最近在看mybatis框架,mybatis是什么呢??先把官网地址贴上。套用官方解释:MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集。MyBatis 可以使用简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原生信息,将接口和 Java 的 POJOs(Plain Old Java Objects,普通的 Java对象)映射成数据库中的记录。
mybatis框架中有一个最重要的类SqlSession,这个类可以有执行sql语句、提交或回滚事务和获取映射器实例的方法。
我们先搭建一个最简单的springboot+mybatis工程:
先看一下工程目录:
1.pom文件如下:
4.0.0
com.jshh
mybatisdemo
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
jar
mybatisdemo
Demo project for Spring Boot
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.0.3.RELEASE
UTF-8
UTF-8
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
1.3.2
mysql
mysql-connector-java
runtime
com.mchange
c3p0
0.9.5.2
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.16.16
provided
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
2.两个配置类(其实也可以在xml文件中配置),一个是数据源的配置类,一个是mybatis的SqlSessesionFactory配置类
数据源的配置类
package com.jshh.config;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.beans.PropertyVetoException;
@Configuration
@MapperScan("com.jshh.dao")
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String jdbcdriver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String jdbcurl;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String jdbcusername;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String jdbcpassword;
@Bean(name = "comboPooledDataSource")
public ComboPooledDataSource getDataSource() throws PropertyVetoException {
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClass(jdbcdriver);
dataSource.setJdbcUrl(jdbcurl);
dataSource.setUser(jdbcusername);
dataSource.setPassword(jdbcpassword);
dataSource.setAutoCommitOnClose(false);
return dataSource;
}
}
SqlSessesionFactory配置类
package com.jshh.config;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Auther: 王明
* @Date: 2018/6/30 15:49
* @Description:
*/
@Configuration
public class SqlSessesionFactoryConfig {
@Value("${mybatis_config_file}")
private String mybatisConfigFilePath;
@Value("${mapper_path}")
private String mapperPath;
@Value("${entity_package}")
private String entitypackage;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("comboPooledDataSource")
private DataSource mDataSource;
@Bean("sqlSessionFactoryBean")
public SqlSessionFactoryBean getSqlSessionFactoryBean() throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
String packageSearchPath = PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX + mapperPath;
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setConfigLocation(new ClassPathResource(mybatisConfigFilePath));
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(resolver.getResources(packageSearchPath));
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(mDataSource);
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setTypeAliasesPackage(entitypackage);
return sqlSessionFactoryBean;
}
}
3.配置文件application.properties
server.port=9036
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatisdemo?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=true
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=mysql
#mybatis
mybatis_config_file=mybatis-config.xml
mapper_path=/mapper/**.xml
entity_package=com.jshh.entity
4.mybatis核心配置文件与mapper映射的sqlxml文件
mybatis核心配置文件mybatis-config.xml,关于使用idea如何快速建立此配置文件可以参考这篇文章
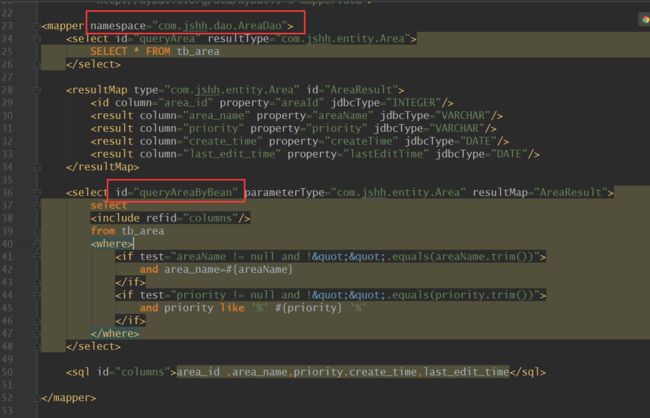
mapper映射sqlxml 文件
area_id ,area_name,priority,create_time,last_edit_time
5.最后交代一下本例中创建的实体类Area
package com.jshh.entity;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @Auther: 王明
* @Description:
*/
@Getter
@Setter
public class Area {
private Integer areaId;
private String areaName;
private String priority;
private Date createTime;
private Date lastEditTime;
}
创建工程到此告一段落,我们来使用mybatis中最重要的一个类SqlSession使一下:
...
Area area = new Area();
area.setAreaName("ss");
area.setPriority("0");
List objects1 = sqlSession.selectList("com.jshh.dao.AreaDao.queryAreaByBean", area);
...
调试结果当然是可以获取正常的返回值,现在我们来分析一下这句核心代码
List objects1 = sqlSession.selectList("com.jshh.dao.AreaDao.queryAreaByBean", area);
别小看这句代码,此处代码至少有四处值得我们分析,com.jshh.dao.AreaDao这是我们的namespace,queryAreaByBean这是关联sql的id,area是我们传入的查询参数, List objects1这个是我们返回的Area实体的集合。这种写法当然是正确的,但是有没有更优的做法呢?既然这么说了那肯定是有的对吧。我们常常从一些书里面或者一些老鸟口中听到“java设计第一原则:面向接口编程,对修改关闭对扩展开放”。是不是有种不明觉厉的感觉?别慌,我们先弄清什么是面向接口编程?
在一个面向对象的系统中,系统的各种功能是由许许多多的不同对象协作完成的。在这种情况下,各个对象内部是如何实现自己的,对系统设计人员来讲就不那么重要了;而各个对象之间的协作关系则成为系统设计的关键。小到不同类之间的通信,大到各模块之间的交互,在系统设计之初都是要着重考虑的,这也是系统设计的主要工作内容。面向接口编程就是指按照这种思想来编程。
是不是还挺迷糊的?确实,编程思想这个东西得需要从大量的经验中慢慢感悟,颇有点“道”的味道。没关系我们继续看上面那句代码,我们有没有发现这种写法有什么弊端?
首先是关于传入的"坐标"(即定位到mapper文件中的namespace和id)"com.jshh.dao.AreaDao.queryAreaByBean",这样手写必然是不安全的,容易疏忽出错。
第二个问题是传入的参数area,因为sqlSession.selectList方法中参数是object,所有我们传入什么参数都可以编译通过(编译通过不一定会执行通过,比如mapper文件中需要的是Area2,你传入Area这样的话就就会执行出错),这样不利于代码的健壮性。
还有一个问题是返回值的问题。同样的道理也是不利于代码健壮。
我们应该如何改造呢???
既然今天谈的是mybatis接口式编程,那肯定是要建立一个接口嘛。
AreaDao接口
package com.jshh.dao;
import com.jshh.entity.Area;
import java.util.List;
public interface AreaDao {
List queryArea();
List queryAreaByBean(Area area);
Area queryAreaById();
}
写个单元测试:
package com.jshh;
import com.jshh.dao.AreaDao;
import com.jshh.entity.Area;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class MybatisdemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
AreaDao areaDao;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
}
@Test
public void queryArea() {
Area area = new Area();
area.setAreaName("ss");
area.setPriority("0");
List areas1 = areaDao.queryAreaByBean(area);
}
}
我们发现改造之后的代码更加清爽。它的执行效果和sqlSession.selectList("com.jshh.dao.AreaDao.queryAreaByBean", area);是一样的。我们不禁要问,凭什么这样我们就能直接调用到mapper中的sql语句呢?对于这两句代码执行效果一样,我们可以通过阅读mybatis源码来找到答案。在阅读源码之前,请先确保对java动态代理相关的知识有所了解,我写过一篇关于java动态代理的文章,记录了我对java动态代理的理解,感兴趣的朋友可以去瞅瞅,文章地址,此处不做赘述。我们先理出一个思路,然后跟着思路去阅读源码。
首先要证明areaDao.queryAreaByBean(area)==sqlSession.selectList("com.jshh.dao.AreaDao.queryAreaByBean", area);
这两句代码等效。
我们有想过areaDao这个实例是怎么来的吗?你可能回答是由spring管理的的。是的没错,但是如果我们不使用spring呢?这个实例怎么来?就是我们之前一直强调的mybatis中最重要的一个类SqlSession类,sqlSession.getMapper(AreaDao.class);可以获取到接口的实例。因此我们可以得到
第一个结论
sqlSession.getMapper(AreaDao.class)=Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{this.mapperInterface}, mapperProxy);
我们往下走之前,我们得先弄清楚为什么areaDao这个没有实现类的接口为什么能执行queryAreaByBean方法,这个里面涉及到动态代理的知识。由动态代理的知识我们知道代理类MapperProxy实现InvocationHandler接口,里面有个invoke方法,当我们执行这句areaDao.queryAreaByBean(area)代码的时候,就会触发代理类中的invoke方法。因此我们可以得到
第二个结论
areaDao==Proxy.newProxyInstance()
areaDao.queryAreaByBean(area)==MapperProxy.invoke
第三个结论(最终结论)
areaDao.queryAreaByBean(area)==sqlSession.selectList("com.jshh.dao.AreaDao.queryAreaByBean", area);
思路理清之后,我们瞅瞅源码,看看我们的猜想是否正确:
sqlSession.getMapper(AreaDao.class)进入
类DefaultSqlSession:
.....
public T getMapper(Class type) {
return this.configuration.getMapper(type, this);
}
....
进入类Configuration:配置文件加载
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return this.mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
进入类MapperRegistry
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package org.apache.ibatis.binding;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import org.apache.ibatis.builder.annotation.MapperAnnotationBuilder;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.ResolverUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.ResolverUtil.IsA;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
public class MapperRegistry {
private final Configuration config;
private final Map, MapperProxyFactory> knownMappers = new HashMap();
public MapperRegistry(Configuration config) {
this.config = config;
}
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory)this.knownMappers.get(type);
if(mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
} else {
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception var5) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + var5, var5);
}
}
}
public boolean hasMapper(Class type) {
return this.knownMappers.containsKey(type);
}
public void addMapper(Class type) {
if(type.isInterface()) {
if(this.hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
this.knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory(type));
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(this.config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if(!loadCompleted) {
this.knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
public Collection> getMappers() {
return Collections.unmodifiableCollection(this.knownMappers.keySet());
}
public void addMappers(String packageName, Class superType) {
ResolverUtil> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil();
resolverUtil.find(new IsA(superType), packageName);
Set>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
Iterator var5 = mapperSet.iterator();
while(var5.hasNext()) {
Class mapperClass = (Class)var5.next();
this.addMapper(mapperClass);
}
}
public void addMappers(String packageName) {
this.addMappers(packageName, Object.class);
}
}
MapperRegistry类方法getMapper说明:这个方法是通过MapperProxyFactory代理工厂获取代理类实例。其中代理工厂是从knownMappers中获取,我们看下knownMappers这个map是在哪进行put的。很容易找到在本类addMapper方法中,这个方法是在加载配置文件时被执行。
进入类MapperProxyFactory
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package org.apache.ibatis.binding;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
public class MapperProxyFactory {
private final Class mapperInterface;
private final Map methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class getMapperInterface() {
return this.mapperInterface;
}
public Map getMethodCache() {
return this.methodCache;
}
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{this.mapperInterface}, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
MapperProxy mapperProxy = new MapperProxy(sqlSession, this.mapperInterface, this.methodCache);
return this.newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
MapperProxyFactory类方法newInstance说明:通过Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{this.mapperInterface}, mapperProxy);这个方法来获取到代理类的实例,第一个参数是类加载器,第二个参数是代理类要实现的接口数组,第三个参数是代理实例的处理程序(这个参数不是很理解,猜想类似装饰模式吧)
进入类MapperProxy(重点类)
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package org.apache.ibatis.binding;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.invoke.MethodHandles.Lookup;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.ibatis.lang.UsesJava7;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ExceptionUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
public class MapperProxy implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class mapperInterface;
private final Map methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class mapperInterface, Map methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if(Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
}
if(this.isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return this.invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable var5) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(var5);
}
MapperMethod mapperMethod = this.cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(this.sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = (MapperMethod)this.methodCache.get(method);
if(mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(this.mapperInterface, method, this.sqlSession.getConfiguration());
this.methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
@UsesJava7
private Object invokeDefaultMethod(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Constructor constructor = Lookup.class.getDeclaredConstructor(new Class[]{Class.class, Integer.TYPE});
if(!constructor.isAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
}
Class declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
return ((Lookup)constructor.newInstance(new Object[]{declaringClass, Integer.valueOf(15)})).unreflectSpecial(method, declaringClass).bindTo(proxy).invokeWithArguments(args);
}
private boolean isDefaultMethod(Method method) {
return (method.getModifiers() & 1033) == 1 && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface();
}
}
MapperProxy类说明;当执行areaDao.queryAreaByBean(area)时其实就执行了invoke这个方法.最终执行了MapperMethod .execute,我们看下cachedMapperMethod这个方法,注意 mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(this.mapperInterface, method, this.sqlSession.getConfiguration());这方法中的参数,我们只需要知道从这个对象中,我们可以获取到namespace.id的值,我们进入到MapperMethod类
类MapperMethod(重点)
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Flush;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.MapKey;
import org.apache.ibatis.cursor.Cursor;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ResultMap;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.SqlCommandType;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.StatementType;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ParamNameResolver;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.TypeParameterResolver;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
public class MapperMethod {
private final MapperMethod.SqlCommand command;
private final MapperMethod.MethodSignature method;
public MapperMethod(Class mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new MapperMethod.SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MapperMethod.MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object param;
Object result;
switch(null.$SwitchMap$org$apache$ibatis$mapping$SqlCommandType[this.command.getType().ordinal()]) {
case 1:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case 2:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case 3:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case 4:
if(this.method.returnsVoid() && this.method.hasResultHandler()) {
this.executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if(this.method.returnsMany()) {
result = this.executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if(this.method.returnsMap()) {
result = this.executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if(this.method.returnsCursor()) {
result = this.executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(this.command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case 5:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + this.command.getName());
}
if(result == null && this.method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !this.method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + this.command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + this.method.getReturnType() + ").");
} else {
return result;
}
}
private Object rowCountResult(int rowCount) {
Object result;
if(this.method.returnsVoid()) {
result = null;
} else if(!Integer.class.equals(this.method.getReturnType()) && !Integer.TYPE.equals(this.method.getReturnType())) {
if(!Long.class.equals(this.method.getReturnType()) && !Long.TYPE.equals(this.method.getReturnType())) {
if(!Boolean.class.equals(this.method.getReturnType()) && !Boolean.TYPE.equals(this.method.getReturnType())) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + this.command.getName() + "' has an unsupported return type: " + this.method.getReturnType());
}
result = Boolean.valueOf(rowCount > 0);
} else {
result = Long.valueOf((long)rowCount);
}
} else {
result = Integer.valueOf(rowCount);
}
return result;
}
private void executeWithResultHandler(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
MappedStatement ms = sqlSession.getConfiguration().getMappedStatement(this.command.getName());
if(!StatementType.CALLABLE.equals(ms.getStatementType()) && Void.TYPE.equals(((ResultMap)ms.getResultMaps().get(0)).getType())) {
throw new BindingException("method " + this.command.getName() + " needs either a @ResultMap annotation, a @ResultType annotation, or a resultType attribute in XML so a ResultHandler can be used as a parameter.");
} else {
Object param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
if(this.method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = this.method.extractRowBounds(args);
sqlSession.select(this.command.getName(), param, rowBounds, this.method.extractResultHandler(args));
} else {
sqlSession.select(this.command.getName(), param, this.method.extractResultHandler(args));
}
}
}
private Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
List result;
if(this.method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = this.method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.selectList(this.command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
result = sqlSession.selectList(this.command.getName(), param);
}
return !this.method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())?(this.method.getReturnType().isArray()?this.convertToArray(result):this.convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result)):result;
}
...
}
类MapperMethod 说明:在这类中execute方法是最终执行类,顺着往下看executeForMany方法中,我们看到了一行熟悉的代码: result = sqlSession.selectList(this.command.getName(), param);终于在最后看到了曙光!!!
至此我们队mybatis的接口式编程有了一个大概的了解,这其中还有很多细节值得深挖,再次感叹学海无涯啊!