c primer plus 专题14:结构和其他数据形式
1 创建图书目录
#include
#include
char *s_gets(char * st, int n);
#define MAXTITL 41 /* 书名最大长度 + 1 */
#define MAXAUTL 31 /* 作者姓名的最大长度 + 1 */
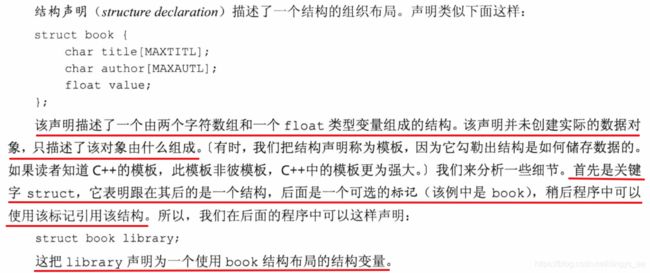
struct book /* 结构模板:标记是 book */
{
char title[MAXTITL];
char author[MAXAUTL];
float value;
}; /* 结构模板结束 */
int main(void)
{
struct book library; /* 把 library 声明为一个 book 类型的变量 */
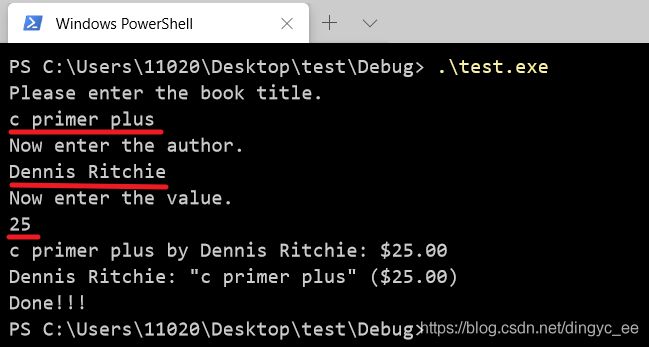
puts("Please enter the book title.");
s_gets(library.title, MAXTITL); /* 访问 title 部分 */
puts("Now enter the author.");
s_gets(library.author, MAXAUTL);
puts("Now enter the value.");
scanf("%f", &library.value);
printf("%s by %s: $%.2f\n", library.title, library.author, library.value);
printf("%s: \"%s\" ($%.2f)\n", library.author, library.title, library.value);
puts("Done!!!");
return 0;
}
char *s_gets(char * st, int n)
{
int i = 0;
char * ret_val;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
while (st[i] != '\n' && st[i] != '\0')
i++;
if (st[i] == '\n')
st[i] = '\0';
else
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
return ret_val;
} 程序执行结果
2 定义结构声明
1 建立结构声明
2 初始化结构
3 访问数组成员
4 结构体的初始化器
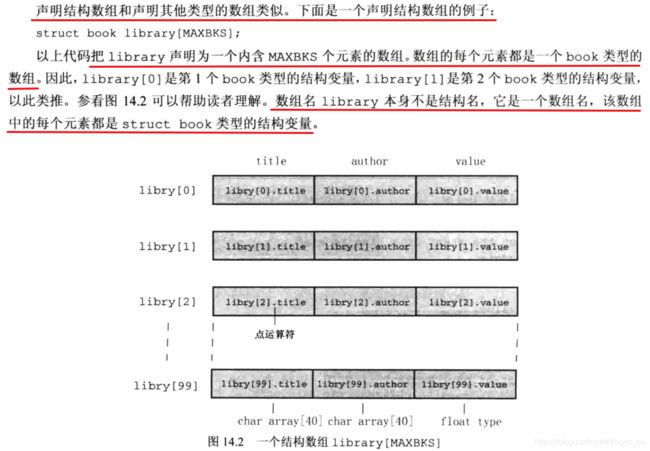
3 结构体数组
#include
#include
#define MAXTITL 40
#define MAXAUTL 30
#define MAXBKS 100
struct book /* 简历 book 模板 */
{
char title[MAXTITL];
char author[MAXAUTL];
float value;
};
int main(void)
{
int i;
char title[MAXTITL];
char author[MAXAUTL];
struct book library[MAXBKS]; /* book 类型结构体数组 */
/* 结构体数组赋值 */
for (i = 0; i < MAXBKS; i++)
{
sprintf(title, "title %d", i);
sprintf(author, "author %d", i);
strncpy(library[i].title, title, MAXTITL);
strncpy(library[i].author, author, MAXAUTL);
library[i].value = i + 0.5f;
}
/* 打印输出 */
for (i = 0; i < MAXBKS; i++)
{
printf("library[%d].title = %s\tlibrary[%d].author = %s\t"
"library[%d].value = %.2f\n", i, library[i].title,
i, library[i].author, i, library[i].value);
}
puts("Done!!!");
return 0;
} 声明结构体数组
4 结构体嵌套
5 指向结构体的指针
#include
#define LEN 20
struct names /* 姓名结构体 */
{
char first[LEN];
char last[LEN];
};
struct guy /* 个人信息结构体 */
{
struct names handle;
char favfood[LEN];
char job[LEN];
float income;
};
int main(void)
{
struct guy fellow[2] = { /* 结构体数组 */
{ { "Even", "Villard" },
"grilled salmon",
"personality coach",
68112.00
},
{ { "Rodney", "Swillbelly" },
"tripe",
"tabloid editor",
432400.00
}
};
struct guy * him; /* 指向结构体的指针 */
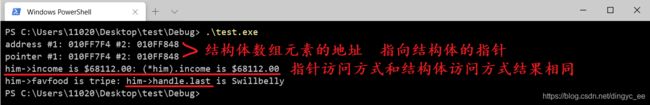
printf("address #1: %p #2: %p\n", &fellow[0], &fellow[1]);
him = &fellow[0]; /* 告诉编译器指针该指向何处 */
printf("pointer #1: %p #2: %p\n", him, him + 1);
printf("him->income is $%.2f: (*him).income is $%.2f\n",
him->income, (*him).income);
him++;
printf("him->favfood is %s: him->handle.last is %s\n",
him->favfood, him->handle.last);
return 0;
} 程序执行结果:
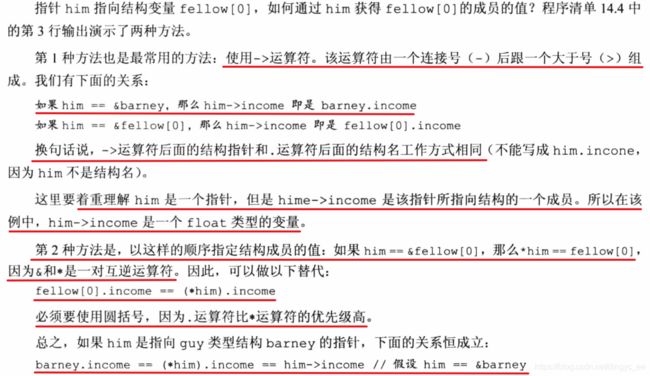
1 声明和初始化结构体指针(和数组不同,结构体名并不是结构体地址)
在有些系统中,一个结构体大小可能大于它各成员大小之和。这是因为系统对数据进行校准的过程中产生了间隔。例如,有些系统把结构体的每个成员放在偶数地址上,或4的倍数地址上。在这种系统中,结构体的内部就存在未使用的空间。
2 用指针访问结构体成员
6 函数与结构体
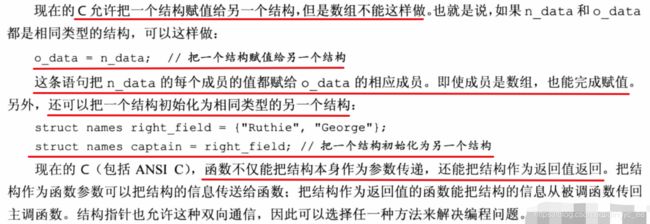
1 结构体允许直接赋值,如下所示
这意味着,我们既可以将结构体本身作为参数传递,也可以传递结构体指针。如何选择?
2 结构体中的字符数组和字符指针
当字符指针没有指向预先设置好的确定地址时,程序可能会出问题。如下所示:
3 结构体、指针和malloc() 函数
如果在结构体中使用字符串指针,一个合理的做法是 malloc() 申请一块内存,将地址传递给字符串指针。
完整的程序如下所示
#include
#include /* 提供 strlen() strcpy() 函数原型 */
#include /* 提供 malloc() free() 函数原型 */
#define SLEN 81
struct namect
{ /* 使用字符串指针 */
char * fname;
char * lname;
int letters;
};
void getinfo(struct namect * pst);
void makeinfo(struct namect * pst);
void showinfo(struct namect * pst);
void cleanup(struct namect * pst);
char *s_gets(char *st, int n);
int main(void)
{
struct namect person;
getinfo(&person);
makeinfo(&person);
showinfo(&person);
cleanup(&person);
return 0;
}
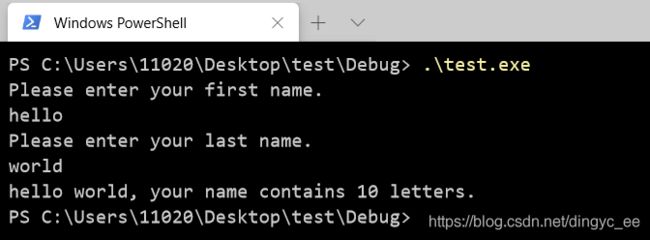
void getinfo(struct namect * pst)
{
char temp[SLEN];
puts("Please enter your first name.");
s_gets(temp, SLEN);
/* 分配刚好容纳字符串大小的内存空间 */
pst->fname = (char *)malloc(strlen(temp) + 1);
/* 将读取到的字符串,从临时数组拷贝至分配的内存 */
strcpy(pst->fname, temp);
puts("Please enter your last name.");
s_gets(temp, SLEN);
pst->lname = (char *)malloc(strlen(temp) + 1);
strcpy(pst->lname, temp);
}
void makeinfo(struct namect * pst)
{
pst->letters = strlen(pst->fname) + strlen(pst->lname);
}
void showinfo(struct namect * pst)
{
printf("%s %s, your name contains %d letters.\n",
pst->fname, pst->lname, pst->letters);
}
void cleanup(struct namect * pst)
{
free(pst->fname); /* 释放动态内存 */
free(pst->lname);
}
char *s_gets(char *st, int n)
{
char * find;
char * ret_val;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n'); /* 查找换行符 */
if (find) /* 如果地址不是NULL */
*find = '\0'; /* 在此处放置一个空字符 */
else
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue; /* 清除缓冲区 */
}
return ret_val;
} 程序执行结果
4 使用结构体数组的函数
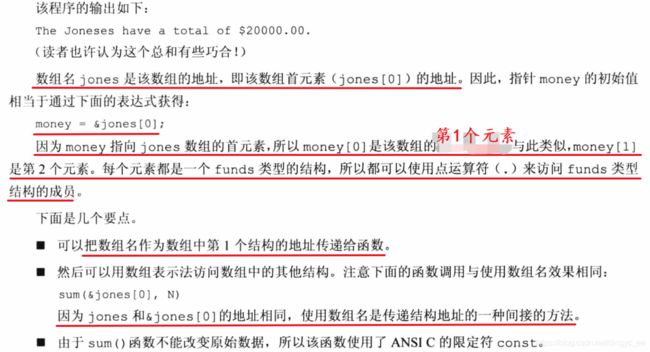
假设一个函数要处理一个结构体数组。由于数组名就是该数组的地址,所以可以把它传递给函数。
#include
#define FUNDLEN 50
#define N 2
struct funds {
char bank[FUNDLEN];
double bankfund;
char save[FUNDLEN];
double savefund;
};
double sum(const struct funds * money, int n);
int main(void)
{
struct funds jones[N] = {
{
"Garlic-Melon bank",
4032.27,
"Lucky's Saving and Loan",
8543.94
},
{
"Honest Jack's bank",
3620.88,
"Party Time Savings",
3802.91
}
};
printf("The joneses have a total of %.2f.\n", sum(jones, N));
return 0;
}
double sum(const struct funds * money, int n)
{
int i;
double total = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// total += money[i].bankfund + money[i].savefund; /* 数组表示 */
total += (*(money + i)).bankfund + (*(money + i)).savefund; /* 指针表示 */
}
return total;
} 7 联合简介 union
当多个数据需要共享内存或者多个数据每次只取其一时,可以利用联合体(union)。
使用 联合体 union
使用 联合体 union 的一个有用的做法:用一个成员把值存储在一个联合中,然后用另一个成员查看内容。这种方式非常重要,在各种通信协议(如 MQTT)中非常流行。
8 枚举类型 enum
1 enum 类型的本质:
2 使用 enum 的很精妙的程序
9 typedef
1 typedef 简介
2 typedef 其他用处
2.1 声明指针
2.2 typedef 定义结构体
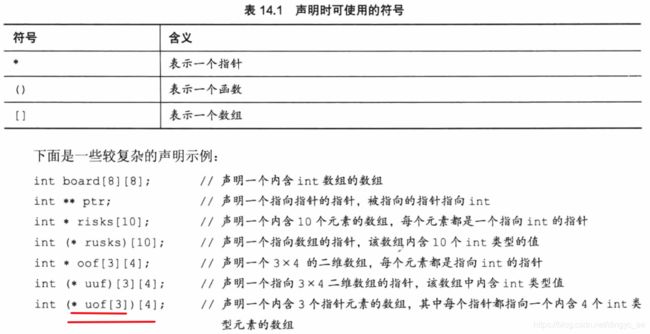
10 复杂类型声明
1 数组和指针
2 函数和指针(重点理解!!!)
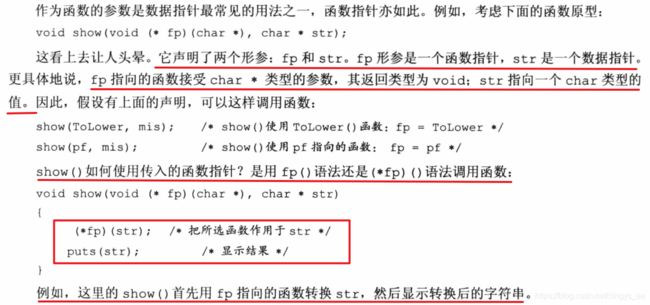
11 函数指针
1 函数指针有什么用?
2 从函数到函数指针
3 函数地址赋值给函数指针
4 通过函数指针,来进行函数调用
5 函数调用函数指针(回调函数)
下面是使用函数指针的实例:
/* func_ptr.c -- 函数指针 */
#include
#include
#include /* 提供 toupper() tolower() isupper() 等函数原型 */
#define LEN 81
char showmenu(void);
void eatline(void); /* 读取至行末尾 */
void ToUpper(char * str); /* 把字符串转换为大写 */
void ToLower(char * str); /* 把字符串转换为小写 */
void Transpose(char * str); /* 大小写转置 */
void Dummy(char * str); /* 不改变字符串 */
void show(void(*fp)(char *), char * str);
char * s_gets(char * st, int n);
int main(void)
{
char line[LEN];
char copy[LEN];
char choice;
void(*pfun)(char *); /* 声明函数指针 */
pfun = NULL; /* 缺少这行,编译器可能会报错 */
puts("Enter a string (empty line to quit):");
while (s_gets(line, LEN) != NULL && line[0] != '\0')
{
while ((choice = showmenu()) != '\n')
{
switch (choice)
{
case 'u': pfun = ToUpper; break;
case 'l': pfun = ToLower; break;
case 't': pfun = Transpose; break;
case 'o': pfun = Dummy; break;
default: break;
}
strcpy(copy, line); /* 为 show() 函数拷贝一份 */
show(pfun, copy);
}
puts("Enter a string (empty line to quit):");
}
puts("Bye!!!");
return 0;
}
char showmenu(void)
{
char ans;
puts("Enter menu choice:");
puts("u) uppercase l) lowercase");
puts("t) transposed case o) original case");
puts("n) next string");
ans = getchar(); /* 获取用户输入 */
ans = tolower(ans); /* 转换为小写 */
eatline(); /* 清除缓冲区 */
while (strchr("ulton", ans) == NULL)
{
puts("Please enter a u, l, t, o, or a n:");
ans = tolower(getchar());
eatline();
}
return ans;
}
void eatline(void)
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
void ToUpper(char * str)
{
while (*str)
{
*str = toupper(*str);
str++;
}
}
void ToLower(char * str)
{
while (*str)
{
*str = tolower(*str);
str++;
}
}
void Transpose(char * str)
{
while (*str)
{
if (isupper(*str))
*str = tolower(*str);
else if (islower(*str))
*str = toupper(*str);
str++;
}
}
void Dummy(char * str)
{
/* 空函数体,不改变字符串 */
}
void show(void(*fp)(char *), char * str)
{
fp(str); /* 把用户选定的函数作用于 str */
puts(str); /* 显示结果 */
}
char * s_gets(char * st, int n)
{
char * find, *ret_val;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n');
if (find)
*find = '\0';
else
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
return ret_val;
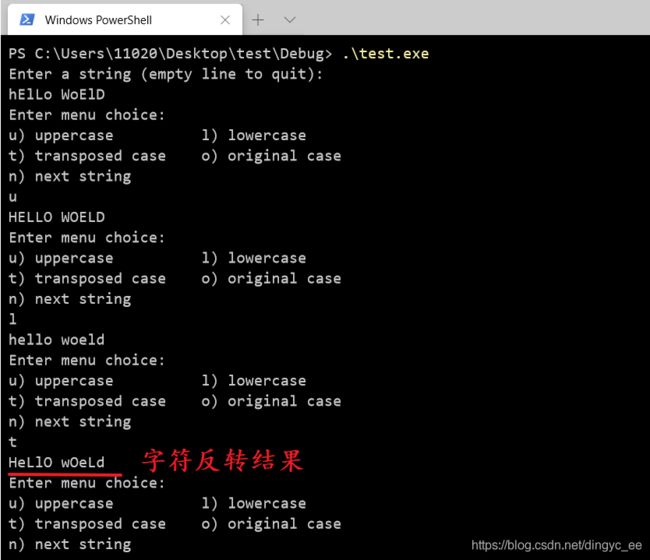
} 程序执行结果
程序改进:
使用 typedef 定义函数指针,作为回调函数的参数传递,如下所示: