1839030562); /* 35 */
HH(b, c, d, a, in[14], S34, 4259657740); /* 36 */
HH(a, b, c, d, in[1], S31, 2763975236); /* 37 */
HH(d, a, b, c, in[4], S32, 1272893353); /* 38 */
HH(c, d, a, b, in[7], S33, 4139469664); /* 39 */
HH(b, c, d, a, in[10], S34, 3200236656); /* 40 */
HH(a, b, c, d, in[13], S31, 681279174); /* 41 */
HH(d, a, b, c, in[0], S32, 3936430074); /* 42 */
HH(c, d, a, b, in[3], S33, 3572445317); /* 43 */
HH(b, c, d, a, in[6], S34, 76029189); /* 44 */
HH(a, b, c, d, in[9], S31, 3654602809); /* 45 */
HH(d, a, b, c, in[12], S32, 3873151461); /* 46 */
HH(c, d, a, b, in[15], S33, 530742520); /* 47 */
HH(b, c, d, a, in[2], S34, 3299628645); /* 48 */
/* Round 4 */
#define S41 6
#define S42 10
#define S43 15
#define S44 21
II(a, b, c, d, in[0], S41, 4096336452); /* 49 */
II(d, a, b, c, in[7], S42, 1126891415); /* 50 */
II(c, d, a, b, in[14], S43, 2878612391); /* 51 */
II(b, c, d, a, in[5], S44, 4237533241); /* 52 */
II(a, b, c, d, in[12], S41, 1700485571); /* 53 */
II(d, a, b, c, in[3], S42, 2399980690); /* 54 */
II(c, d, a, b, in[10], S43, 4293915773); /* 55 */
II(b, c, d, a, in[1], S44, 2240044497); /* 56 */
II(a, b, c, d, in[8], S41, 1873313359); /* 57 */
II(d, a, b, c, in[15], S42, 4264355552); /* 58 */
II(c, d, a, b, in[6], S43, 2734768916); /* 59 */
II(b, c, d, a, in[13], S44, 1309151649); /* 60 */
II(a, b, c, d, in[4], S41, 4149444226); /* 61 */
II(d, a, b, c, in[11], S42, 3174756917); /* 62 */
II(c, d, a, b, in[2], S43, 718787259); /* 63 */
II(b, c, d, a, in[9], S44, 3951481745); /* 64 */
buf[0] += a;
buf[1] += b;
buf[2] += c;
buf[3] += d;
}
/*
**********************************************************************
** End of md5.h **
******************************* (cut) ********************************
*/
测试:
病毒所在文件:
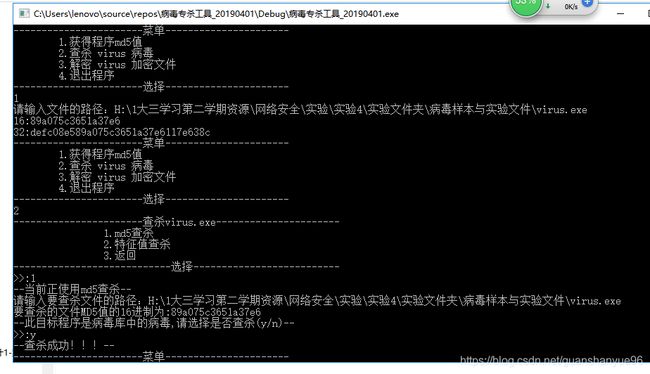
点击运行专杀程序:
(1)使用功能查看程序的MD5值,使用MD5进行查杀
病毒已经被杀死
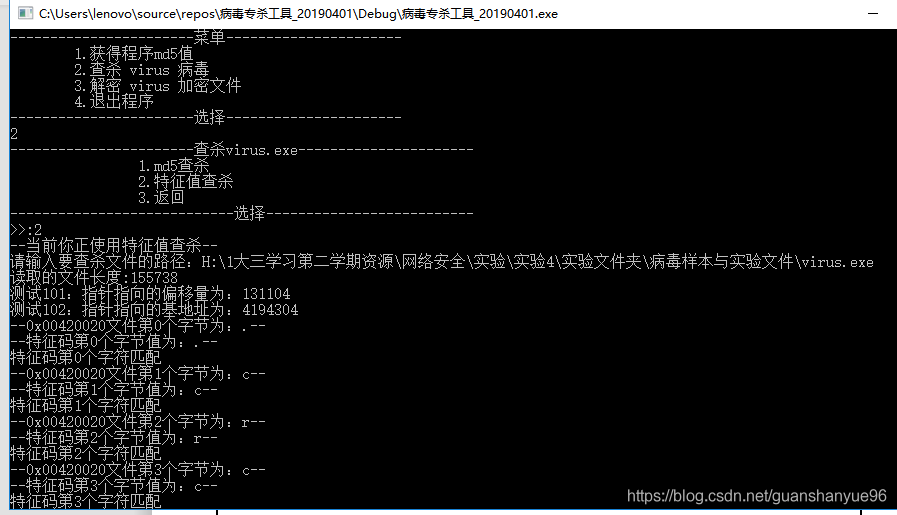
(2)重新准备病毒样本,这次使用特征码进行查杀
结果:查杀成功!
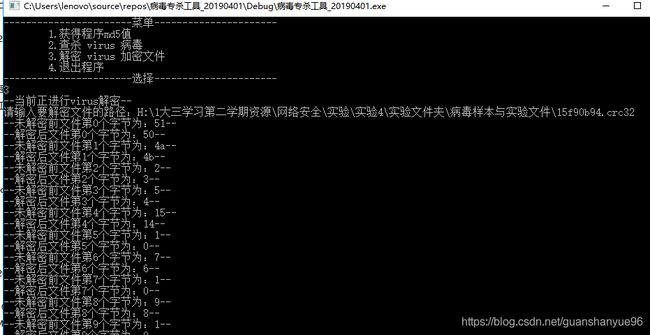
解密文件
再次准备病毒样本,修改后缀名,运行,可以看到病毒已加密
查看文件夹:
打开1.docx,可以看到解密后的文件内容,解密成功!
本次实验的体会
本次实验我们学习了怎么分析病毒样本,怎么使用编写专杀程序杀死病毒,和对病毒加密后的文本进行解密。对于怎样分析病毒样本,这个我们在之前的实验也学习了不少,分析病毒样本最重要的是从病毒的重要行为为突破口进行分析,例如这个virus.exe勒索病毒,它的主要行为有加密文本,删除自身,创建勒索文本,查找docx文本,这些都是重要行为,所以我们着重分析它,在有限的时间内分析病毒样本,只能找最关键的地方分析,这是快速病毒分析的思想所在。
对于编写病毒专杀工具,有两种方法。一种是取MD5,每个程序独有hash值;这个如果病毒进行变种的话,MD5值会改变,所以我们推荐使用第二种获取特征码,根据特征码进行查杀。但这个获取特征码要有技巧,这个特征码一定要是这个程序的显著特征,其他程序代码很大几率不会这样写,如果随便找了一个特征码,很可能会造成误杀。
解密文件的技巧就是通过分析病毒样本和把加密前和加密后的样本查看它的每个地址16进制值(这个看是什么工具),找到不同的地方。再结合两者进行分析,得出它的加密算法。
期间我编写专杀工具,在seekg这个地方卡了很久,主要是不知道怎么才能使指针指向特征码的地址,特征码有基地址和偏移量,我一开始写进去的是它们的和,程序报错,指向的地址被保护,说明我使用的指针可能指向了程序外,不被此程序访问的地址。期间google,baidu还是一知半解,也问了同学,后来自己认真想了想,基地之所以存在的原因是因为硬件地址本来就不够,所以使用基地址,最重要在高位加上偏移量得到一个虚拟地址,而偏移量的最大值就是硬件(内存)的容量,使用偏移量就可以访问到程序在内存中的真正地址,通过使用偏移量作为参数,问题解决。此时在写实验报告时,仿佛记起老师上课也说过使用指针偏移只用偏移量就可以了。走了不少弯路。下面是基地址和偏移量的概念。还有一个推荐就是姜晔老师的博客,把使用MD5和特征值对病毒进行专杀说得很好,在下面也推荐一下