http://blog.csdn.net/qq_23547831/article/details/51285804
1.在ActivityThread中通过handleMessage来运行activity。
2.准备activity需要的配置信息(Context,主题,Instrumentation,ActivityThread),并且通过反射的机制创建
3.创建的同时会调用activity的onCreate,onStart方法。(Instrumentaion)
4.在onReume中通过调用windowManager的makeVisable方法让视图显示,wm--WindowManagerImp---updataViewLayout---viewRootImp.setLayoutParams()---scheduleTraversals-- doTraversal();
一、在ActivityThread中触法整个生命周期的流程
1.在ActivityThread有main方法。android中所有的消息都是通过handler的Binder机制来处理的。包括activity的运行,service的执行等等。
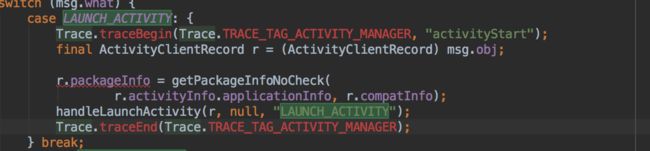
2.在ActivityThread的scheduleLaunchActivity方法中通过sendMessage方法给handler发消息,
// we use token to identify this activity without having to send the
// activity itself back to the activity manager. (matters more with ipc)
@Override
public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident,
ActivityInfo info, Configuration curConfig, Configuration overrideConfig ) {
//刷新进程的信息
updateProcessState(procState, false);
ActivityClientRecord r = new ActivityClientRecord();
r.token = token;
r.ident = ident;
.....
updatePendingConfiguration(curConfig);
//这里是handler方法的封装
sendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r);
}
3.在handleMessage里执行activity的构建任务
4.handlLauncherActivity
private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent, String reason) {
//如果我们在后台准备gc了,跳过这次gc,这里也是通过handler来
//控制的
unscheduleGcIdler();
mSomeActivitiesChanged = true;
if (r.profilerInfo != null) {
mProfiler.setProfiler(r.profilerInfo);
mProfiler.startProfiling();
}
//在创建activity之前,确保创建它的信息是最新的
handleConfigurationChanged(null, null);
// 创建一个windowmanager的实例WindowManagerGlobal
WindowManagerGlobal.initialize();
//这里是创建activity的地方,onCreate,onStart 以及activity的window创建调用的地方,下面有讲解
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
if (a != null) {
.......
//紧接着调用resume方法 看下面的源码。
handleResumeActivity(r.token, false, r.isForward,
!r.activity.mFinished && !r.startsNotResumed, r.lastProcessedSeq, reason);
if (!r.activity.mFinished && r.startsNotResumed) {
//当activity不在前台但是仍然希望自身可见的时候执行onPause。activity期望在window呈现之前调用onResume方法。在这里并不需要执行全部pause周期,因为activity manager 假定当前activity能够维持现在的状态(在后台不被回收)
performPauseActivityIfNeeded(r, reason);
// We need to keep around the original state, in case we need to be created again.
// But we only do this for pre-Honeycomb apps, which always save their state when
// pausing, so we can not have them save their state when restarting from a paused
// state. For HC and later, we want to (and can) let the state be saved as the
// normal part of stopping the activity.
if (r.isPreHoneycomb()) {
r.state = oldState;
}
}
} else {
// If there was an error, for any reason, tell the activity manager to stop us.
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()
.finishActivity(r.token, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null,
Activity.DONT_FINISH_TASK_WITH_ACTIVITY);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
}
performLaunchActivity这里根据所有配置信息Instrumentation对象创建一个activity,Instrumentation相当于管理activity的一个对象,负责实际执行activity的方法,ActivityClientRecord对象会保存启动过的activity的信息,并通过一个arraymap维护起来,这里执行两个生命周期的方法oncreate-onstart
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
.....
.....
Activity activity = null;
try {
//通过Instrumentation创建一个activity
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
......
try {
//为每一个activity创建一个application对象,以及其他的信息,
//通过activity的attch方法给activity的信息进行赋值
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
....
if (activity != null) {
//创建这个activity的上下文环境
Context appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r, activity);
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration);
if (r.overrideConfig != null) {
config.updateFrom(r.overrideConfig);
}
//创建一个window对象
Window window = null;
if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow != null && r.mPreserveWindow) {
window = r.mPendingRemoveWindow;......
}
//把所有activity需要的信息都交给它,同时创建activity需要的window,windowManager
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token, r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent, r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window);
if (customIntent != null) {
activity.mIntent = customIntent;
}
r.lastNonConfigurationInstances = null;
activity.mStartedActivity = false;
//设置主题
int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource();
if (theme != 0) {
activity.setTheme(theme);
}
activity.mCalled = false;
if (r.isPersistable()) {
//调用activity的onCreate方法
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);
} else {
//调用activity的onCreate方法 这里会触发onCreate方法
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
}
......
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
activity.performStart();
r.stopped = false;
}
if (!r.activity.mFinished) {
if (r.isPersistable()) {
if (r.state != null || r.persistentState != null) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state,
r.persistentState);
}
} else if (r.state != null) { mInstrumentation.callActivityOnRestoreInstanceState(activity, r.state);
}
}
........
}
r.paused = true;
mActivities.put(r.token, r);
}
.......
}
return activity;
}
attach配置activity需要的内容
配置了context,application,window,以及通过window为当前activity创建了windowManager对象
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info.....) {
attachBaseContext(context);
mFragments.attachHost(null /*parent*/);
mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this);
....
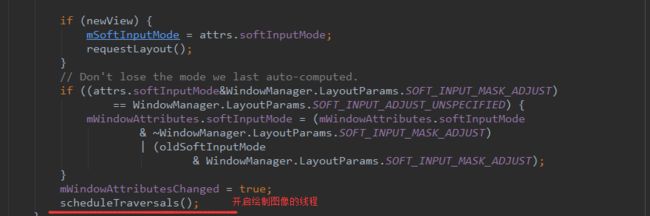
if (info.softInputMode != WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_STATE_UNSPECIFIED) {
mWindow.setSoftInputMode(info.softInputMode);
}
if (info.uiOptions != 0) {
mWindow.setUiOptions(info.uiOptions);
}
mUiThread = Thread.currentThread();
mMainThread = aThread;
mInstrumentation = instr;
mApplication = application;
mIntent = intent;
Parent = parent
....
mWindow.setWindowManager(
(WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE),
mToken, mComponent.flattenToString(),
(info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0);
if (mParent != null) {
mWindow.setContainer(mParent.getWindow());
}
mWindowManager = mWindow.getWindowManager();
mCurrentConfig = config;
}
windowManager实际上是由WindowManagerImpl对象来创建一个windowManagerImp对象,它集成windowmanager对象,负责真正的管理view的工作
public void setWindowManager(WindowManager wm, IBinder appToken, String appName,
boolean hardwareAccelerated) {
......
mWindowManager = ((WindowManagerImpl)wm).createLocalWindowManager(this);
}
handleResumeActivity调用activity的onResume以及之前的准备,如果这个activity的window还没有交给一个windowManager管理,而且没有启动新的activity,添加一个window给它。添加成功后,让这个window可见
final void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token,
boolean clearHide, boolean isForward, boolean reallyResume, int seq, String reason) {
//获取当前activity的信息
ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token);
if (!checkAndUpdateLifecycleSeq(seq, r, "resumeActivity")) {
return;
}
// 核心的地方 创建window的参数,以及onResume方法的调用
r = performResumeActivity(token, clearHide, reason);
if (r != null) {
final Activity a = r.activity;
.....
//如果没有添加windowmanager和decoreview 创建一个
boolean willBeVisible = !a.mStartedActivity;
.....
if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) {
r.window = r.activity.getWindow();
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
a.mDecor = decor;
l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION;
l.softInputMode |= forwardBit;
if (r.mPreserveWindow) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
r.mPreserveWindow = false;
// 通过ViewRootImp的setView方法我们已经和activity建立的回调,必须通知decoreView,因为布局已经发生了改变
ViewRootImpl impl = decor.getViewRootImpl();
if (impl != null) {
impl.notifyChildRebuilt();
}
}
if (a.mVisibleFromClient && !a.mWindowAdded) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
//这里就是建立联系的地方
wm.addView(decor, l);
}
//如果已经设置好了windowmanager,并且没有启动新的activity,让window显示,通过ac的makeVisiable。
} else if (!willBeVisible) {
// The window is now visible if it has been added, we are not
// simply finishing, and we are not starting another activity.
if (!r.activity.mFinished && willBeVisible
&& r.activity.mDecor != null && !r.hideForNow) {
if (r.newConfig != null) {
........
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
......
if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
//这里是开始渲染视图的地方,wm--WindowManagerImp---updataViewLayout---viewRootImp.setLayoutParams()---scheduleTraversals-- doTraversal();
wm.updateViewLayout(decor, l);
}
}
.....
if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {
//让activity中的window的decorView显示
r.activity.makeVisible();
}
}
//activity的makeVisiable
void makeVisible() {
if (!mWindowAdded) {
ViewManager wm = getWindowManager();
wm.addView(mDecor, getWindow().getAttributes());
....
}
mDecor.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
makeVisiable让显示布局
performResumeActivity
最重要的就是deliverNewIntents,这里会调用activity的onNewIntent方法:如果设置启动方式设置为SingleTop,那么onNewIntent方法被触发,拿到上一次调用记录保存的intent引用。接着执行
onRestart--onStart--OnResume。如果没有执行OnResume。
public final ActivityClientRecord performResumeActivity(IBinder token,
boolean clearHide) {
ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token);
if (r != null && !r.activity.mFinished) {
try {
if (r.pendingIntents != null) {
//这里会调用activity的onNewIntent
deliverNewIntents(r, r.pendingIntents);
r.pendingIntents = null;
}
if (r.pendingResults != null) {
deliverResults(r, r.pendingResults);
r.pendingResults = null;
}
r.activity.performResume();
..
}
return r;
}
View开始渲染的流程
WindowManagerImp的updateLayoutParmas
@Override
public void updateViewLayout(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
mGlobal.updateViewLayout(view, params);
}
//WindowManagerGlobal的setLayoutParams
//setLayoutParams部分方法
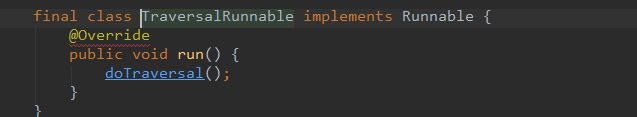
//scheduleTraversals最后开开启一个线程调用doTraversal方法,doTraversal方法执行的是所有的绘制任务
setContentView
实际上调用的window的setContentView,这里的window是phonewindow。
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) {
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}
phoneWindow的inflate方法最终会调用addView/setLayoutParams,这两个方法都会调用requestLayout方法,requestLayout方法最终会调用scheduleTraversals方法
//phonewindow的setContentView方法
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
}