SIM71004G模块使用Linux C语言实现打电话发短信
为了方便查看博客,特意申请了一个公众号,附上二维码,有兴趣的朋友可以关注,和我一起讨论学习,一起享受技术,一起成长。
一、实验目的:
SIM71004G模块使用Linux C语言实现打电话发短信.
二、实验平台:
迅为itop4412开发板(运行Linux最小系统),SIM7100 4G模块.
三、实验流程
(1)串口编程
串口设置其实就相当于串口通信的协议: 主要是初始化设置。
波特率:是为了两者信号流能同步,;
数据位:是指又几位数据封装成一帧 ;
结束位:是指以帧传输数据时,协定好结束位,便于提取有效数据 ;
奇偶校验:检验数据的一种手段 .
(2)实现代码:
#include (3)编译测试:
将dial.c文件拷贝到ubuntu下,在该目录下使用:
arm-none-linux-gnueabi-gcc -o dial dial.c -static 进行编译,得到编译出来的dial执行文件,使用U盘拷贝到开发板上。
chmod 777 dial :修改权限
./dial :执行
可以得到:
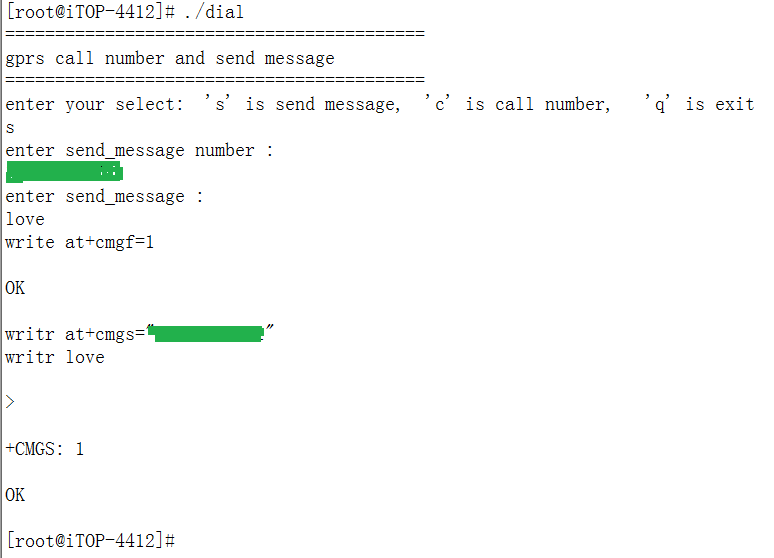
发短信执行成功!!!打电话同样可以实现。
四、感谢
参考:
sim900GPRS使用C语言打电话发短信
