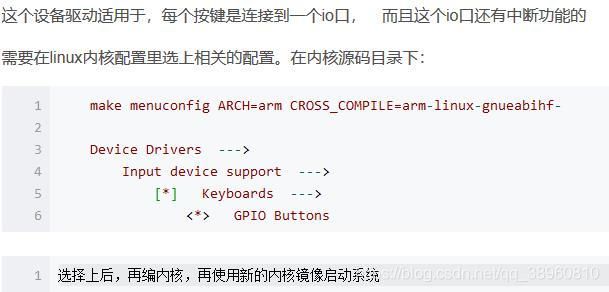
(3.8)一个按键所能涉及的:内核按键标准驱动gpio-keys
/* AUTHOR: Pinus
* Creat on : 2018-10-30
* KERNEL : linux-4.4.145
* BOARD : JZ2440(arm9 s3c2440)
* REFS : 内核 gpio-keys.c
Linux驱动子系统之输入子系统(6)-gpio-keys
47 使用linux内核源码里的按键驱动
解析gpio-keys(kernel-4.7)
*/
分析
从入口函数开始
static int __init gpio_keys_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&gpio_keys_device_driver); // 注册平台设备
}显然其采用了platform bus的方法设计驱动,由此也可以猜想出,我们若想要实现该驱动,理想情况下不用更改gpio-keys.c中的任何一个字,只需要编写其需要的平台设备资源。但是我们要提供哪些资源呢?显然这就需要通过阅读驱动代码确定。
static struct platform_driver gpio_keys_device_driver = {
.probe = gpio_keys_probe, // 驱动和设备匹配后调用该函数
.remove = gpio_keys_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "gpio-keys", /*platform driver和platform device通过name来匹配 */
.pm = &gpio_keys_pm_ops, // 写了但并未具体赋值,无意义
.of_match_table = of_match_ptr(gpio_keys_of_match), // 匹配列表
}
};platform_driver 是用于平台驱动注册的结构体,其中各项含义皆有注释。前文中也有分析。
当驱动和设备的.name匹配,必然会去调用gpio_keys_probe,为方便阅读只保留重要部分,完整代码可再内核源码中获取。
// probe主要完成初始化引脚,注册输入设备input_dev,在sys目录下产生相应的文件
static int gpio_keys_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct device *dev = &pdev->dev;
const struct gpio_keys_platform_data *pdata = dev_get_platdata(dev); //获取具体的设备platform_data资源;可得知我们写的平台设备的platform_data成员应当提供gpio_keys_platform_data类型数据
struct gpio_keys_drvdata *ddata; //定义一个结构体,用来整合关联各类信息
struct input_dev *input; // 声明输入子系统结构
...
input = devm_input_allocate_device(dev); // 实例化结构体
...
ddata->pdata = pdata; // 将平台资源整合在,ddate中
ddata->input = input; // 将输入子系统设备整合在,ddate中
mutex_init(&ddata->disable_lock); // 初始化ddate中的互斥锁
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, ddata); // 把ddate保存在平台设备pdev中 pdev->dev->driver_data = ddata
input_set_drvdata(input, ddata); // 同理, input->dev->driver_data = ddata
/*设置input相关属性*/
input->name = pdata->name ? : pdev->name; // 优先使用在设备资源里定义的name
input->phys = "gpio-keys/input0";
input->dev.parent = &pdev->dev;
input->open = gpio_keys_open; // input打开操作
input->close = gpio_keys_close; // input关闭操作
input->id.bustype = BUS_HOST;
input->id.vendor = 0x0001;
input->id.product = 0x0001;
input->id.version = 0x0100;
/* Enable auto repeat feature of Linux input subsystem 使能输入子系统 自动重复上报的特点*/
if (pdata->rep)
__set_bit(EV_REP, input->evbit);
for (i = 0; i < pdata->nbuttons; i++) { // 根据按键数目循环设置所有按键
const struct gpio_keys_button *button = &pdata->buttons[i];
struct gpio_button_data *bdata = &ddata->data[i];
error = gpio_keys_setup_key(pdev, input, bdata, button); // 初始化按键,将按键信息也保存在ddate中
...
}
error = sysfs_create_group(&pdev->dev.kobj, &gpio_keys_attr_group);
...
error = input_register_device(input); // 注册input设备
...
device_init_wakeup(&pdev->dev, wakeup);
...
}代码一开始就定义了两个很重要的结构体,弄清楚这两个结构体的组成,对理解代码有河大帮助。
其一:
const struct gpio_keys_platform_data *pdata = dev_get_platdata(dev); //获取具体的设备platform_data资源;可得知我们写的平台设备的platform_data成员应当提供
由注释也可以看出这个的作用了,他就是我们在平台设备侧应该给出的数据
/**
* struct gpio_keys_platform_data - platform data for gpio_keys driver
* @buttons: pointer to array of &gpio_keys_button structures
* describing buttons attached to the device
* @nbuttons: number of elements in @buttons array
* @poll_interval: polling interval in msecs - for polling driver only
* @rep: enable input subsystem auto repeat
* @enable: platform hook for enabling the device
* @disable: platform hook for disabling the device
* @name: input device name
*/
struct gpio_keys_platform_data {
struct gpio_keys_button *buttons; // 按键设置信息
int nbuttons; // 按键数目
unsigned int poll_interval;
unsigned int rep:1;
int (*enable)(struct device *dev);
void (*disable)(struct device *dev);
const char *name;
};这其中又有一个结构体gpio_keys_button
/**
* struct gpio_keys_button - configuration parameters
* @code: input event code (KEY_*, SW_*)
* @gpio: %-1 if this key does not support gpio
* @active_low: %true indicates that button is considered // 1 低电平有效,低电平表示按下
* depressed when gpio is low
* @desc: label that will be attached to button's gpio // 按键的描述 名字
* @type: input event type 输入事件类型(%EV_KEY, %EV_SW, %EV_ABS)
* @wakeup: configure the button as a wake-up source 配置一个按键为唤醒源
* @debounce_interval: debounce ticks interval in msecs
* @can_disable: %true indicates that userspace is allowed to
* disable button via sysfs 1 表示可以在用户空间内disable
* @value: axis value for %EV_ABS 坐标值,EV_ABS专用
* @irq: Irq number in case of interrupt keys 中断号
* @gpiod: GPIO descriptor
*/
struct gpio_keys_button {
unsigned int code; //此按键对应的键码
int gpio; //此按键对应的一个io口
int active_low; // 1 低电平有效,低电平表示按下
const char *desc; //就是申请io口,申请中断时使用的名字
unsigned int type; //输入设备的事件类型,按键用EV_KEY
int wakeup; //表示按键按下时是否唤醒系统, 这个需要io口硬件上有这功能
int debounce_interval; // 去抖动间隔 防抖动用,间隔多久时间
bool can_disable;
int value;
unsigned int irq;
struct gpio_desc *gpiod;
};看其各项含义,不由让我联想到我们在学习用input子系统实现按键时所进行的设置,显然这些都应该是设备资源的一部分。
其二:struct gpio_keys_drvdata *ddata; //定义一个结构体,用来整合关联各类信息
struct gpio_keys_drvdata {
const struct gpio_keys_platform_data *pdata; // 平台设备资源
struct input_dev *input; // 指向定义的输入子系统设备
struct mutex disable_lock; // 定义一个互斥锁
struct gpio_button_data data[0]; // 按键设置信息
};它就是驱动定义的结构体,用来关联各设备相关项,其内也有一个结构体gpio_button_data
struct gpio_button_data {
const struct gpio_keys_button *button; // 按键的设置
struct input_dev *input;
struct timer_list release_timer; // 防抖动定时器
unsigned int release_delay; /* in msecs, for IRQ-only buttons ms, 按下的延迟,超过表示一直按 */
struct delayed_work work;
unsigned int software_debounce; /* 去抖动 in msecs, for GPIO-driven buttons */
unsigned int irq;
spinlock_t lock;
bool disabled;
bool key_pressed;
};其中有关于定时的设置,显然是用来防抖动的。
大致介绍这两个结构体,继续向下看,
error = gpio_keys_setup_key(pdev, input, bdata, button); // 初始化按键,将按键信息也保存在ddate中
static int gpio_keys_setup_key(struct platform_device *pdev, struct input_dev *input, struct gpio_button_data *bdata, const struct gpio_keys_button *button)
{
const char *desc = button->desc ? button->desc : "gpio_keys";
struct device *dev = &pdev->dev;
irq_handler_t isr;
unsigned long irqflags;
int irq;
int error;
bdata->input = input; // 关联进ddate
bdata->button = button;
spin_lock_init(&bdata->lock);
if (gpio_is_valid(button->gpio)) { // 如果设置的io口有效根据io脚设置,否则根据IRQ设置,都没有返回错误
error = devm_gpio_request_one(&pdev->dev, button->gpio, GPIOF_IN, desc); // 申请io引脚
...
if (button->debounce_interval) {
error = gpio_set_debounce(button->gpio, button->debounce_interval * 1000);
/* use timer if gpiolib doesn't provide debounce */
if (error < 0)
bdata->software_debounce = button->debounce_interval;
}
if (button->irq) {
bdata->irq = button->irq; // 如果设置了中断号就用没有就自动申请
} else {
irq = gpio_to_irq(button->gpio);
...
bdata->irq = irq;
}
INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&bdata->work, gpio_keys_gpio_work_func);// 定时器的超时处理函数,用于按键后信息上报
isr = gpio_keys_gpio_isr; // 按键中断handler
irqflags = IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING | IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING;
...
input_set_capability(input, button->type ?: EV_KEY, button->code); // 设置按键产生哪一类事件下的哪一些事件 L,S,ENTER,LEFTSHIFT
...
error = devm_request_any_context_irq(&pdev->dev, bdata->irq, isr, irqflags, desc, bdata); // 注册按键中断
/* 内部调用 rc = request_any_context_irq(irq, handler, irqflags, devname, bdata);
isr = gpio_keys_gpio_isr; // 按键中断handler
irqflags = IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING | IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING;
const char *desc = button->desc ? button->desc : "gpio_keys"
struct gpio_button_data *bdata
==> request_any_context_irq(bdata->irq, gpio_keys_gpio_isr, IRQF_TRIGGER_RISING | IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, button->desc, gpio_button_data);
* 以前我们这么做 request_irq(IRQ_EINT0, button_irq_handle, IRQF_TRIGGER_FALLING, "S2", &pins_desc[0]);
*/
...
}实现
/* realize gpio-keys @pinus 2018-10-30 */
static struct gpio_keys_button jz2440_buttons[] = {
[0] = {
.code = KEY_L,
.gpio = S3C2410_GPF(0),
.desc = "S2",
.active_low = 1,
},
[1] = {
.code = KEY_S,
.gpio = S3C2410_GPF(2),
.desc = "S3",
.active_low = 1,
},
[2] = {
.code = KEY_ENTER,
.gpio = S3C2410_GPG(3),
.desc = "S4",
.active_low = 1,
},
[3] = {
.code = KEY_LEFTSHIFT,
.gpio = S3C2410_GPG(11),
.desc = "S5",
.active_low = 1,
},
};
static struct gpio_keys_platform_data jz2440_keys_pdata = {
.buttons = jz2440_buttons,
.nbuttons = ARRAY_SIZE(jz2440_buttons),
};
static struct platform_device jz2440_buttons_device = {
.name = "gpio-keys",
.id = -1,
.dev = {
.platform_data = &jz2440_keys_pdata,
},
};
static struct platform_device *smdk2440_devices[] __initdata = {
...
/* modify by pinus 2018-10-30 */
&jz2440_buttons_device,
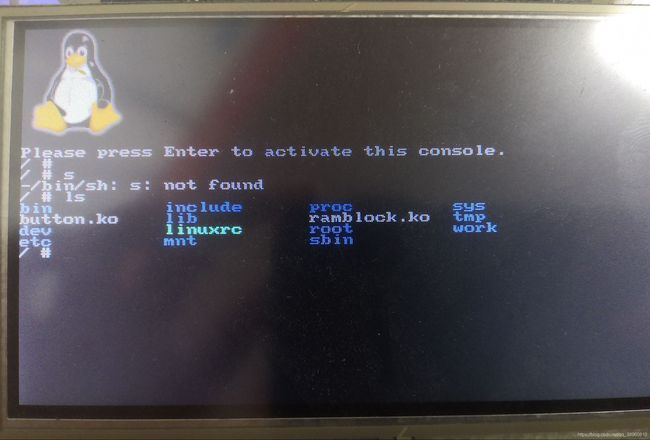
};演示
以前没试过,正好实现演示一下