ES9_ES11新特性语法
一、 ES9
1.正则拓展–命名捕获分组
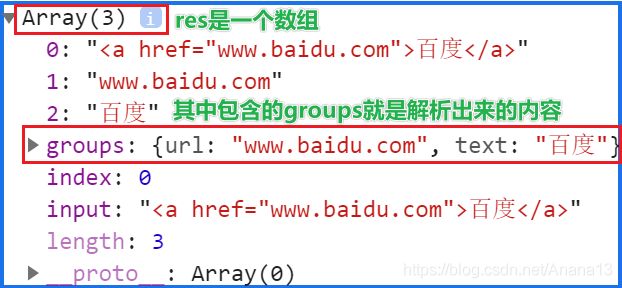
let str = '百度'
const reg = /<a href="(?.*)" >(?<text>.*)<\/a>/ // 正则
const res = reg.exec(str)
console.log(res)
// 查找'JS123243哈哈哈包括222咔咔' 中的 222
// 正向断言
let str1 = 'JS123243哈哈哈包括222咔咔'
let reg1 = /\d+(?=咔)/
const res1 = reg1.exec(str1)
console.log('正向断言',res1)
// 反向断言
let str2 = 'JS123243哈哈哈包括222咔咔'
let reg2 = /(?<=括)\d+/ // ?<=XX 这是匹配前边的固定写法
const res2 = reg2.exec(str2)
console.log('反向断言',res2)
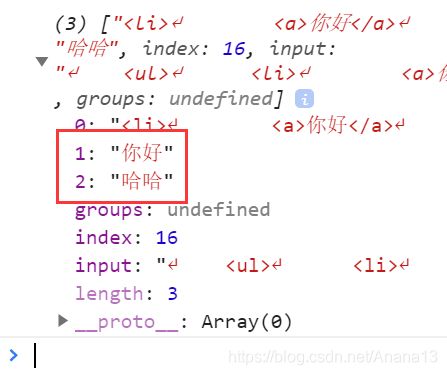
// 匹配a标签和p标签中的文字
let str = `
`
let reg = /<li>.*?<a>(.*?)<\/a>.*?<p>(.*?)<\/p>/s
const res = reg.exec(str)
console.log(res)
二、ES10
Object.fromEntries():转换为对象的新方法
// 二维数组 ==> 对象
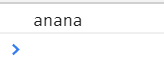
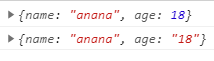
let arr = [['name','anana'],['age', 18]]
const res1 = Object.fromEntries(arr)
console.log(res1)
// Map ==> 对象
let m = new Map()
m.set('name', 'anana')
m.set('age', '18')
const res2 = Object.fromEntries(m)
console.log(res2)
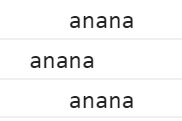
2. trimStart(),trimEnd()去除字符串两侧空格的新方法
let str = ' anana '
console.log(str)
console.log(str.trimStart()) // 去除开始空格
console.log(str.trimEnd()) // 去除结尾空格
let arr = [1,2,3,4,[5,6,[7,8,9]]]
console.log(arr.flat()) // 将数组降维,默认降一个维度
console.log(arr.flat(2)) // 将数组降维,可传参数,为降几个维度
let s = Symbol('我是字符串')
console.log(s.description) // 将Symbol类型转换为普通类型
![]()
三、ES11
- 私有属性
class Person {
name; // 公有属性
#age; // 私有属性,前边加# 的就是私有属性
#weight;// 私有属性
constructor (name, age, weight) {
this.name = name
this.#age = age
this.#weight = weight
}
}
const girl = new Person('anana', 18, '45kg')
console.log(this.name)
// 在类的外边打印类的私有属性会报错
console.log(this.#age)
console.log(this.#weight)
![]()
class Person {
name; // 公有属性
#age; // 私有属性,前边加# 的就是私有属性
#weight;// 私有属性
constructor (name, age, weight) {
this.name = name
this.#age = age
this.#weight = weight
}
// 定义一个方法来打印私有属性
showInfo () {
console.log(this.name)
console.log(this.#age)
console.log(this.#weight)
}
}
const girl = new Person('anana', 18, '45kg')
girl.showInfo() // 调用类中的方法,才可以打印私有属性

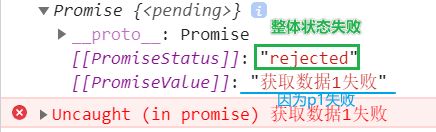
2. Promise新方法: Promise.allSettled(Array)。它始终返回一个成功的状态。
// 定义两个Promise
const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
reject('获取数据1失败')
}, 1000);
})
const p2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('获取数据2成功')
}, 1000);
})
// allSettled([p1,p2])要Promise数组作为参数
const res = Promise.allSettled([p1,p2])
console.log(res)
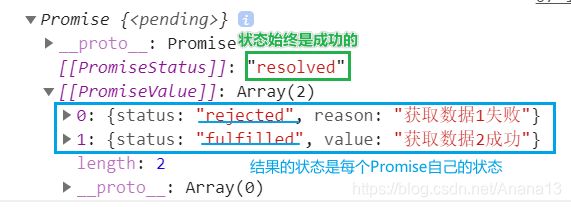
与其形成对比的是Promise的all 方法,也是传一个Promise数组作为参数,它需要数组中的Promise都成功,才成功,只有有一个失败就失败
const res = Promise.all([p1,p2])
console.log(res)
function main (config) {
// const res = config && config.db && config.db.username
const res = config ?. db ?. username // 相当于上边的判断
console.log(res)
}
main({
db: {
host: '192.168.1.1',
username: 'anana'
},
my: {
host: '192.168.1.2',
username: 'bnbnb'
}
})
- 大整型模式
let n = 123n // 大整型是整数后边加n
console.log(n, typeof n)
- 大整型函数
// 函数
let n = 123
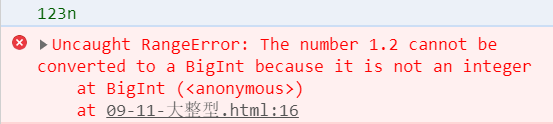
console.log(BigInt(n)) // 123n
console.log(BigInt(1.2)) // 会报错,只能转换整数
- 大整型应用场景
// 应用场景:大数值计算
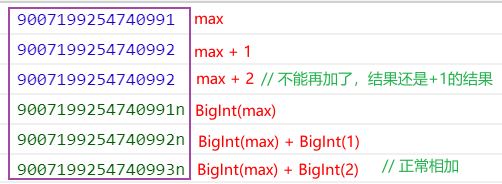
let max = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER // 最大数
console.log(max)
console.log(max + 1)
console.log(max + 2) // 计算不准确,不能再加了
console.log(BigInt(max))
console.log(BigInt(max) + BigInt(1))
console.log(BigInt(max) + BigInt(2)) // 正常相加