【 C# 】(一) --------- 泛型带头节点的单链表,双向链表实现
在编程领域,数据结构与算法向来都是提升编程能力的重点。而一般常见的数据结构是链表,栈,队列,树等。事实上C#也已经封装好了这些数据结构,在头文件 System.Collections.Generic 中,直接创建并调用其成员方法就行。不过我们学习当然要知其然,亦知其所以然。
本文实现的是链表中的单链表和双向链表,并且实现了一些基本方法
一. 定义一个链表接口 MyList
接口里声明了我们要实现的方法:
interface MyList{ int GetLength(); //获取链表长度 void Clear(); //清空链表 bool IsEmpty(); //判断链表是否为空 void Add(T item); //在链表尾部添加新节点 void AddPre(T item,int index); //在指定节点前添加新节点 void AddPost(T item,int index); //在指定节点后添加新节点 T Delete(int index); //按索引删除节点 T Delete(T item,bool isSecond = true); //按内容删除节点,如果有多个内容相同点,则删除第一个 T this[int index] { get; } //实现下标访问 T GetElem(int index); //根据索引返回元素 int GetPos(T item); //根据元素返回索引地址 void Print(); //打印 }
二. 实现单链表
2.1 节点类
先定义一个单链表所用的节点类,Node。而且我们要实现泛型
先定义一个数据域和下一节点(“Next”),并进行封装,然后给出数个重载构造器。这一步比较简单,这里直接给出代码
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace 线性表 { ////// 单向链表节点 /// ///class Node { private T data; //内容域 private Node next; //下一节点 public Node() { this.data = default(T); this.next = null; } public Node(T value) { this.data = value; this.next = null; } public Node(T value,Node next) { this.data = value; this.next = next; } public T Data { get { return data; } set { data = value; } } public Node Next { get { return next; } set { next = value; } } } }
2.2 链表类
创建一个链表类,命名为 LinkList 并继承 MyList。
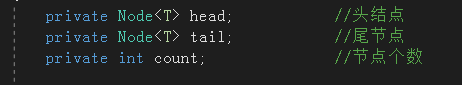
先定义一个头结点,尾节点和一个 count;
其中,head 表示该链表的头部,不包含数据;
tail 表示尾节点,指向该链表最后一个节点,当链表中只有 head 时,tail 指向 head。定义 tail 会方便接下来的操作
count 用来表示该链表中除了 head 以外的节点个数
构造函数:
////// 构造器 /// public LinkList() { head = new Node(); tail = head; count = 0; } 在我们实现成员函数之前,先实现两个特别的方法,因为在许多的成员方法中都要做两个操作:
- 判断索引 index 是否合法,即是否小于0或者大于当前链表的节点个数
- 寻找到 index 所代表的节点
①. 判断索引是否合法,然后可以根据其返回的数值进行判断操作
②. 寻找节点。
定义这两个方法主要是它们的重复使用率高,所以把它们的代码抽出来。
相对于数组,链表的插入与删除更方便,而查找却更加费时,一般都是从头结点开始遍历链表,时间复杂度为 O(n) ,而跳跃链表则会对查询进行优化,当然这会在下一篇中详述。现在继续来实现成员方法。
1. 获取链表长度
这个方法实际上是比较简单的,因为 count 会随着添加,删除等操作自动增减,所以直接返回 count 就相当于 链表长度。
需要注意的是,本文中的 count 是不计算空头结点的,即 head 不会计算入内
2. 清空链表
这里要注意对 tail 的操作,而 head.Next 原本所指的节点不再被引用后,会被GC自动回收
3. 判断链表是否为空
因为本文实现的链表是带空头结点的,所以这里认为,当除了头结点外没有别的节点时,则为空链表
4. 在链表尾部添加节点
在链表尾添加节点一般考虑两种情况:
- 当前除了头结点没有别的节点,此时相当于创建第一个节点
- 寻找到最后一个节点
对于带空头结点的链表来说,这两种情况有着一样的操作,只不过第一种情况要多做一步:让 head 指向新创建的节点
定义了 tail 节点省去了 遍历寻找最后节点的步骤,如果此时是空链表的话,tail 则指向 head
5. 在指定索引的前或后添加节点
这两个方法的思路实际上相差无几的
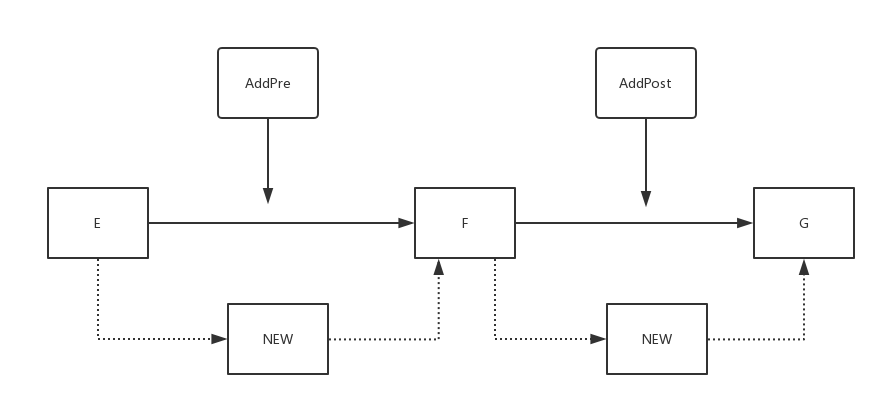
如图,当 index 为 F 时:
- AddPost: ① 找到 F 节点 ②创建 NEW 节点;③ NEW 节点指向 G;④ F 指向 NEW 节点
- AddPre : ① 找到 E 节点 ②创建 NEW 节点;③ NEW 节点指向 F ;④ E 指向 NEW 节点
AddPre 相当于 index - 1 处的 AddPost;AddPost 相当于 index + 1 处的 AddPre(当然,这是在 index -1 与 index + 1 合法的情况下)
6. 两种删除节点方法
- 按索引删除:找到索引所指节点,删除
- 按元素删除:找元素所在的索引;当找不到该元素时表明链表中不存在应该删除的节点,不执行删除操作;当链表中存在多个相同的元素时,找到并删除第一个
两种删除方法操作都是相似的,只是搜索节点的方法不同,删除时要严格注意节点间指向的,即注意书写代码时的顺序
7. 实现下标访问
这是个比较有趣的实现。前文说过对比于数组,链表胜于增减,弱于访问。对链表实现下标式访问,虽然它的内核依然是遍历链表,然后返回节点,但在使用上会方便许多,如同使用数组一般。
8. 根据索引返回元素
这个和 GetNode 方法一致
9. 根据元素返回索引地址
这个方法也是比较简单的,只是需要注意的一点是:while循环条件中 && 号两端的条件不能调换位置。因为如果调换位置后,当链表遍历到最后一个节点仍没找到元素时,pstr 会被赋值下一节点(此时为NULL),然后循环继续执行,执行到 !pstr.Data.Equals(item) 这一句时会报空指针,因为此时 pstr 就是空指针;还有因为这是泛型,所以判断两个值是否相等不能用 == 号,除非你重载 == 号。
10.打印链表
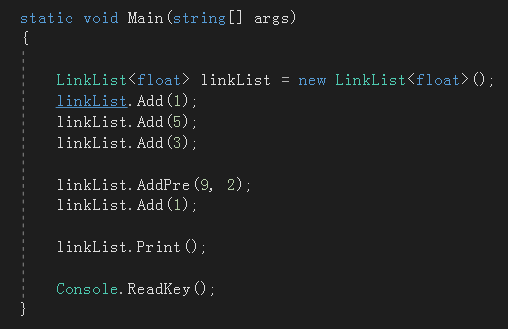
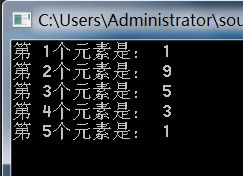
至此,所以的成员方法都实现了,先来测试一下。
1
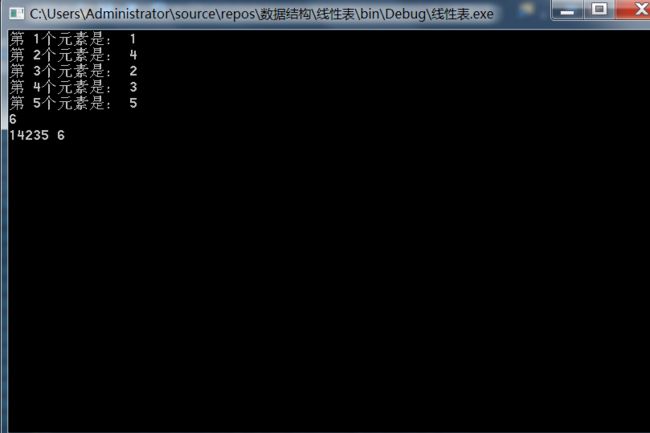
其它功能读者可以自行测试,完整代码:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace 线性表 { class LinkList: MyList { private Node head; //头结点 private Node tail; //尾节点 private int count; //节点个数 /// /// 构造器 /// public LinkList() { head = new Node(); tail = head; count = 0; } /// /// 实现下标访问法 /// /// ///public T this[int index] { get { int i = IsIndexVaild(index); if(i == -1) return default(T); int k = 0; Node pstr = head; while (k++ < index ) { pstr = pstr.Next; } return pstr.Data; } } /// /// 在链表最末端添加新节点 /// /// public void Add(T item) { NodetailNode = new Node (item); tail.Next = tailNode; tail = tailNode; if (count == 0) head.Next = tailNode; count++; } /// /// 在第 index 号元素后插入一个节点 /// /// public void AddPost(T item, int index) { int i = IsIndexVaild(index); if (i == -1) return; //找到索引元素 Node pstr = GetNode(index); //链接新节点 Node node = new Node (item); node.Next = pstr.Next; pstr.Next = node; if (index == count) tail = node; count++; pstr = null; } /// /// 在第 index 号元素前插入一个节点 /// /// /// public void AddPre(T item, int index) { int i = IsIndexVaild(index); if (i == -1) return; //找到索引的前一位元素 Nodepstr = GetNode(index - 1); //链接新节点 Node node = new Node (item); node.Next = pstr.Next; pstr.Next = node; count++; pstr = null; } /// /// 清空链表 /// public void Clear() { head.Next = null; tail = head; } ////// 删除指定位置的元素 /// /// ///public T Delete(int index) { int i = IsIndexVaild(index); if (i == -1) return default(T); //找到索引的前一位元素 Node pstr = GetNode(index - 1); if (pstr.Next == null) return default(T); Node qstr = pstr.Next; pstr.Next = qstr.Next; T t = qstr.Data; pstr = null; qstr.Next = null; qstr = null; count--; return t; } /// /// 按内容删除 /// /// /// ///public T Delete(T item,bool isSecond = true) { int k = GetPos(item); if (k == -1) return default(T); int i = 0; Node pstr = head; while (i++ < k -1) { pstr = pstr.Next; } Node qstr = pstr.Next; pstr.Next = qstr.Next; T t = qstr.Data; pstr = null; qstr.Next = null; qstr = null; count--; return t; } /// /// 返回指定索引的元素 /// /// ///public T GetElem(int index) { int i = IsIndexVaild(index); if (i == -1) return default(T); return GetNode(index).Data; } /// /// 返回链表长度 /// ///public int GetLength() { return count; } /// /// 根据元素返回其索引值 /// /// ///public int GetPos(T item) { int k = 0; Node pstr = head.Next; while (pstr != null && item != null && !pstr.Data.Equals(item)) { pstr = pstr.Next; k++; } if (pstr == null) { Console.WriteLine("所查找元素不存在"); return -1; } return k ; } /// /// 判断链表是否为空 /// ///public bool IsEmpty() { if (head == null || head.Next == null) return true; return false; } /// /// 打印 /// public void Print() { Nodepstr = head.Next; int i = 1; while(pstr != null) { Console.WriteLine("第 " + i++ + "个元素是: " + pstr.Data); pstr = pstr.Next; } } /// /// 判断索引是否错误 /// /// ///public int IsIndexVaild(int index) { //判断索引是否越界 if (index < 0 || index > count) { Console.WriteLine("索引越界,不存在该元素"); return -1; } return 0; } /// /// 根据索引找到元素 /// /// ///public Node GetNode(int index) { int k = 0; Node pstr = head; while (k++ < index) { pstr = pstr.Next; } return pstr; } } }
三. 双向链表
双向链表在思路上和单链表差不多,只是多了一个指向上一个节点的 Prev,所以代码上要更小心地处理。具体就不多赘述了,直接给出代码吧
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace 线性表 { class DBNode{ private T data; private DBNode next; private DBNode prev; public DBNode() { this.data = default(T); this.next = null; this.prev = null; } public DBNode(T value) { this.data = value; this.next = null; this.prev = null; } public DBNode(T value, DBNode next) { this.data = value; this.next = next; this.prev = null; } public T Data { get { return data; } set { data = value; } } public DBNode Next { get { return next; } set { next = value; } } public DBNode Prev { get { return prev; } set { prev = value; } } } }
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace 线性表 { class DBLinkList: MyList { private DBNode head; private DBNode tail; private int count; /// /// 构造器 /// public DBLinkList() { head = new DBNode(); tail = head; count = 0; } /// /// 实现下标访问法 /// /// ///public T this[int index] { get { int i = IsIndexVaild(index); if (i == -1) return default(T); int k = 0; DBNode pstr = head; while (k++ < index) { pstr = pstr.Next; } return pstr.Data; } } /// /// 在链表最末端添加新节点 /// /// public void Add(T item) { if (count == 0) { DBNodeDbNode = new DBNode (item); DbNode.Prev = head; head.Next = DbNode; tail = DbNode; count++; return; } DBNode tailDBNode = new DBNode (item); tailDBNode.Prev = tail; tail.Next = tailDBNode; tail = tailDBNode; count++; } /// /// 在第 index 号元素后插入一个节点,index 为 1,2,3,4..... /// /// /// public void AddPost(T item, int index) { //判断索引是否越界 int i = IsIndexVaild(index); if (i == -1) return; //找到索引元素 DBNodepstr = GetNode(index); //链接新节点 DBNode newNode = new DBNode (item); newNode.Next = pstr.Next; newNode.Prev = pstr; if(pstr.Next != null) pstr.Next.Prev = newNode; pstr.Next = newNode; //如果是在最后节点添加 if (index == count) tail = newNode; count++; pstr = null; } /// /// 在第 index 号元素前插入一个节点,index 为 1,2,3,4..... /// /// /// public void AddPre(T item, int index) { //判断索引是否越界 int i = IsIndexVaild(index); if (i == -1) return; //找到索引的前一位元素 DBNodepstr = GetNode(index - 1); //链接新节点 DBNode newNode = new DBNode (item); newNode.Next = pstr.Next; newNode.Prev = pstr; pstr.Next.Prev = newNode; pstr.Next = newNode; count++; pstr = null; //在 index 处AddPre相当于在 index - 1 处 AddPost,不过并不需要判断尾节点 } /// /// 清空链表 /// public void Clear() { head.Next = null; tail = head; } ////// 删除指定位置的元素 /// /// ///public T Delete(int index) { //判断索引是否越界 int i = IsIndexVaild(index); if (i == -1) return default(T); //找到索引的前一位元素 DBNode pstr = head; int k = 0; while (k++ < index - 1 && pstr != null) { pstr = pstr.Next; } if (pstr.Next == null) return default(T); DBNode qstr = pstr.Next; T t = qstr.Data; pstr.Next = qstr.Next; qstr.Next.Prev = pstr; pstr = null; qstr.Next = null; qstr = null; count--; return t; } /// /// 按内容删除 /// /// /// ///public T Delete(T item,bool isSecond = true) { int k = GetPos(item); if (k == -1) return default(T); int i = 0; DBNode pstr = head; while (i++ < k - 1) { pstr = pstr.Next; } DBNode qstr = pstr.Next; T t = qstr.Data; pstr.Next = qstr.Next; if(qstr.Next != null) qstr.Next.Prev = pstr; pstr = null; qstr.Next = null; qstr = null; count--; return t; } /// /// 返回指定索引的元素 /// /// ///public T GetElem(int index) { int i = IsIndexVaild(index); if (i == -1) return default(T); int k = 0; DBNode pstr = head; while (k++ < index) { pstr = pstr.Next; } return pstr.Data; } /// /// 返回链表长度 /// ///public int GetLength() { return count; } /// /// 根据元素返回其索引值 /// /// ///public int GetPos(T item) { int k = 0; DBNode pstr = head.Next; while (pstr != null && item != null && !pstr.Data.Equals(item)) { pstr = pstr.Next; k++; } if (pstr == null) { Console.WriteLine("所查找元素不存在"); return -1; } return k; } /// /// 判断链表是否为空 /// ///public bool IsEmpty() { if (head == null || head.Next == null) return true; return false; } /// /// 打印 /// public void Print() { DBNodepstr = head.Next; while (pstr != null) { Console.WriteLine(pstr.Data); pstr = pstr.Next; } } /// /// 判断索引是否错误 /// /// ///public int IsIndexVaild(int index) { //判断索引是否越界 if (index < 0 || index > count) { Console.WriteLine("索引越界,不存在该元素"); return -1; } return 0; } /// /// 根据索引找到元素 /// /// ///public DBNode GetNode(int index) { int k = 0; DBNode pstr = head; while (k++ < index) { pstr = pstr.Next; } return pstr; } } }
总结
事实上,链表是一种比较简单且常用的数据结构。实现起来并不困难,只是要小心谨慎。下一篇会说到跳跃链表,跳跃链表的效率更高。好了,希望本文能对大家有所帮助