API
API (Application Programming Interface) 应用程序接口
结构:左上package 左下:对应的类和接口 右:方法和属性说明
java.lang包下:Java语言包 ,任何类中,该包中的类都会被自动导入。
java.util包: 工具包
java.io包:文件操作
java.net:网络
Object
它是所有类的超类,是唯一没有父类的类
java.lang.Object
hashcode:该方法返回对象的哈希码,十六进制
toString:类的完全限定名@hashcode
equals:比较两个引用类型的地址是否相等
public class TestObject {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestObject to = new TestObject();
System.out.println(to.hashCode());
TestObject to1 = new TestObject();
System.out.println(to1.hashCode());
System.out.println(to.toString());
System.out.println(to);
}
}
equals:
if(to.equals(to1)){
System.out.println("相等");
}else{
System.out.println("不相等");
}
equals ==区别
equals:只能比较引用类型,比较引用类型时,常规的是比较他的引用地址。但是很多类都对equals方法进行重写,重写后比较值相等
==:基本类型和引用类型 比较基本类型时就直接比较值是否相等,比较引用类型时也是比较地址是否相等不能被覆盖
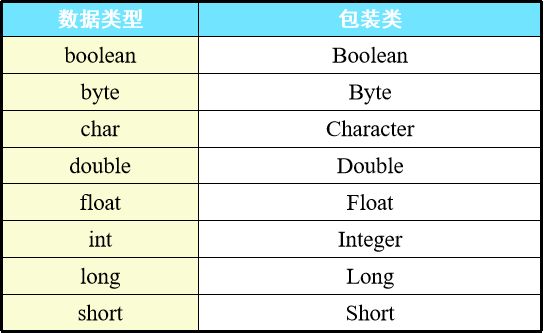
包装类
类型转换:
public void test2() {
//基本类型转包装类
Integer i=new Integer(123);
System.out.println(i.toString());
System.out.println("int的最大值"+Integer.MAX_VALUE);
Integer j=new Integer(2147483647+1);
System.out.println("j="+j);
}
@Test
public void test3() {
//包装类转基本类型
Integer a=new Integer(123);
int i_a=a.intValue();
System.out.println(i_a);
}
@Test
public void test10() {
//自动转换 自动拆箱封箱
Integer a=123;
int b=a;
}
@Test
public void test4() {
//包装类转String *.toString()
Integer a=new Integer(123);
String s=a.toString();
System.out.println(s);
}
@Test
public void test5() {
//String转包装类 两种方式
Integer wInt = new Integer("500");//优先掌握
Integer wInt2 = Integer.valueOf("500");
}
@Test
public void test6() {
//String转int
String sInt = "500";
int pInt = Integer.parseInt (sInt);
System.out.println(pInt);
}
包装类常用的方法
Character对字符的判断
String
不可变字符串
String的创建
有两种方式:
1)静态方式(常用)。像是给变量直接赋值一样来使用。如:String s1 = “abc”; String s2 = “abc”;
2)动态方式。动态的内存分配,使用new运算符。如:String s3= new String(“abc”); String s4= new String(“abc”);
3)两种方式创建的字符串区别:
使用静态方式创建的字符串,在方法区的常量池中只会产生唯一一个字符串对象,使用该方式产生同样一个字符串时,内存中不再开辟另外一块空间,而是两个引用变量指向同一个字符串对象。
使用动态方式创建的字符串,在堆内存中会产生出不同的对象。
equals 默认比较引用类型时比较地址 String对它进行了重写,改为比较字面量,也就是字符串的值是否相等。
如: 判断登录用户是普通用户还是管理员
@Test
public void test3() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String username = sc.next();
// 判断用户名是不是root/admin
if (username.equals("admin") || username.equals("root")) {
// 如果是,就认为他是管理员,否则是普通用户
System.out.println("欢迎管理员登录");
} else {// 否则是普通用户
System.out.println("请充值后再登录。");
}
}
}
课堂练习
@Test
public void test4(){
System.out.println(5+6+'A');//76
System.out.println(5+6+"A");//11A
System.out.println(5+"A"+6);//5A6
}
常用方法
1.equals
2.equalsIgnoreCase
@Test
public void test5() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String username = sc.next();
// 判断用户名是不是root/admin
if (username.equalsIgnoreCase("admin") || username.equalsIgnoreCase("root")) {
// 如果是,就认为他是管理员,否则是普通用户
System.out.println("欢迎管理员登录");
} else {// 否则是普通用户
System.out.println("请充值后再登录。");
}
}
}
3.substring(int begin) 字符串截取
返回一个新字符串,该字符串是从begin开始的字符串的内容
@Test
public void test6() {
String a="abcenglish";
String sub_a=a.substring(3);
System.out.println(sub_a);
}
返回一个新字符串,该字符串是从begin开始到end-1结束的字符串的内容
@Test
public void test7() {
String a="abcenglishefg";
String sub_a=a.substring(3,10);
String sub_b=a.substring(3,a.length()-3);
System.out.println(sub_a);
System.out.println(sub_b);
}
indexOf/lastIndexOf
indexOf和lastIndexOf也接受字符串类型
@Test
public void test8() {
//indexOf 判断子串在字符串中第一次出现的索引。如果不存在,就返回-1
String a="abcenglisheafg";
int loc=a.indexOf('a');
System.out.println(loc);
//lastIndexOf判断子串在字符串中最后一次出现的索引。如果不存在,就返回-1
int last_loc=a.lastIndexOf('a');
System.out.println(last_loc);
}
课堂练习
从控制台输入一个邮箱地址,并用程序判断,邮箱地址里面是不是只有一个@
@Test
public void test9() {
//indexOf 判断子串在字符串中第一次出现的索引。如果不存在,就返回-1
System.out.println("请输入邮箱:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String email = sc.next();
int loc=email.indexOf("wangqj");
System.out.println(loc);
}
trim 去掉首尾空格
@Test
public void test10() {
String a=" abcenglisheafg ";
System.out.println(a.trim());
}
replace替换
@Test
public void test11() {
String a=" abcenglisheafg ";
System.out.println(a.replaceAll(" ", ""));
System.out.println(a.replaceAll("abc", "123"));
System.out.println(a.replaceAll("e", "f"));
}
split分隔
@Test
public void test12() {
String a="李海峰#男;王均仪#女;王晓宇#男";
String[] names=a.split(";");
for(int i=0;i编码方式比较
@Test
public void test13() {
String a="中";
try {
byte[] byte_a=a.getBytes("utf-8");
System.out.println(byte_a.length);//3byte
String s_a=new String(byte_a,"utf-8");
System.out.println(s_a);
byte[] byte_gbk=a.getBytes("gbk");
System.out.println(byte_gbk.length);//2byte
byte[] byte_iso8859_1=a.getBytes("ISO8859-1");//1byte
System.out.println(byte_iso8859_1.length);
String s_8859=new String(byte_iso8859_1,"ISO8859-1");//乱码 因为ISO8859-1不包括汉字
System.out.println(s_8859);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
StringBuffer
可变字符串
追加方法append
@Test
public void test(){
//Stringbuffer可变字符串
//经常用他来拼接sql语句
//假设用户从控制台输入用户名和密码,根据用户名和密码去t_user表里查询用户信息
//select * from t_user where username=? and password=?
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String name=sc.next();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String password=sc.next();
StringBuffer sql=new StringBuffer("select * from t_user where username is not null ");
if(name!=null){
sql.append(" and username="+name);//append 是追加
}
if(password!=null){
sql.append(" and password="+password);//append 是追加
}
System.out.println(sql.toString());
}
反转方法 (倒叙)
@Test
public void test1(){
StringBuffer sql=new StringBuffer("中华人民共和国");
System.out.println(sql.reverse());
}
练习:输入一个手机号码,将中间四位使用星号替代。
@Test
public void test2(){
StringBuffer phone=new StringBuffer("13904001139");
StringBuffer new_phone=phone.replace(3, 7, "****");
System.out.println(new_phone);
}
Math
常量PI E
方法:大多与mysql类似
sqrt:开方
课堂练习
海伦公式,从键盘输入三个整数作为三角形的三边,使用海伦公式求出该三角形的面积。
@Test
public void test3(){
//从键盘输入三个整数作为三角形的三边,使用海伦公式求出该三角形的面积。
System.out.println("请输入三边");
int a=new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
int b=new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
int c=new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
double p=(a+b+c)/2.0;
double s=Math.sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c));
System.out.println(s);
}
日期类
@Test
public void test1() {
Date d=new Date();
System.out.println(d.getMonth());
System.out.println(d.getDay());
}
//SUN MON TUE WED THU FRI SAT
// 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
@Test
public void test2(){
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
//Date now=c.getTime();
//System.out.println(now);
System.out.println("年:"+c.get(c.YEAR));
System.out.println("月:"+c.get(c.MONTH));
//需要加1
System.out.println("日:"+c.get(c.DAY_OF_MONTH));
System.out.println("时:"+c.get(c.HOUR_OF_DAY));
System.out.println("分:"+c.get(c.MINUTE));
System.out.println("秒:"+c.get(c.SECOND));
//1~7来表示:星期天,星期一,星期二,星期三,星期四,星期五,星期六
System.out.println("星期:"+c.get(c.DAY_OF_WEEK));
}
@Test
public void test3(){
//首先定义一下日期格式 HH24小时制 hh 12小时制
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
String str_d=sdf.format(new Date());
System.out.println(str_d);
//字符串转成日期
try {
Date d=sdf.parse(str_d);
System.out.println(d);
} catch (ParseException e) {
System.out.println("出错了");
}
}
@Test
public void test4(){
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.set(2018, 10, 10);
System.out.println(c.get(c.YEAR));
System.out.println(c.get(c.MONTH));
}
//编写一个方法,找到两个日期格式的字符串的最大值
@Test
public void test5() throws ParseException{
System.out.println("请输入两个日期格式的字符串");
String d1=new Scanner(System.in).next();
String d2=new Scanner(System.in).next();
System.out.println(DateTest.max(d1, d2).toString());
}
public static Date max(String date1,String date2) throws ParseException{
//date1>date2 输出 date1
//date1add给指定参数增加/减少
加上指定天数后的日期
@Test
public void test6() throws ParseException{
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.add(c.DATE, 15);
System.out.println(c.getTime());
}
实战演练
输入日期格式字符串作为商品的生产日期,输入保质期(天);计算截止到今天,该商品还有多少天会过保质期
1、控制台输入字符串转为日期格式
2、将输入日期增加保质期天数
3、取得当前系统日期,比较两个日期,如果过期输出“该商品已经过期”
@Test
public void test7() throws ParseException{
System.out.println("请输入生产日期和过期时间");
//得到生产日期
String date_str=new Scanner(System.in).next();
//得到过期时间
int days=new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
//指定日期转换格式
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
//把用户输入的字符串转成日期型
Date d1=sdf.parse(date_str);
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.setTime(d1);
//加上n天
c.add(c.DATE, days);
//过期日期
Date d_guo=c.getTime();
//打印过期日期
System.out.println("过期日期为:"+d_guo);
//获取当前日期
Date now=sdf.parse(sdf.format(new Date()));
System.out.println("当前日期为:"+now);
//比较两个日期先后,得到结果
if(now.before(d_guo)){
System.out.println("已过期");
}else{
System.out.println("未过期");
}
}
请编写一个方法,计算两个日期相差的天数
改写上面的程序
public static long days(String begin,String end) throws ParseException{
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date d1=sdf.parse(begin);
Date d2=sdf.parse(end);
long begintime=d1.getTime();
System.out.println("毫秒数:"+begintime);
long endtime=d2.getTime();
//毫秒数换数成天 1天=24小时 1小时=60分 1分=60秒 1秒=1000毫秒
long day=(endtime-begintime)/24/60/60/1000;
System.out.println(day);
return day;
}
@Test
public void test8() throws ParseException{
System.out.println("请输入生产日期和过期时间");
//得到生产日期
String date_str=new Scanner(System.in).next();
//得到过期时间
int days=new Scanner(System.in).nextInt();
//算当前日期与生产日期之间相差的天数
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
String now=sdf.format(new Date());
System.out.println(now);
//相差的天数
int dis_days=(int)DateTest.days(date_str, now);
if(dis_days>days){
System.out.println("已过期");
}else{
System.out.println("没过期");
}
}