Kafka日志储存介绍:压缩消息机制
Kafka压缩消息
在介绍MemoryRecords.append()方法中,不断的写入消息并且压缩,我们看Compressor的构造函数:
public class Compressor {
public Compressor(ByteBuffer buffer, CompressionType type) {
//初始化字段
this.type = type;
this.initPos = buffer.position();
this.numRecords = 0;
this.writtenUncompressed = 0;
this.compressionRate = 1;
this.maxTimestamp = Record.NO_TIMESTAMP;
if (type != CompressionType.NONE) {
// 如果要进行压缩,需要在buffer的首部提前空出offset和size的空间,以及CRC32等字段的空间。
buffer.position(initPos + Records.LOG_OVERHEAD + Record.RECORD_OVERHEAD);
}
// 初始化流
bufferStream = new ByteBufferOutputStream(buffer);
appendStream = wrapForOutput(bufferStream, type, COMPRESSION_DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE);
}
}在MemoryRecords不断写入写满后,会调用Compressor.close()方法,完成offset,size,CRC32的字段的写入,之后就可以发送给服务端了。
public class Compressor {
public void close() {
try {
//压缩的消息已经写完了,关闭输出流
appendStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new KafkaException(e);
}
//若使用了压缩算法
if (type != CompressionType.NONE) {
ByteBuffer buffer = bufferStream.buffer();
//保留offset的尾部位置
int pos = buffer.position();
// 移动position指针到buffer头部
buffer.position(initPos);
//写入offset,写入的是消息个数
buffer.putLong(numRecords - 1);
//写入size
buffer.putInt(pos - initPos - Records.LOG_OVERHEAD);
// 写入压缩的相关信息,例如时间戳,压缩算法等。
Record.write(buffer, maxTimestamp, null, null, type, 0, -1);
// 整个压缩消息的value长度
int valueSize = pos - initPos - Records.LOG_OVERHEAD - Record.RECORD_OVERHEAD;
buffer.putInt(initPos + Records.LOG_OVERHEAD + Record.KEY_OFFSET_V1, valueSize);
// CRC校验码
long crc = Record.computeChecksum(buffer,
initPos + Records.LOG_OVERHEAD + Record.MAGIC_OFFSET,
pos - initPos - Records.LOG_OVERHEAD - Record.MAGIC_OFFSET);
Utils.writeUnsignedInt(buffer, initPos + Records.LOG_OVERHEAD + Record.CRC_OFFSET, crc);
// reset the position
buffer.position(pos);
// 更新压缩率
this.compressionRate = (float) buffer.position() / this.writtenUncompressed;
TYPE_TO_RATE[type.id] = TYPE_TO_RATE[type.id] * COMPRESSION_RATE_DAMPING_FACTOR +
compressionRate * (1 - COMPRESSION_RATE_DAMPING_FACTOR);
}
}
}服务端为每个消息分配offset,是不需要解压缩的。原理如下:
1. 当生产者创建消息的时候,设置的offset是内部的offset,分别是0,1,2,....
2. 在Kafka服务端给消息分配offset的时候,根据外层信息中记录的内存压缩消息的个数为外层分配offset,为外层消息分配的offset是内层消息中最后一个消息的offset值。
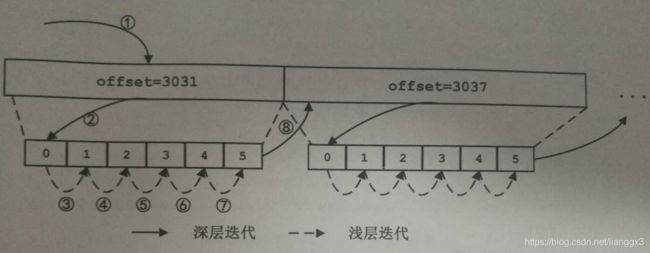
如相邻的按个外层的消息的offset值是3031,3037,3038,offset为3037的这个外层消息的内部压缩消息有6条,offset分别是0,1,2,3,4,5,。
3. 当消费者获取压缩消息后进行解压,根据内部消息的相对的offset和外层的offset计算出每个消息的offset值。
迭代压缩消息
消费者获取到的压缩后的信息和生产者直接发送给服务端的消息是一模一样的,那消费者取得消息后,需要对MemoryRecords进行迭代。MemoryRecords的迭代器是基层了AbstractIterator的接口,AbstractIterator使用next字段指向迭代的下一项,使用state字段标识当前迭代器的状态。
public abstract class AbstractIterator implements Iterator {
private static enum State {
READY, NOT_READY, DONE, FAILED
};
private State state = State.NOT_READY;
private T next;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
switch (state) {
case FAILED:
throw new IllegalStateException("Iterator is in failed state");
//迭代结束,返回false
case DONE:
return false;
// next已经准备好,返回true
case READY:
return true;
// notReady状态,调用maybeComputeNext方法获取next项
default:
return maybeComputeNext();
}
}
@Override
public T next() {
if (!hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
state = State.NOT_READY;
if (next == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Expected item but none found.");
return next;
}
@Override
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Removal not supported");
}
public T peek() {
if (!hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return next;
}
//使整个迭代结束
protected T allDone() {
state = State.DONE;
return null;
}
// 子类实现,返回迭代的下个迭代项
protected abstract T makeNext();
private Boolean maybeComputeNext() {
state = State.FAILED;
next = makeNext();
if (state == State.DONE) {
return false;
} else {
state = State.READY;
return true;
}
}
} MemoryRecords.RecordsIterator分为两层迭代,使用shallow参数进行区分,当shallow是true时,则消息是非压缩的,只用迭代这一层消息,称为浅迭代。反之,不仅仅迭代当前消息,还会再创建一个inner iterator内部迭代器来迭代压缩的消息,称为深迭代。
public static class RecordsIterator extends AbstractIterator {
//指向buffer字段,压缩或者没有压缩的消息。
private final ByteBuffer buffer;
//读取buffer的输入流,如果是压缩的消息则是对应解压缩输入流
private final DataInputStream stream;
private final CompressionType type;
private final boolean shallow;
private RecordsIterator innerIter;
// 内部迭代器需要的压缩信息集合
private final ArrayDeque logEntries;
//内 部迭代器中使用,记录消息的第一个的offset
private final long absoluteBaseOffset;
private RecordsIterator(LogEntry entry) {
this.type = entry.record().compressionType();
this.buffer = entry.record().value();
this.shallow = true;
this.stream = Compressor.wrapForInput(new ByteBufferInputStream(this.buffer), type, entry.record().magic());
long wrapperRecordOffset = entry.offset();
// If relative offset is used, we need to decompress the entire message first to compute
// the absolute offset.
if (entry.record().magic() > Record.MAGIC_VALUE_V0) {
this.logEntries = new ArrayDeque<>();
long wrapperRecordTimestamp = entry.record().timestamp();
//本次循环中,把内部消息解压出来添加到logEntries集合中。
while (true) {
try {
//对于内层消息,getNextEntryFromStream为读取ging解压,外层则是直接读取。
LogEntry logEntry = getNextEntryFromStream();
Record recordWithTimestamp = new Record(logEntry.record().buffer(),
wrapperRecordTimestamp,
entry.record().timestampType());
logEntries.add(new LogEntry(logEntry.offset(), recordWithTimestamp));
} catch (EOFException e) {
break;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new KafkaException(e);
}
}
this.absoluteBaseOffset = wrapperRecordOffset - logEntries.getLast().offset();
} else {
this.logEntries = null;
this.absoluteBaseOffset = -1;
}
}
}
makeNext方法演示整个迭代过程:
public static class RecordsIterator extends AbstractIterator {
protected LogEntry makeNext() {
if (innerDone()) {
try {
// 获取消息
LogEntry entry = getNextEntry();
// No more record to return.
if (entry == null)
return allDone();
// 在inner iterator中获取每个消息的absoluteOffset
if (absoluteBaseOffset >= 0) {
long absoluteOffset = absoluteBaseOffset + entry.offset();
entry = new LogEntry(absoluteOffset, entry.record());
}
// decide whether to go shallow or deep iteration if it is compressed
CompressionType compression = entry.record().compressionType();
// 根据shallow参数和压缩类型决定是否创建inner iterato
if (compression == CompressionType.NONE || shallow) {
return entry;
} else {
// 创建inner iterator,迭代内层消息
innerIter = new RecordsIterator(entry);
return innerIter.next();
}
} catch (EOFException e) {
return allDone();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new KafkaException(e);
}
} else {
return innerIter.next();
}
}
}
public static class RecordsIterator extends AbstractIterator {
private LogEntry getNextEntryFromStream() throws IOException {
// read the offset
long offset = stream.readLong();
// read record size
int size = stream.readInt();
if (size < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException("Record with size " + size);
// read the record, if compression is used we cannot depend on size
// and hence has to do extra copy
ByteBuffer rec;
if (type == CompressionType.NONE) {
//未压缩的消息处理rec是buffer的分片
rec = buffer.slice();
int newPos = buffer.position() + size;
if (newPos > buffer.limit())
return null;
buffer.position(newPos);
rec.limit(size);
} else {
//处理压缩的消息,从stream中读取消息,这个过程会解压.
byte[] recordBuffer = new byte[size];
stream.readFully(recordBuffer, 0, size);
rec = ByteBuffer.wrap(recordBuffer);
}
return new LogEntry(offset, new Record(rec));
}
} 迭代的过程:
1. 首先创建浅层迭代器调用next方法,低啊用makeNext准备迭代项.在makeNext中会判断深层迭代器中是否完成,当前未开始深层迭代,则调用getNextEntryFromStream方法获取offset为3031的消息(①),
2. 检测3031消息压缩格式,创建深层迭代器,getNextEntryFromStream方法解压病放入logEntries队列。
3. 调用next方法,从logEntries中获取消息并返回②
4. ③到⑦重复这个过程,当深层迭代完成后,调用getNextEntryFromStream获取offset为3037的消息。