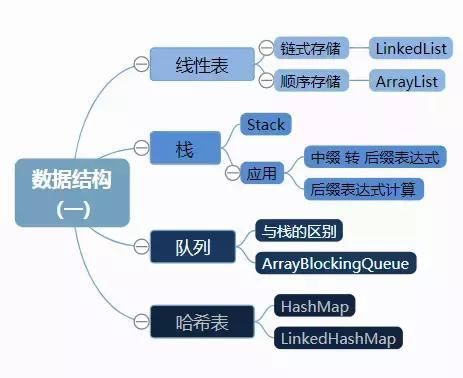
几张动态图捋清Java常用数据结构及其设计原理
最近在整理数据结构方面的知识, 系统化看了下Java中常用数据结构, 突发奇想用动画来绘制数据流转过程.
主要基于jdk8, 可能会有些特性与jdk7之前不相同, 例如LinkedList LinkedHashMap中的双向列表不再是回环的.
HashMap中的单链表是尾插, 而不是头插入等等, 后文不再赘叙这些差异, 本文目录结构如下:
LinkedList
经典的双链表结构, 适用于乱序插入, 删除. 指定序列操作则性能不如ArrayList, 这也是其数据结构决定的.
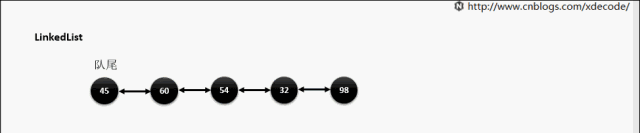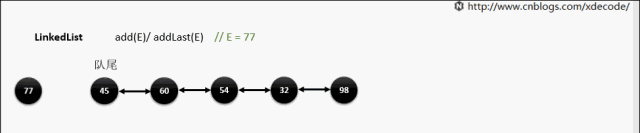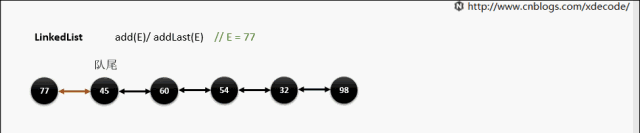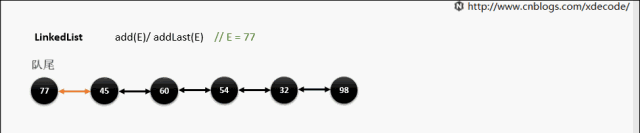
add(E) / addLast(E)
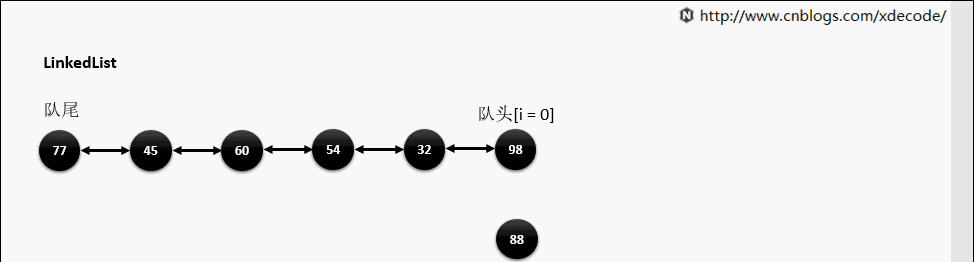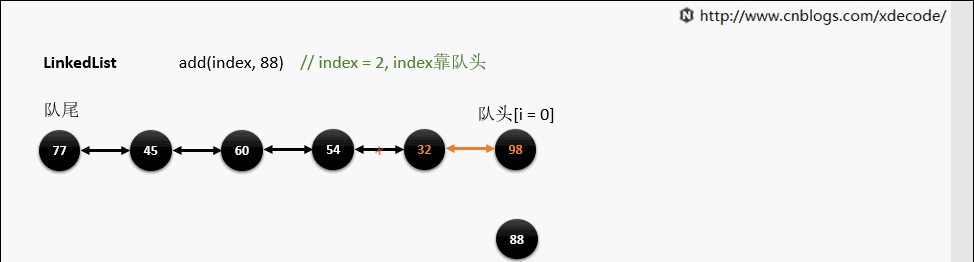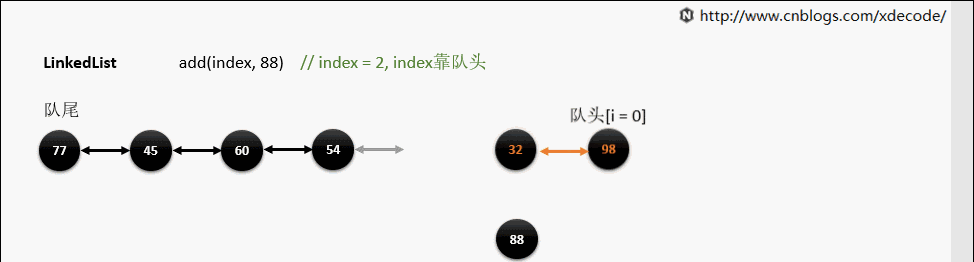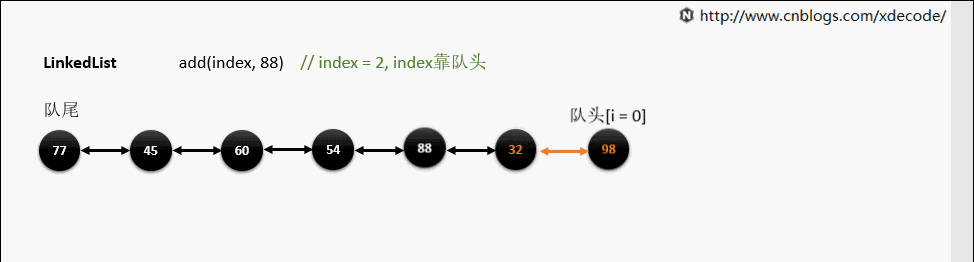
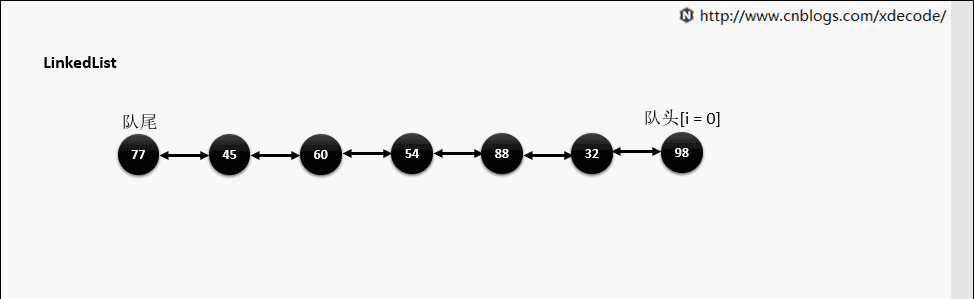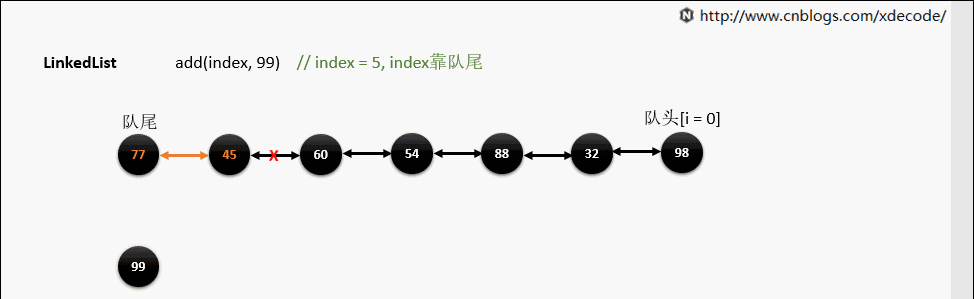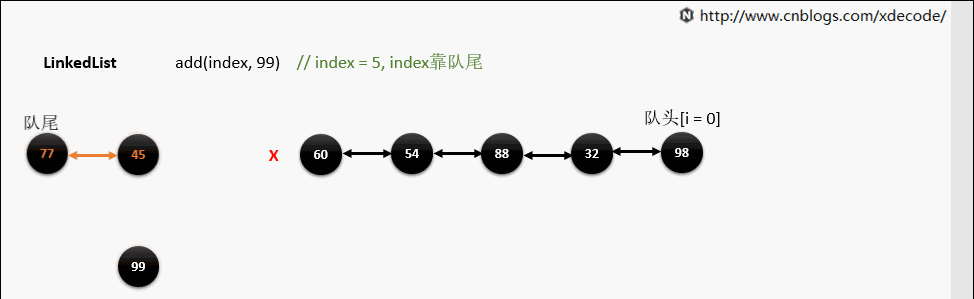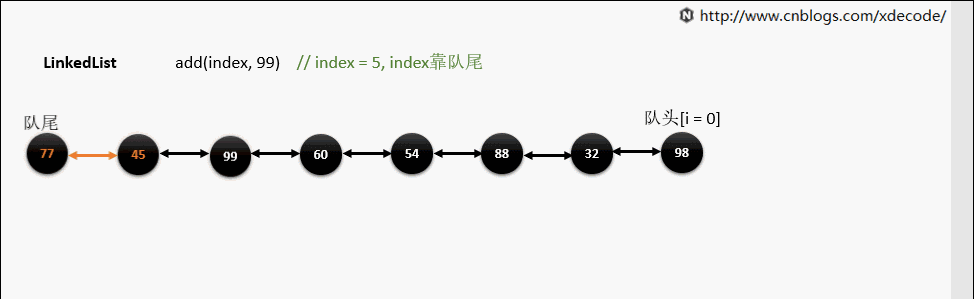
add(index, E)
这边有个小的优化, 他会先判断index是靠近队头还是队尾, 来确定从哪个方向遍历链入.
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #add}.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
/**
* Links e as first element.
*/
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node f = first;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node l = last;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
靠队尾
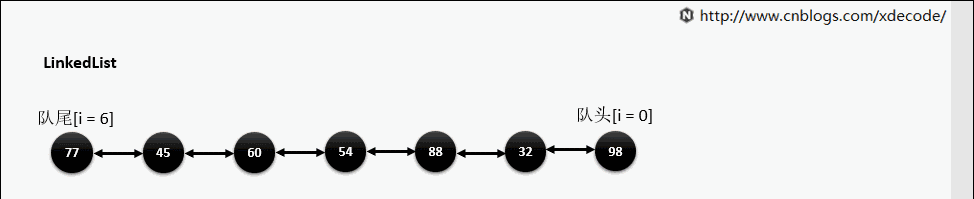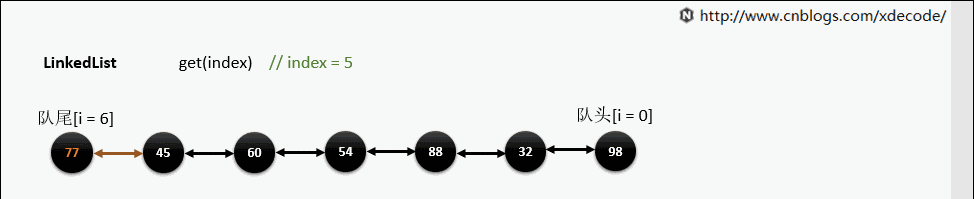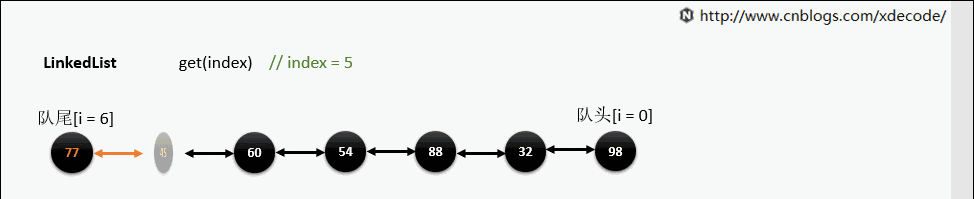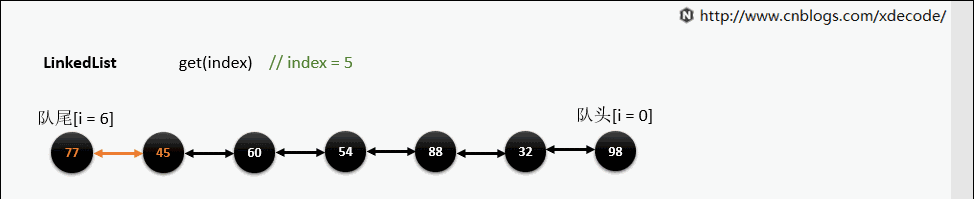
get(index)
也是会先判断index, 不过性能依然不好, 这也是为什么不推荐用for(int i = 0; i
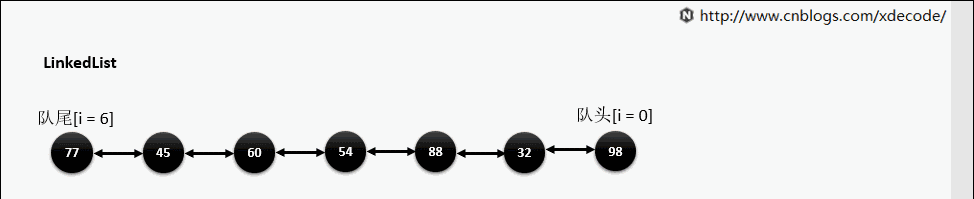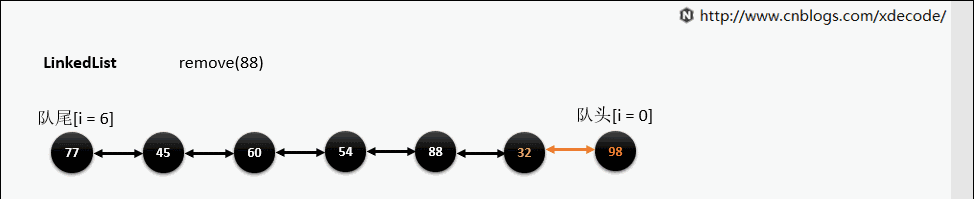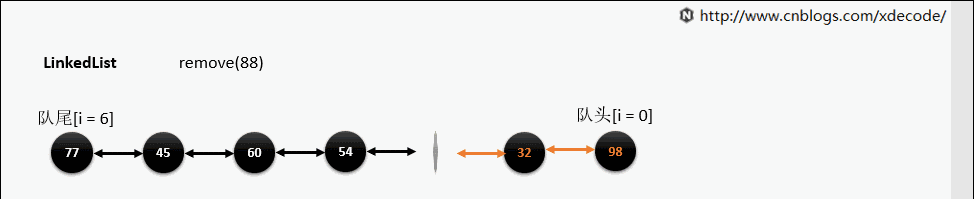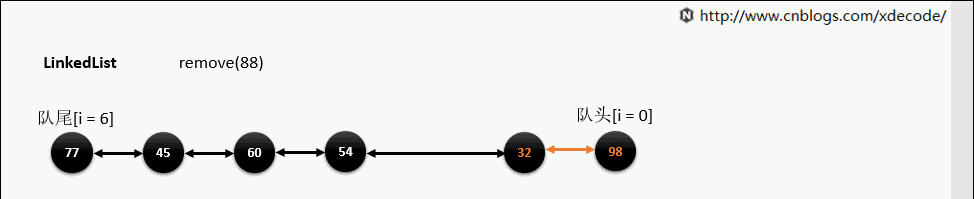
remove(E)
ArrayList
底层就是一个数组, 因此按序查找快, 乱序插入, 删除因为涉及到后面元素移位所以性能慢.
add(index, E)
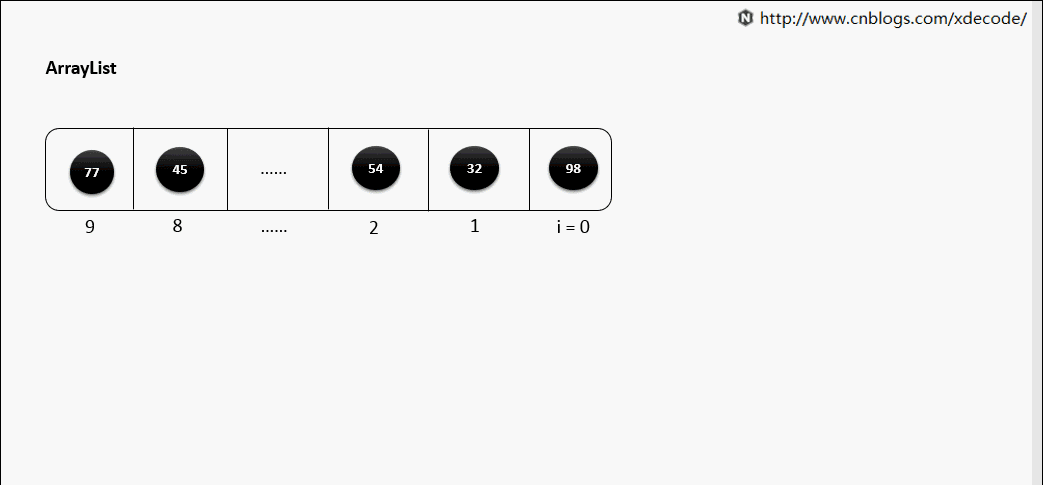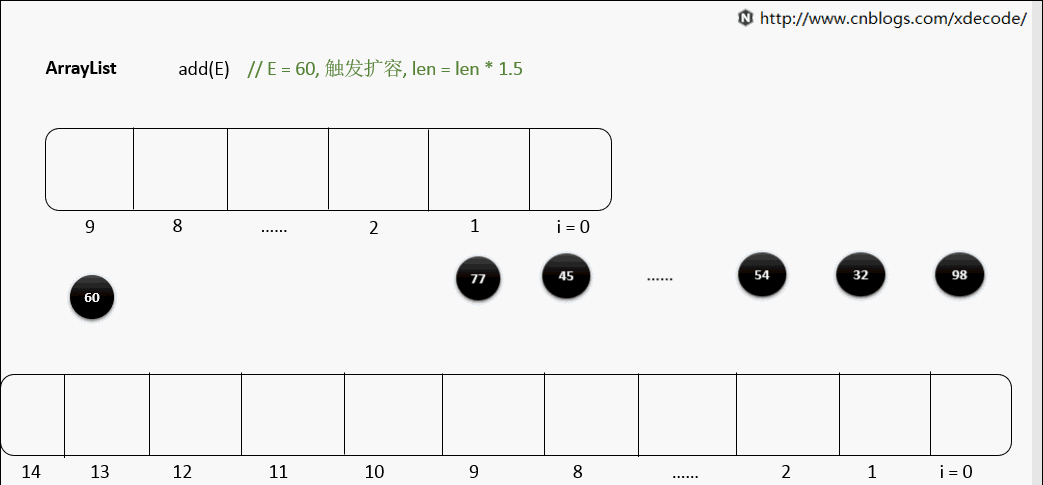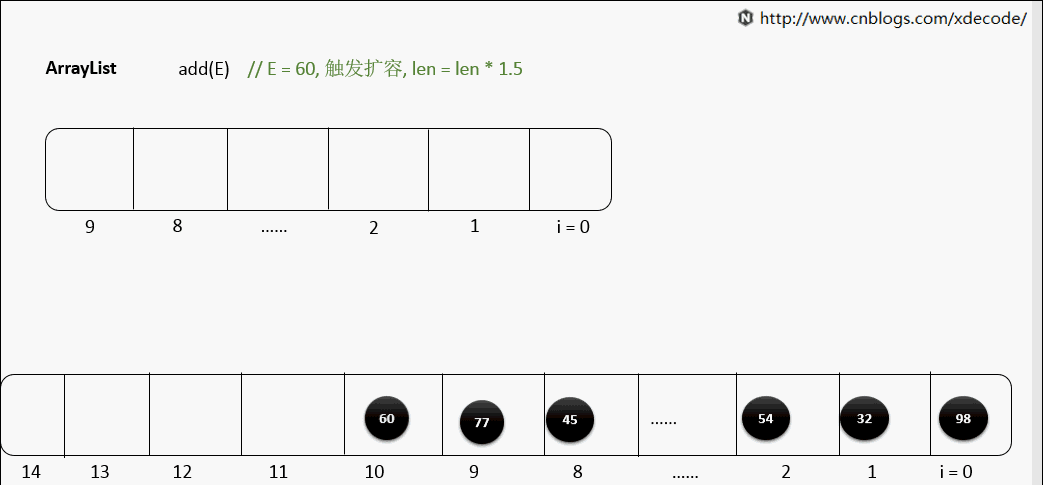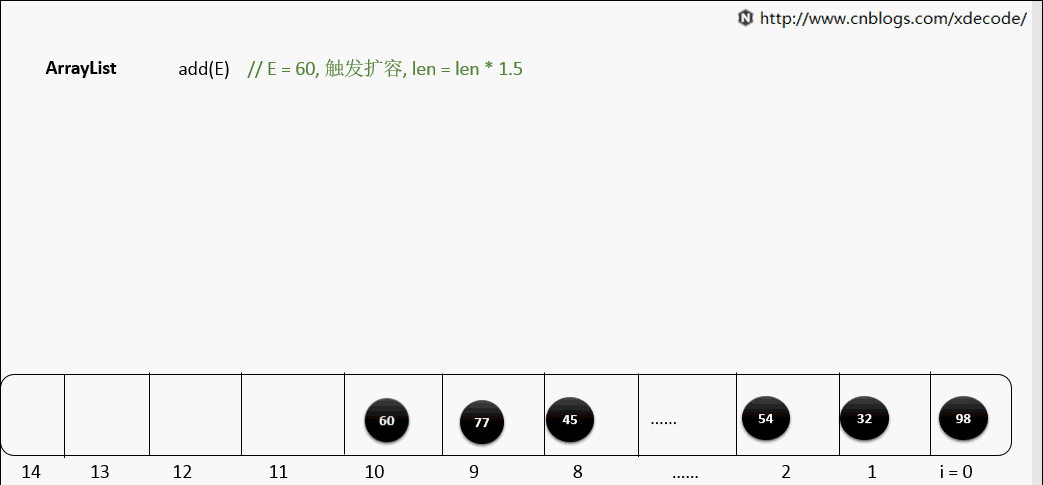
扩容
一般默认容量是10, 扩容后, 会length*1.5.
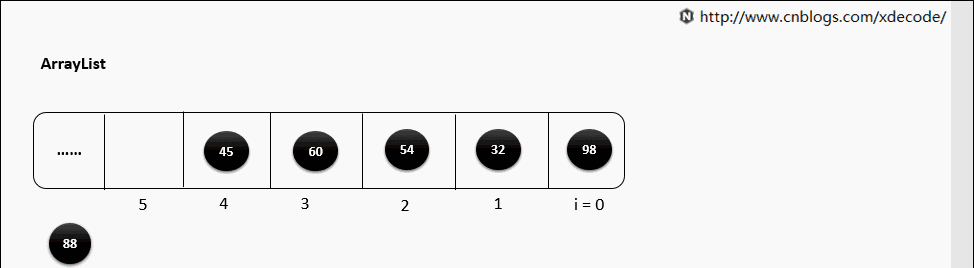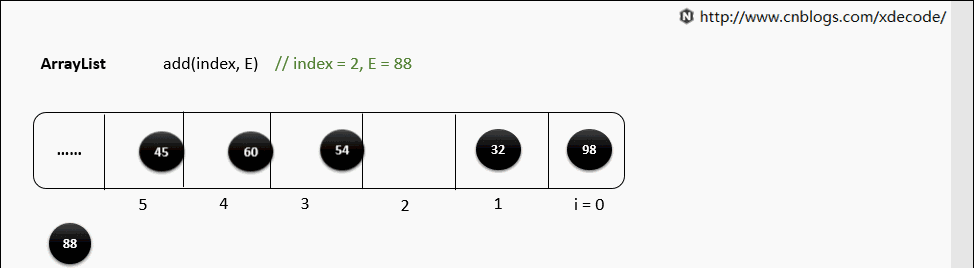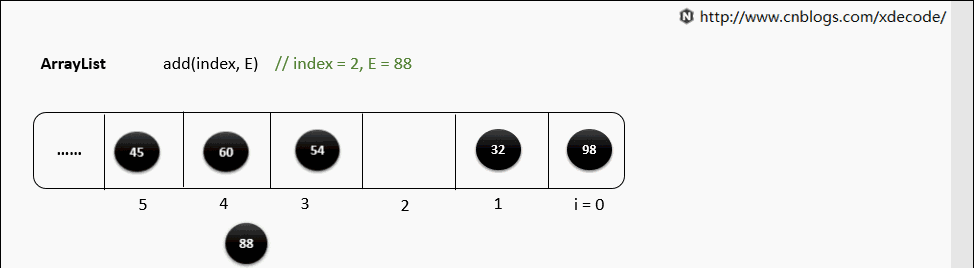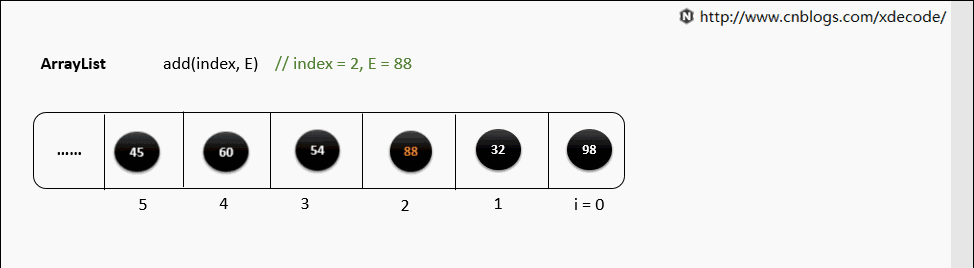
remove(E)
循环遍历数组, 判断E是否equals当前元素, 删除性能不如LinkedList.
Stack
经典的数据结构, 底层也是数组, 继承自Vector, 先进后出FILO, 默认new Stack()容量为10, 超出自动扩容.
push(E)
pop()
后缀表达式
Stack的一个典型应用就是计算表达式如 9 + (3 - 1) * 3 + 10 / 2, 计算机将中缀表达式转为后缀表达式, 再对后缀表达式进行计算.
中缀转后缀
数字直接输出栈为空时,遇到运算符,直接入栈遇到左括号, 将其入栈遇到右括号, 执行出栈操作,并将出栈的元素输出,直到弹出栈的是左括号,左括号不输出。遇到运算符(加减乘除):弹出所有优先级大于或者等于该运算符的栈顶元素,然后将该运算符入栈最终将栈中的元素依次出栈,输出。
计算后缀表达
遇到数字时,将数字压入堆栈遇到运算符时,弹出栈顶的两个数,用运算符对它们做相应的计算, 并将结果入栈重复上述过程直到表达式最右端运算得出的值即为表达式的结果
队列
与Stack的区别在于, Stack的删除与添加都在队尾进行, 而Queue删除在队头, 添加在队尾.
ArrayBlockingQueue
生产消费者中常用的阻塞有界队列, FIFO.
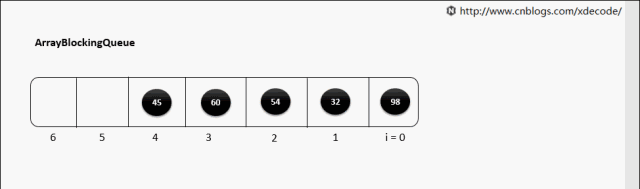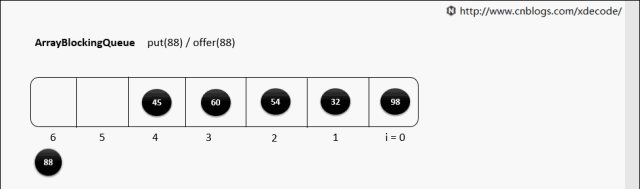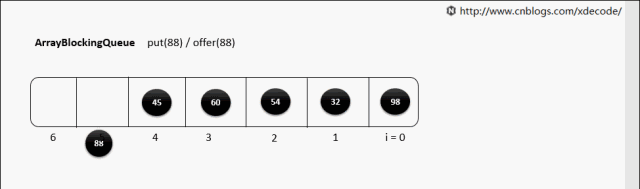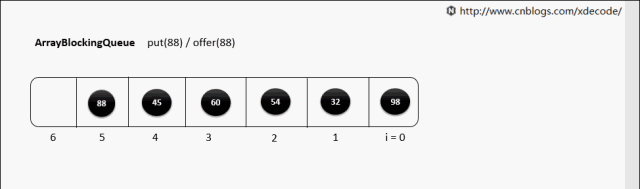
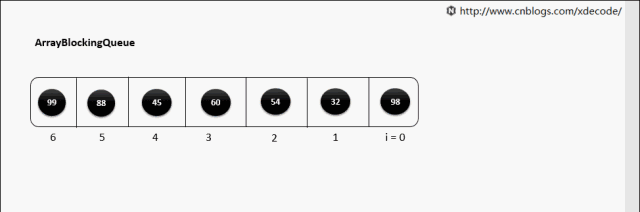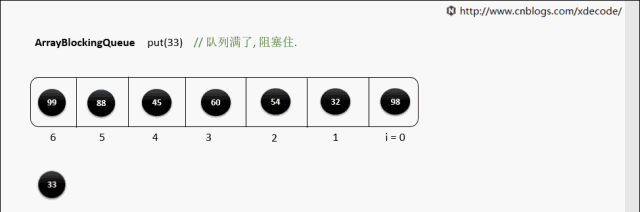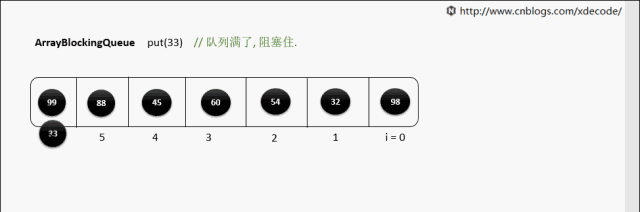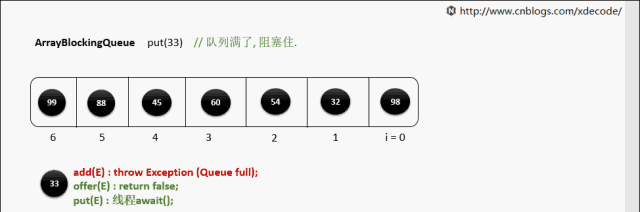
put(E)
put(E) 队列满了
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue, waiting
* for space to become available if the queue is full.
*
* @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await();
enqueue(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
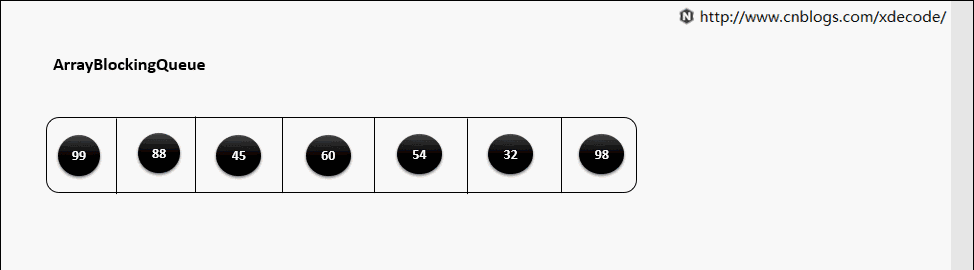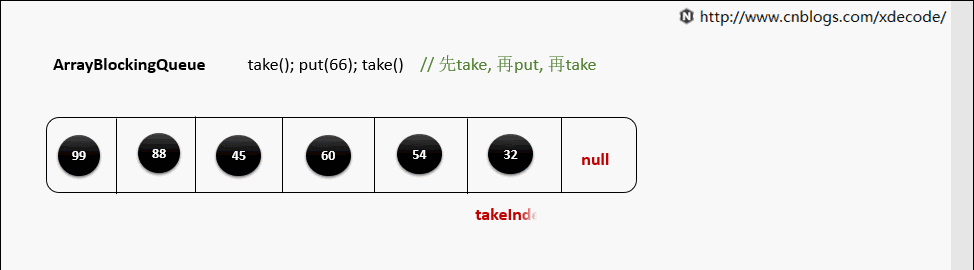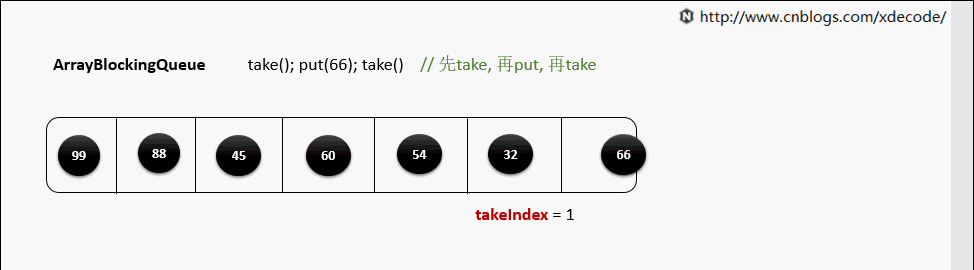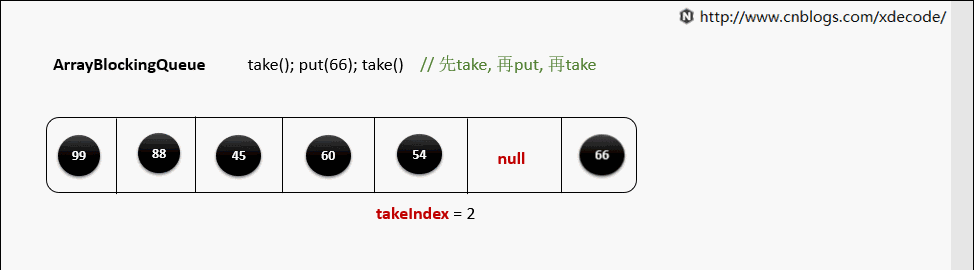
take()
当元素被取出后, 并没有对数组后面的元素位移, 而是更新takeIndex来指向下一个元素.
takeIndex是一个环形的增长, 当移动到队列尾部时, 会指向0, 再次循环.
/**
* Extracts element at current take position, advances, and signals.
* Call only when holding lock.
*/
private E dequeue() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[takeIndex] != null;
final Object[] items = this.items;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E x = (E) items[takeIndex];
items[takeIndex] = null;
if (++takeIndex == items.length)
takeIndex = 0;
count--;
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();
notFull.signal();
return x;
}
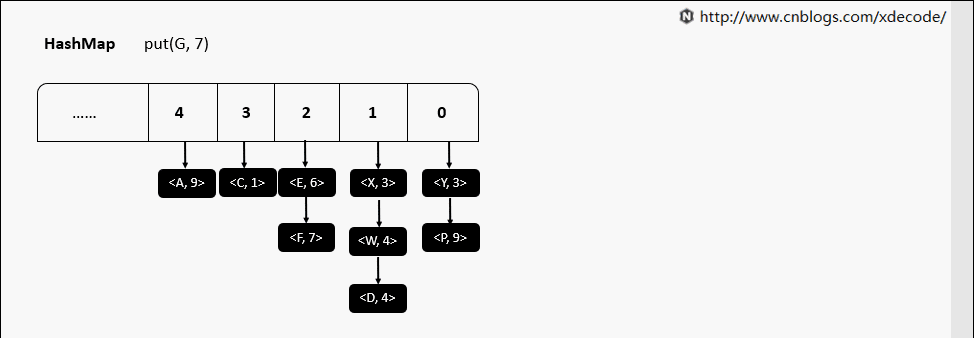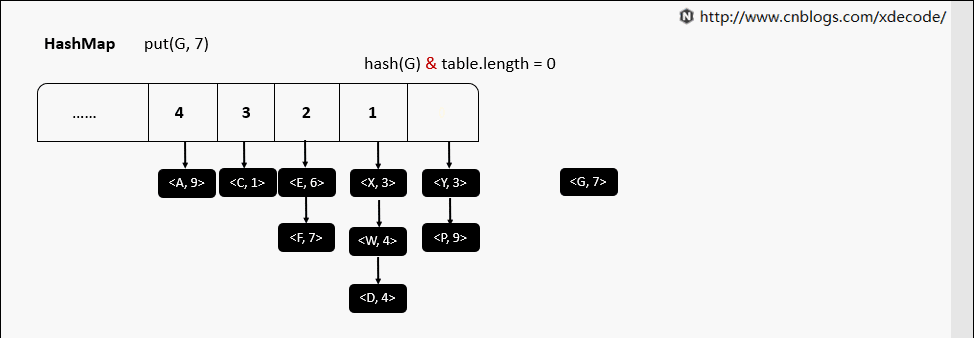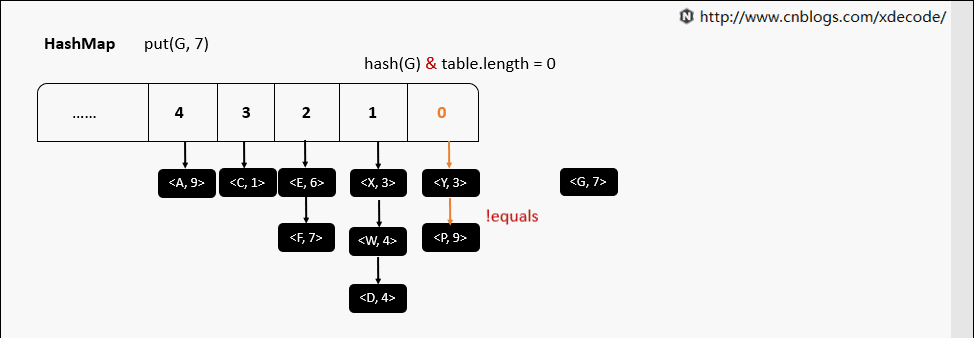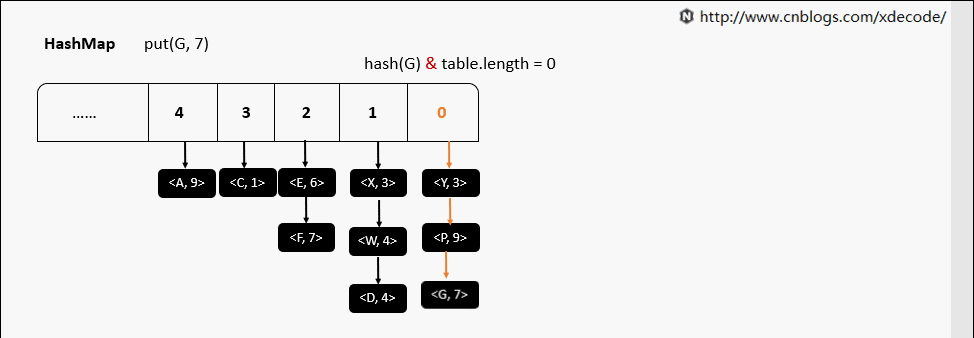
HashMap
最常用的哈希表, 面试的童鞋必备知识了, 内部通过数组 + 单链表的方式实现. jdk8中引入了红黑树对长度 > 8的链表进行优化, 我们另外篇幅再讲.
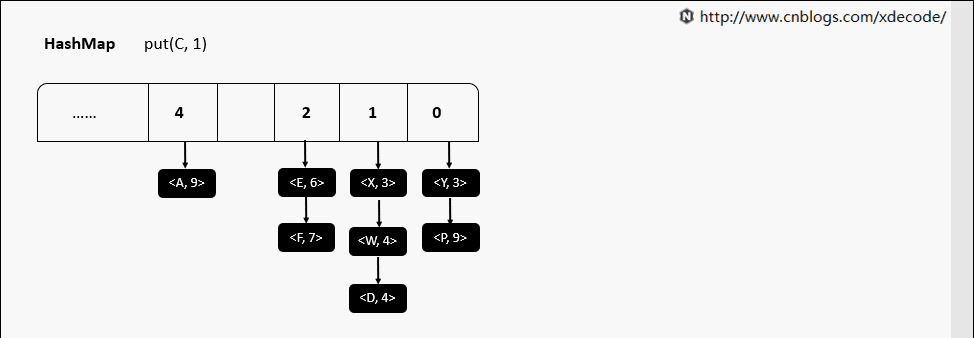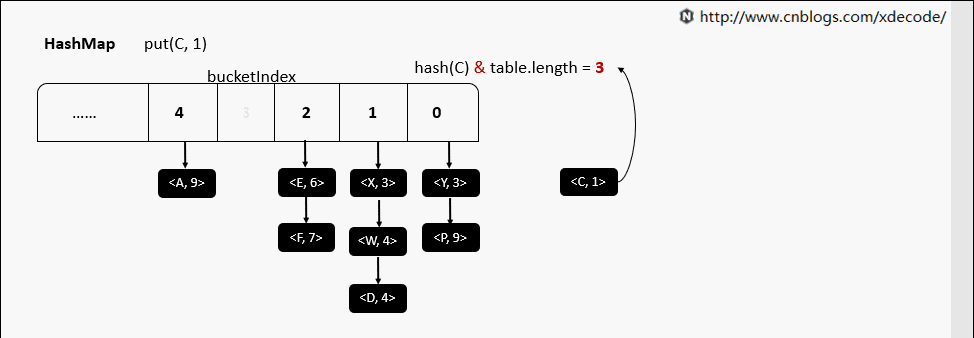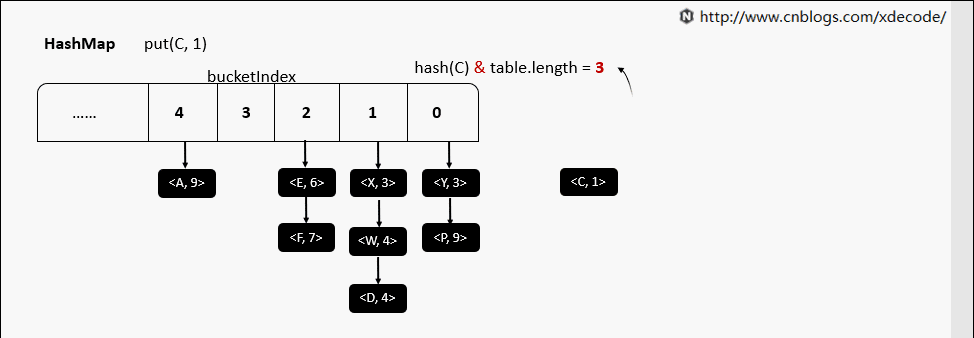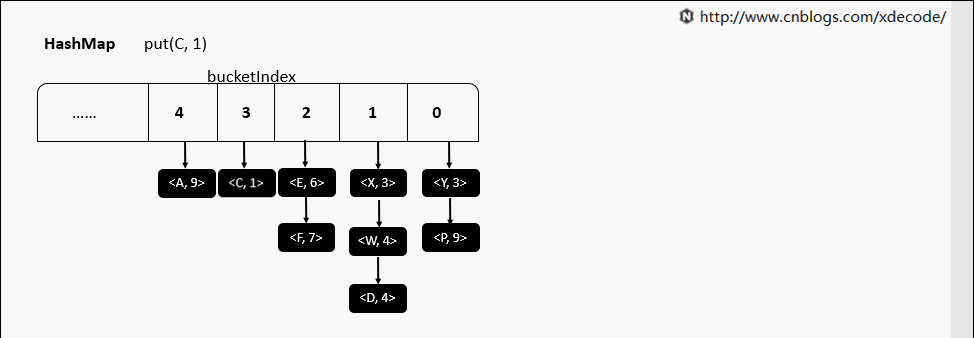
put(K, V)
put(K, V) 相同hash值
resize 动态扩容
当map中元素超出设定的阈值后, 会进行resize (length * 2)操作, 扩容过程中对元素一通操作, 并放置到新的位置.
具体操作如下:
在jdk7中对所有元素直接rehash, 并放到新的位置.在jdk8中判断元素原hash值新增的bit位是0还是1, 0则索引不变, 1则索引变成"原索引 + oldTable.length".
/**
* Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in
* accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold.
* Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the
* elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move
* with a power of two offset in the new table.
*
* @return the table
*/
final Node[] resize() {
Node[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node[] newTab = (Node[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node next;
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
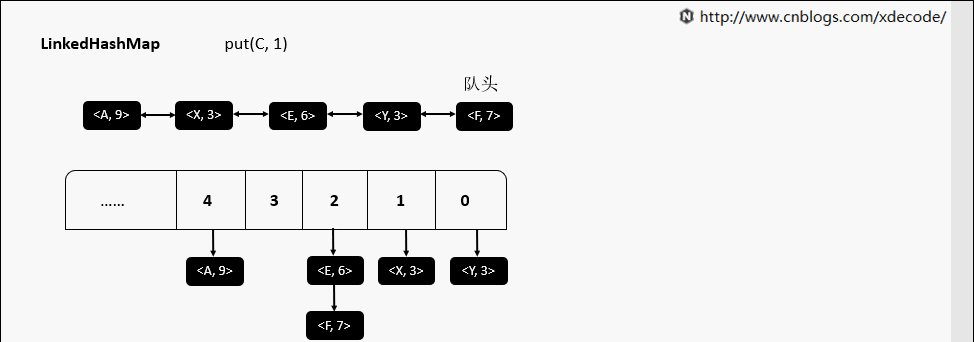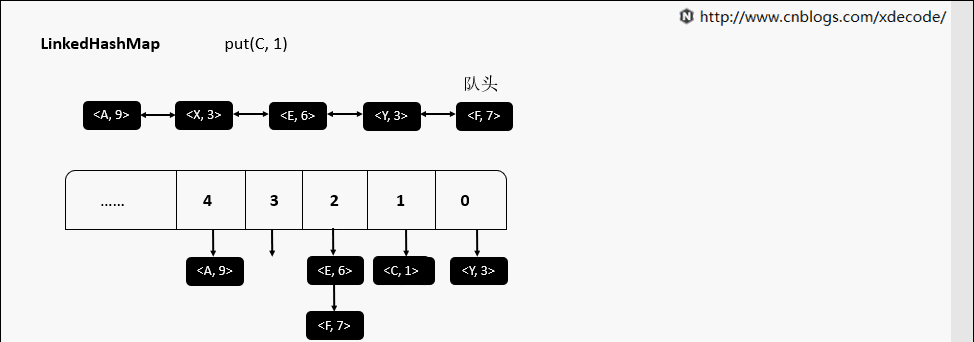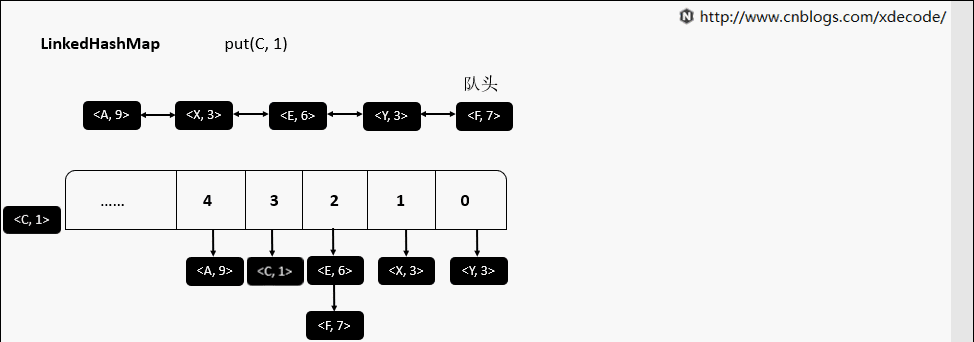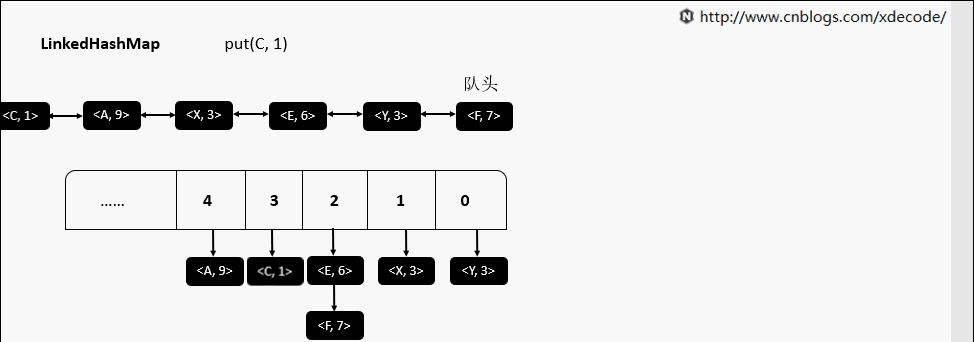
LinkedHashMap
继承自HashMap, 底层额外维护了一个双向链表来维持数据有序. 可以通过设置accessOrder来实现FIFO(插入有序)或者LRU(访问有序)缓存.
put(K, V)
get(K)
accessOrder为false的时候, 直接返回元素就行了, 不需要调整位置.
accessOrder为true的时候, 需要将最近访问的元素, 放置到队尾.
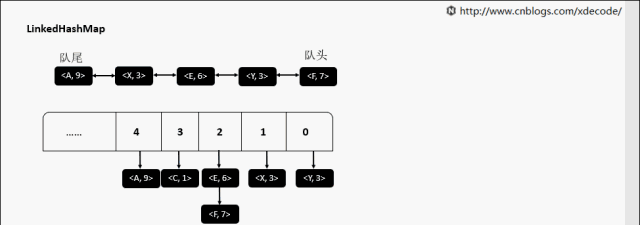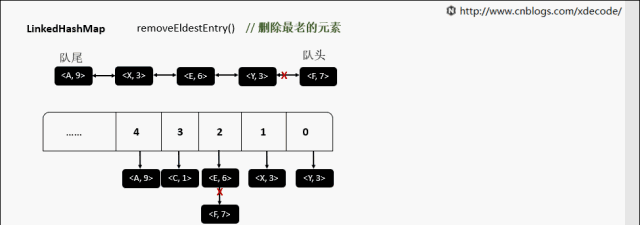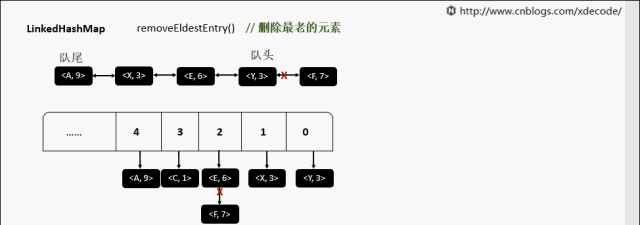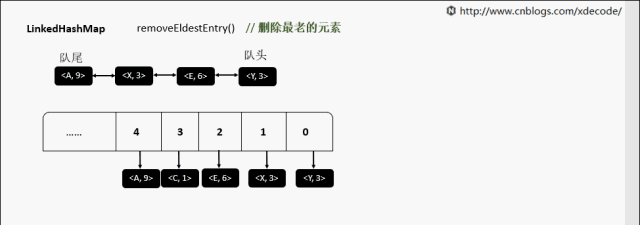
removeEldestEntry 删除最老的元素
PS:如果觉得我的分享不错,欢迎大家随手点赞、转发。
- 欢迎关注微博:http://weibo.com/jankinWang 获取更多笔记动态图片
- 欢迎加入QQ群:724100835 讨论交流,下载学习资料
- 欢迎转载,订阅关注哦!