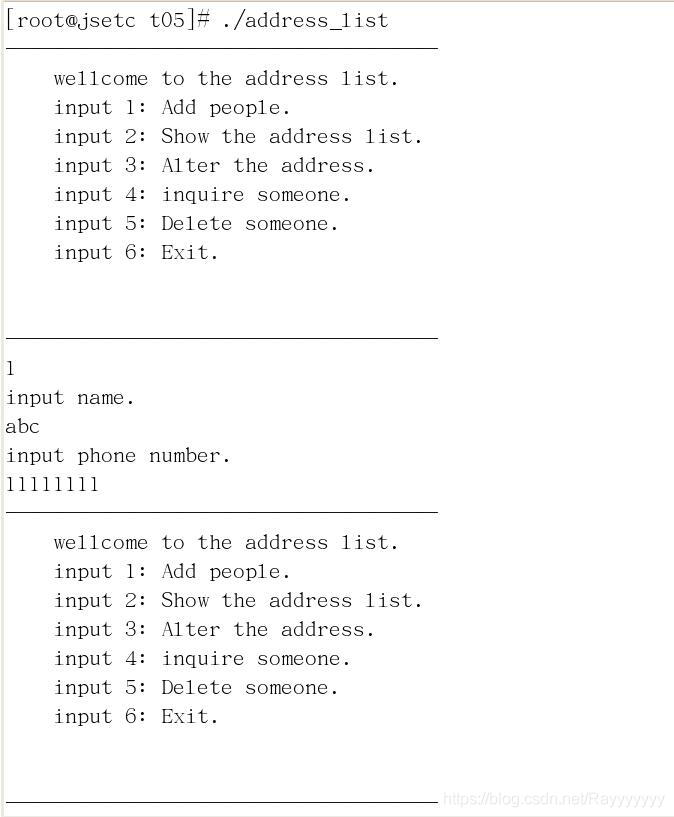
通讯录1 + C语言练习题(201812.13)
通信录:
程序:
#include
#include
#include
#define MAL_OK 1
#define MAL_ERR 0
struct node
{
char name[20];
int num;
struct node * next;
};
typedef struct node Node;
typedef struct node * Link;
void wellcome()
{
printf("------------------------------------\n");
printf(" wellcome to the address list. \n");
printf(" input 1: Add people. \n");
printf(" input 2: Show the address list.\n");
printf(" input 3: Alter the address.\n");
printf(" input 4: inquire someone.\n");
printf(" input 5: Delete someone.\n");
printf(" input 6: Exit.\n");
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
printf("------------------------------------\n");
}
int malloc_ok(Link new_node)
{
if(new_node == NULL)
{
return MAL_ERR;
}
else
{
return MAL_OK;
}
}
void create_node(Link *new_node)
{
(*new_node) = (Link)malloc(sizeof(Node));
while(malloc_ok(*new_node) == MAL_ERR)
{
(*new_node) = (Link)malloc(sizeof(Node));
}
}
void create_link(Link * head)
{
create_node(head);
(*head)->next = NULL;
}
void inser_node_tail(Link head,Link new_node)
{
Link p;
p = head;
while(p->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
}
p->next = new_node;
new_node->next = NULL;
}
void input_people(Link new_node)
{
Link p;
p = new_node;
printf("input name.\n");
getchar();
gets(p->name);
printf("input phone number.\n");
scanf("%d",&p->num);
}
void create_address(Link * head,Link * new_node)
{
if((*head) == NULL)
{
create_link(head);
}
create_node(new_node);
inser_node_tail(*head,*new_node);
input_people(*new_node);
}
void display(Link head)
{
Link p;
p = head;
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("No fine link.\n");
}
else if(p->next != NULL)
{
while(p->next != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
printf("name:%s\t",p->name);
printf("phone number:%d\n",p->num);
}
}
}
void alter_address(Link head)
{
Link p;
int order;
p = head->next;
char temp[20];
printf("请输入要修改的人的名字。\n");
getchar();
gets(temp);
printf("输入1为修改名字,输入2为修改电话。\n");
scanf("%d",&order);
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("Address is empty!.\n");
}
else
{
while(p != NULL)
{
if(strcmp(temp,p->name) == 0)
{
break;
}
p = p->next;
}
if(order == 1)
{
printf("Input name:\n");
getchar();
gets(p->name);
}
else if(order == 2)
{
printf("Input number.\n");
scanf("%d",&p->num);
}
else
{
printf("输入错误。\n");
}
}
}
void inquire_address(Link head)
{
Link p;
char temp[20];
p = head->next;
printf("输入要查询的人的名字。\n");
getchar();
gets(temp);
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("Address is empty.\n");
}
else
{
while(p != NULL)
{
if(strcmp(temp,p->name) == 0)
{
printf("查询为:\n");
printf("name:%s\t",p->name);
printf("num:%d\n",p->num);
}
p = p->next;
}
}
}
void del_node(Link head)
{
Link p,q;
char name[20];
q = head;
p = head->next;
printf("请输入要删除的人的名字。\n");
getchar();
gets(name);
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("Link is empty.\n");
}
else
{
while(strcmp(p->name,name) != 0 && p->next != NULL)
{
q = p;
p = p->next;
}
if(p->next == NULL && strcmp(p->name,name) != 0)
{
printf("没有找到。\n");
}
else
{
q->next = p->next;
free(p);
}
}
}
void release_link(Link * head)
{
Link p;
p = *head;
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("No link\n");
}
else
{
while(*head != NULL)
{
*head = (*head)->next;
free(p);
p = *head;
}
}
}
int main()
{
Link head = NULL;
Link new_node = NULL;
int order;
do
{
wellcome();
scanf("%d",&order);
if(order == 1)
{
create_address(&head,&new_node);
}
if(order == 2)
{
display(head);
}
if(order == 3)
{
alter_address(head);
}
if(order == 4)
{
inquire_address(head);
}
if(order == 5)
{
del_node(head);
}
}while(order != 6);
release_link(&head);
return 0;
}
1、 设计一个算法,将x插入一个有序(从大到小排序)的线性表(顺序存储结构)的适当位置,并保持线性表的有序性。
#include
int main()
{
int a[10],b[11],i,j,k,c;
printf("请输入10个数\n");
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
for(j=i;j<10;j++)
if(a[i] 2、 题目1 中如果采用链式存储,怎样实现
#include
#include
#define NULL 0
struct shu
{
int num;
struct shu *next;
};
int n;//节点数n
struct shu *creat(void)//建立链表并且输入值
{
struct shu *head;
struct shu *p1,*p2;
int i=1;
p1=p2=(struct shu *)malloc(sizeof(struct shu));
scanf("%d",&p1->num);
head=NULL;
while(inext=p1;
p2=p1;
p1=(struct shu *)malloc(sizeof(struct shu));
scanf("%d",&p1->num);
i++;
}
p2->next=NULL;
return(head);
}
struct shu * insert(struct shu *head,struct shu *charushu)//使插入数插入链表之中
{
struct shu *p0,*p1,*p2;
p1=head;
p0=charushu;
if(head==NULL)//判断是否是空链表
{
head=p0;p0->next=NULL;//是则输出插入的数
}
else
{
while((p0->num>p1->num) && (p1->next!=NULL))//判断大小及位置
{
p2=p1;
p1=p1->next;
}
if(p0->num<=p1->num)//插入
{
if(head==p1)
head=p0;
else p2->next=p0;
p0->next=p1;
}
else
{
p1->next=p0;
p0->next=NULL;
}
}
n=n+1;
return(head);
}
void print(struct shu *head)//输出链表里面的数的函数
{
struct shu *p;
int i;
p=head;
if(inum);
p=p->next;//使p指向下一个结点
i++;
}while(i #include
#include
#include
struct btnode
{
int d;
struct btnode *lchild;
struct btnode *rchild;
};
struct btnode *bt;
int k;
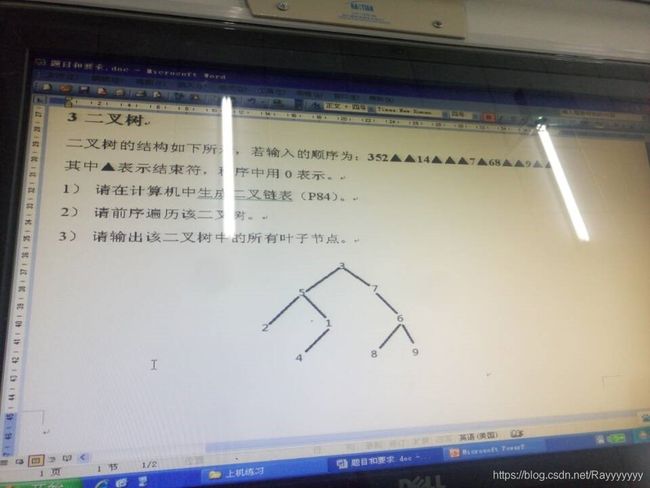
struct btnode *creatbt(struct btnode *bt,int k)//二叉树的生成
{
int b;
struct btnode *p,*t;
printf("输入");
scanf("%d",&b);
if(b!=0)//判断是否为结束符,并输入链表的值
{
p=(struct btnode *)malloc(sizeof(struct btnode));//取新的结点
p->d=b;
p->lchild=NULL;
p->rchild=NULL;//至新的结点的值域为b以及左右的指针域为空
if(k==0)
t=p;
if(k==1)
bt->lchild=p;
if(k==2)
bt->rchild=p;
creatbt(p,1);
creatbt(p,2);
}
return(t);
}
void pretrav(struct btnode *bt)//二叉树的前序遍历,输出结点
{
if(bt!=NULL)
{
printf("%d\n",bt->d);
pretrav(bt->lchild);
pretrav(bt->rchild);
}
return;
}
int main()//主函数
{
printf("请输入要输入的数\n");
bt=creatbt(bt,k);
pretrav(bt);
return 0;
}