【天融信TOS防火墙故障排除及定位方法】网络数据抓包~温权~
文章目录
- 一、 TOS设备抓包命令以及注意事项:
- 二、 wireshark的抓包方法以及数据过滤
- 三、典型故障抓包技巧

一、 TOS设备抓包命令以及注意事项:
NAT源地址转换抓目的地址,目的地址转换抓源地址,双向转换源和目的都抓,老tos的trunk抓包需要带上vlan,下一代NG可以不带,多抓抓就能看出效果了。>
1.抓包命令的格式以及使用方法:
System tcpdump –ni any 后续可以添加具体的ip(host)、端口(port)、应用层协议(tcp、udp)和逻辑关系(and、or)。
常用参数说明:
-n,不进行ip地址到主机名称的转换。
-i,需要监听的接口。(any为所有接口)
-e,显示数据包的2层信息。
-vvv,输出详细的内容。(v的个数没有限制)
-xxx,输出包头内容。(x的个数没有限制)
2.抓包范例与说明:
监听所有接口抓取与192.168.7.168相关的数据包,如下:
system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.168
198# system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.168
tcpdump: WARNING: Promiscuous mode not supported on the “any” device
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on any, link-type LINUX_SLL (Linux cooked), capture size 68 bytes
16:43:17.870968 X@dummy IP 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 812682594:812682819(225) ack 3712242358 win 65494
16:43:17.871001 X@eth0 IP 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 0:225(225) ack 1 win 65494
16:43:18.078489 R@eth0 IP 192.168.7.168.57862 > 192.168.7.198.23: . ack 225 win 64240
16:43:18.078507 X@dummy IP 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 225:441(216) ack 1 win 65494
16:43:18.078513 X@eth0 IP 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 225:441(216) ack 1 win 65494
监听所有接口抓取与192.168.7.168并且端口为23相关的数据包,如下:
system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.168 and port 23
198# system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.198 and port 23
tcpdump: WARNING: Promiscuous mode not supported on the “any” device
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on any, link-type LINUX_SLL (Linux cooked), capture size 68 bytes
16:49:48.610370 X@dummy IP 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 812689585:812689810(225) ack 3712245552 win 65494
16:49:48.610407 X@eth0 IP 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 0:225(225) ack 1 win 65494
16:49:48.822413 R@eth0 IP 192.168.7.168.57862 > 192.168.7.198.23: . ack 225 win 63168
16:49:48.822432 X@dummy IP 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 225:441(216) ack 1 win 65494
16:49:48.822438 X@eth0 IP 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 225:441(216) ack 1 win 65494
监听所有接口抓取与192.168.7.168相关的ping数据包,如下:
system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.168 and icmp
198# system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.198 and icmp
tcpdump: WARNING: Promiscuous mode not supported on the “any” device
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on any, link-type LINUX_SLL (Linux cooked), capture size 68 bytes
16:51:22.112614 R@eth0 IP 192.168.7.109 > 192.168.7.198: ICMP echo request, id 50025, seq 1, length 119
16:51:22.112648 X@dummy IP 192.168.7.198 > 192.168.7.109: ICMP echo reply, id 50025, seq 1, length 119
16:51:22.112659 X@eth0 IP 192.168.7.198 > 192.168.7.109: ICMP echo reply, id 50025, seq 1, length 119
监听所有接口抓取与192.168.7.168和192.168.7.144相关的数据包,如下:
system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.1 and host 192.168.7.168
198# system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.1 and host 192.168.7.168
tcpdump: WARNING: Promiscuous mode not supported on the “any” device
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on any, link-type LINUX_SLL (Linux cooked), capture size 68 bytes
17:09:14.394896 R@eth0 arp who-has 192.168.7.168 tell 192.168.7.1
监听所有接口抓取与192.168.7.168或者端口为443的数据包,如下:
system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.168 or port 443
198# system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.168 or port 443
tcpdump: WARNING: Promiscuous mode not supported on the “any” device
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on any, link-type LINUX_SLL (Linux cooked), capture size 68 bytes
17:11:05.479615 R@eth0 IP 192.168.7.168.57862 > 192.168.7.198.23: . ack 812694394 win 63440
17:11:05.479637 X@dummy IP 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 1:224(223) ack 0 win 65494
17:11:05.479644 X@eth0 IP 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 1:224(223) ack 0 win 65494
17:11:05.664013 R@eth0 IP 192.168.7.211.48202 > 74.125.235.224.443: S 430095593:430095593(0) win 14600
17:11:05.664032 X@ppp0 IP 219.143.82.112.48202 > 74.125.235.224.443: S 430095593:430095593(0) win 14600
17:11:05.697993 R@eth0 IP 192.168.7.168.57862 > 192.168.7.198.23: . ack 224 win 63217
17:11:05.698012 X@dummy IP 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 224:801(577) ack 0 win 65494
17:11:05.698019 X@eth0 IP 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 224:801(577) ack 0 win 65494
监听所有接口抓取与192.168.7.168相关的数据包,同时要显示二层信息。如下:
system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.168 -e
198# system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.168 -e
tcpdump: WARNING: Promiscuous mode not supported on the “any” device
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on any, link-type LINUX_SLL (Linux cooked), capture size 68 bytes
17:13:37.554389 X@dummy Out ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 281: 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 812696932:812697157(225) ack 3712245773 win 65494
17:13:37.554422 X@eth0 Out 00:13:32:01:13:66 ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 281: 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 0:225(225) ack 1 win 65494
抓取与192.168.7.168相关的数据包,同时要显示源和目的mac地址。如下:
system tcpdump -ni eth0 host 192.168.7.168 -e
198# system tcpdump -ni eth0 host 192.168.7.168 -e
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 68 bytes
17:15:43.488737 R@eth0 3c:97:0e:c0:2d:9c > 00:13:32:01:13:66, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 60: 192.168.7.168.57862 > 192.168.7.198.23: . ack 812700467 win 63855
17:15:43.488763 X@eth0 00:13:32:01:13:66 > 3c:97:0e:c0:2d:9c, ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 201: 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 1:148(147) ack 0 win 65494
抓取与192.168.7.168相关的icmp数据包,同时输出详细的内容。如下:
system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.168 and icmp -vvvvv
198# system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.168 and icmp -vvvvv
tcpdump: WARNING: Promiscuous mode not supported on the “any” device
tcpdump: listening on any, link-type LINUX_SLL (Linux cooked), capture size 68 bytes
17:17:12.991054 R@eth0 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 128, id 7925, offset 0, flags [none], proto: ICMP (1), length: 60) 192.168.7.168 > 192.168.7.198: ICMP echo request, id 1, seq 11, length 40
17:17:12.991096 X@dummy IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 8890, offset 0, flags [none], proto: ICMP (1), length: 60) 192.168.7.198 > 192.168.7.168: ICMP echo reply, id 1, seq 11, length 40
17:17:12.991105 X@eth0 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 8890, offset 0, flags [none], proto: ICMP (1), length: 60) 192.168.7.198 > 192.168.7.168: ICMP echo reply, id 1, seq 11, length 40
抓取与192.168.7.168相关的telnet数据包,同时输出详细的包头内容。如下:
system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.168 and port 23 -xxxxx
198# system tcpdump -ni any host 192.168.7.168 and port 23 -xxxxx
tcpdump: WARNING: Promiscuous mode not supported on the “any” device
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on any, link-type LINUX_SLL (Linux cooked), capture size 68 bytes
17:19:42.379794 R@eth0 IP 192.168.7.168.57862 > 192.168.7.198.23: . ack 225 win 64240
0x0000: 0000 0001 0006 3c97 0ec0 2d9c 0000 0800
0x0010: 4500 0028 27cf 4000 8006 4242 c0a8 07a8
0x0020: c0a8 07c6 e206 0017 dd44 6105 3070 e475
0x0030: 5010 faf0 eed6 0000 0000 0000 0000
17:19:42.379815 X@dummy IP 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 225:961(736) ack 1 win 65494
0x0000: 0004 0200 0000 3c97 0ec0 2d9c 0000 0800
0x0010: 4500 0308 c1c6 4000 4006 e56a c0a8 07c6
0x0020: c0a8 07a8 0017 e206 3070 e475 dd44 6105
0x0030: 5018 ffd6 a242 0000 3137 3a31 393a 3432
0x0040: 2e31 3831
17:19:42.379821 X@eth0 IP 192.168.7.198.23 > 192.168.7.168.57862: P 225:961(736) ack 1 win 65494
0x0000: 0004 0001 0006 0013 3201 1366 0000 0800
0x0010: 4500 0308 c1c6 4000 4006 e56a c0a8 07c6
0x0020: c0a8 07a8 0017 e206 3070 e475 dd44 6105
0x0030: 5018 ffd6 a242 0000 3137 3a31 393a 3432
0x0040: 2e31 3831
3.抓包注意事项:
a.需要抓取mac地址时,如果接口为any将只会显示源mac。当需要抓取源和目的mac
时必须指定单独接口。
b.抓包定位故障时为了确保抓取的数据全面,需要考虑是否有NAT的情况。源NAT需要抓取目的ip、目的nat需要抓取源ip、双向nat需要开启2个窗口,一个抓取源ip,另一个抓取目的ip。
c.抓包参数中的详细信息例如-v和-x参数没有个数限制,一般输入6个即可。
d.抓包参数可以组合使用以便输出更加详细和精确的信息。
e.dummy接口为设备的本机接口,当数据包终结到设备时,由dummy口先响应然后再从物
理接口发出。
f.不加接口,带evv抓源mac。加接口,带evv抓源和目的mac。
二、 wireshark的抓包方法以及数据过滤
1.wireshark抓包方法
a.软件安装完毕后,点击图标。如下:
![]()
b.在功能菜单中选取需要监听的物理网卡。
Capture——Interface,在弹出的Capture Interfaces窗口中选择监听的网卡后点击Start即可。如下:

c.以下为抓包的工作界面
2.wireshark的数据过滤
在使用wireshark抓包时,默认会显示很多的数据包。在排除故障时我们可能更关心与故障相关的数据信息,以便高效、准确的定位故障。此时就会使用到wireshark的过滤功能。以下为大家介绍一些常用的过滤命令。
过滤指定的ip地址。如下:
Ip.addr==192.168.7.168

过滤192.168.7.198和192.168.7.168相关的数据包,如下:
Ip.addr== 192.168.7.198 and ip.addr==192.168.7.168
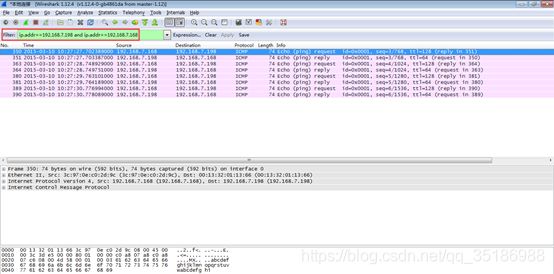
过滤源ip为192.168.7.168的数据包,如下:
Ip.src==192.168.7.168

过滤目的ip为192.168.7.168的数据包,如下:
Ip.dst==192.168.7.168

过滤TCP源端口为80的数据包,如下:
Tcp.srcport==80
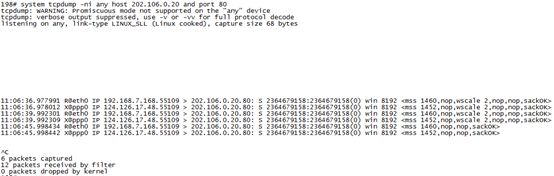
过滤udp目的端口为53的数据包,如下:
Udp.dstport==53

三、典型故障抓包技巧
案例1故障描述:
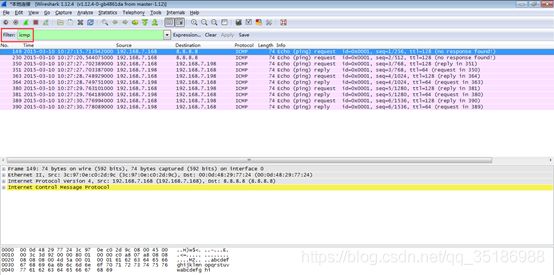
内网一台pc无法正常ping通公网地址8.8.8.8
抓包内容:

故障分析:
通过抓包得知,设备的内网接口eth0收到了192.168.7.168 ping 8.8.8.8的icmp请求包,但是设备没有将该请求包转发出去。出现该问题需要检查设备的访问控制是否开放了icmp和ping。
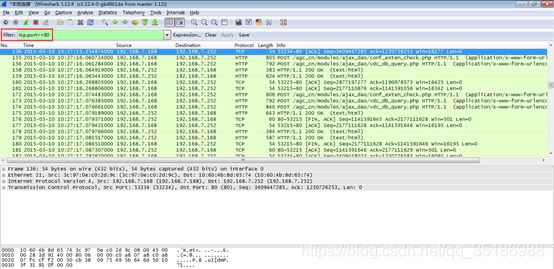
案例2故障描述:
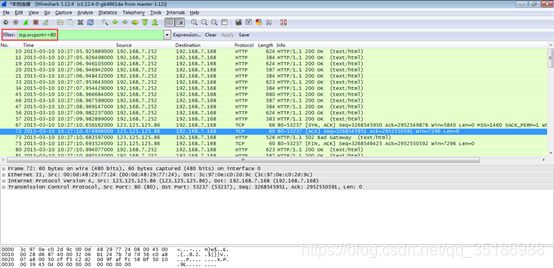
内网一台pc无法正常访问202.106.0.20的80端口
抓包内容:
故障分析:
通过抓包得知,设备正常转发了去往公网地址80端口的syn包,但是没有收到公网服务器返回的syn+ack包,导致三次握手没有正常建立,所以无法访问。出现该问题一般是ISP针对具体的公网ip没有开放80端口或者是目标服务器80端口服务出现故障所致。
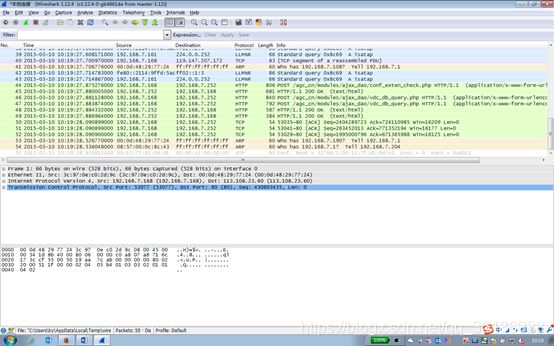
案例3故障描述:
2台设备无法建立起OSPF邻居关系,导致路由无法正常学习。
抓包内容:

故障分析:
通过抓包发现设备收到ospf的hello包开启了简单密码认证功能但是没有配置密钥,而本机发出的ospf hello开启了简单密码认证功能同时配置了密钥为cisco。添加对端设备的密钥配置即可。