Spring Boot2.0版本源码(二):Spring Boot初始化器
1. 系统初始化器
通过ApplicationContextInitializer类可以实现在springboot容器刷新之前注册属性

2. 演示
FirstInitializer类实现ApplicationContextInitializer接口,重写其中的initialize方法,可以通过下面的代码,向springboot中注入map.put("key1", "value1");这样的键值对。
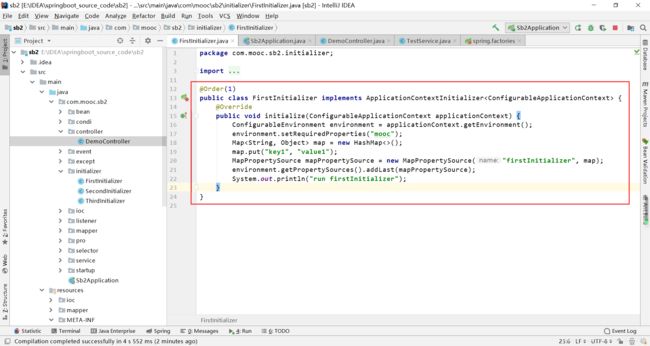
在spring.factories文件中配置刚刚的FirstInitializer
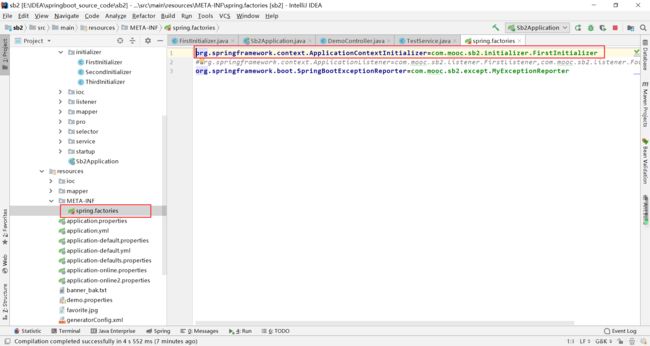
实现ApplicationContextAware接口,获取到applicationContext,可以从其中获取到刚注入的key1数据
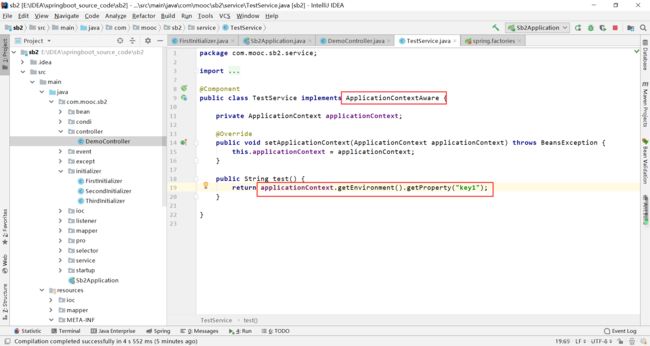
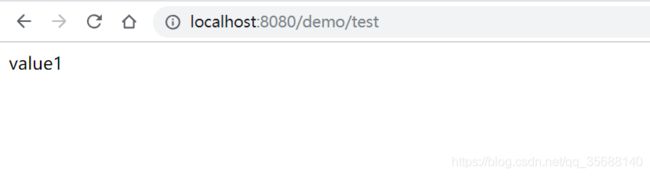
写一个controller调用上面的TestService.test()方法,看到如下结果:
3.SpringFactoriesLoader类如何实现将初始化器加载到spring容器

在下面的地方打上断点,跟进代码
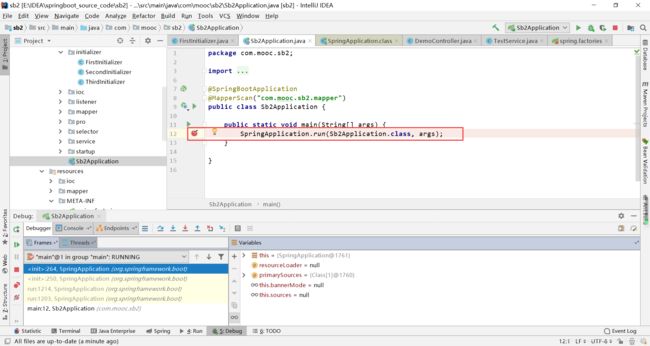
不断跟进源码,发现在SpringApplication类的构造函数中发现了ApplicationContextInitializer初始化器的初始化过程。
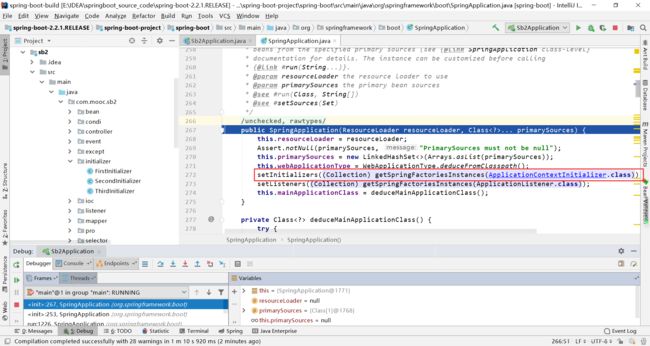
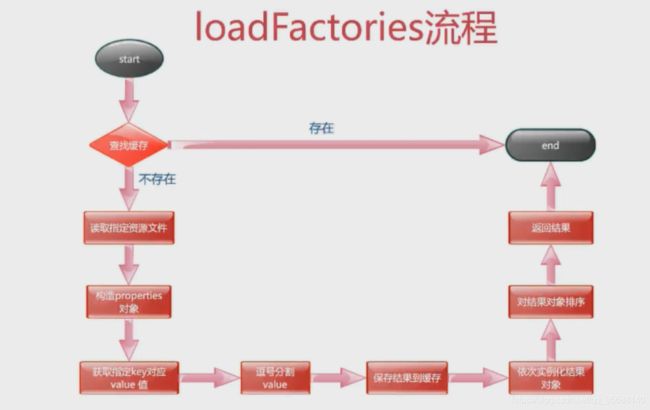
不断跟进源码,getSpringFactoriesInstances大概分为下面三步:
1.通过"META-INF/spring.factories"文件,获得所有的重写了带有ApplicationContextInitializer的全路径名
2.将这些类实例化
3.对这些类排序
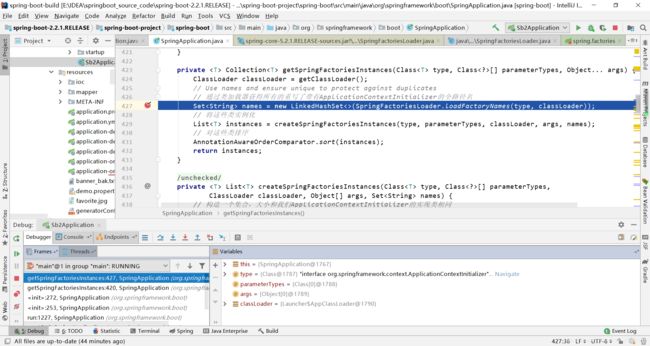
3.1 SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader)
/**
* Load the fully qualified class names of factory implementations of the
* given type from {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION}, using the given
* class loader.
* @param factoryType the interface or abstract class representing the factory
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use for loading resources; can be
* {@code null} to use the default
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if an error occurs while loading factory names
* @see #loadFactories
*/
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 传入的是ApplicationContextInitializer的工厂的名字
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
// 将某个类加载器的实现类实例化加入到Map(以此实现加入到spring容器中)
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 如果之前已经初始化过了,那么缓存中存在全路径名
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
// FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION默认就是"META-INF/spring.factories"
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
// 判断META-INF/spring.factories中的文件是否存在
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
// 利用PropertiesLoaderUtils将我们的资源路径中的"META-INF/spring.factories"加载成Properties对象
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
// properties是一个类型,k就是我们的ApplicationContextInitializer,v就是它的实现类
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
// v因为是实现类,所以可能是一个数组,将他加到result中
for (String factoryImplementationName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) {
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
3.2 createSpringFactoriesInstances源码
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) {
// 构造一个集合,大小和我们ApplicationContextInitializer的实现类相同
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
// 通过constructor构造器实例化一个对象
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
// 加入instances数组
instances.add(instance);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
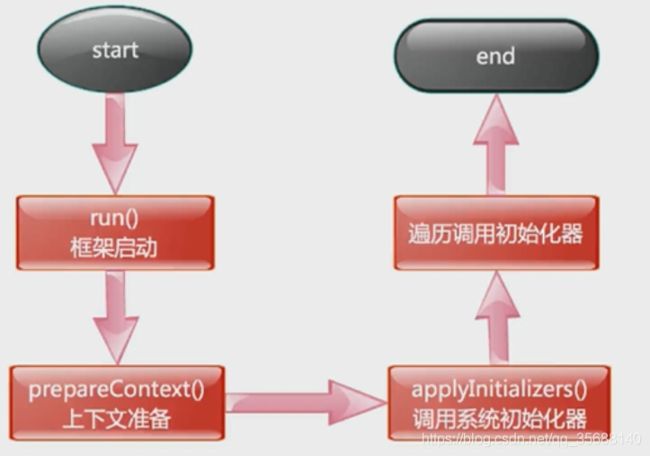
整体流程
4. 初始化器的调用和使用原理
ApplicationContextInitializer的官方描述
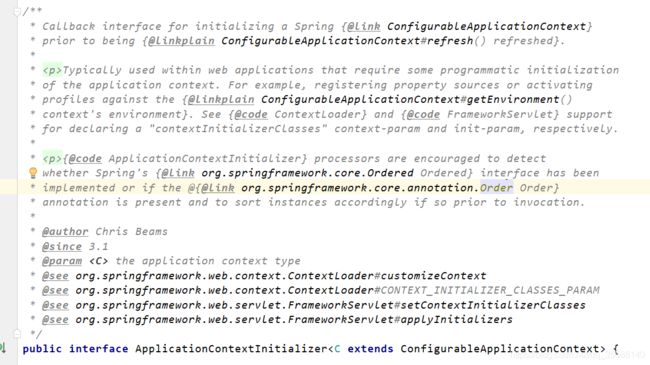
中文大概是下面三种意思:

回顾一下springboot启动的大致流程:
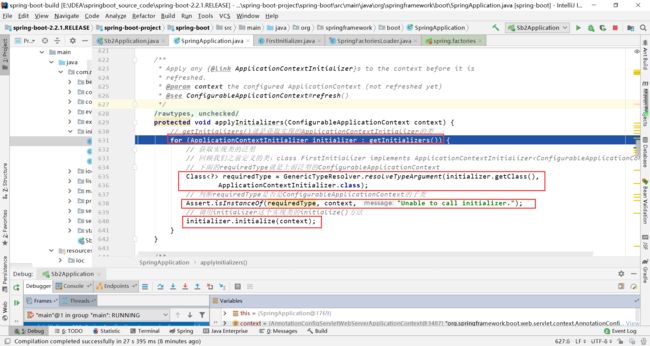
在遍历initalizers的inittialize方法中加入断点。

在系统初始化器中加入断点
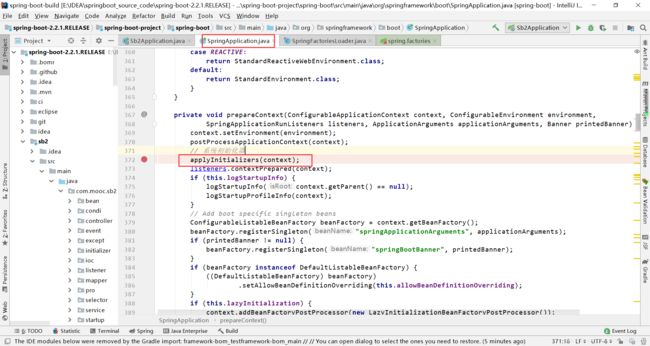
此时会调用ApplicationContextInitializer实现类的initialize()方法