c primer plus 专题17:高级数据表示
1 从数组到链表
1 从结构体延申至链表(linked list)
2 从概念上理解链表
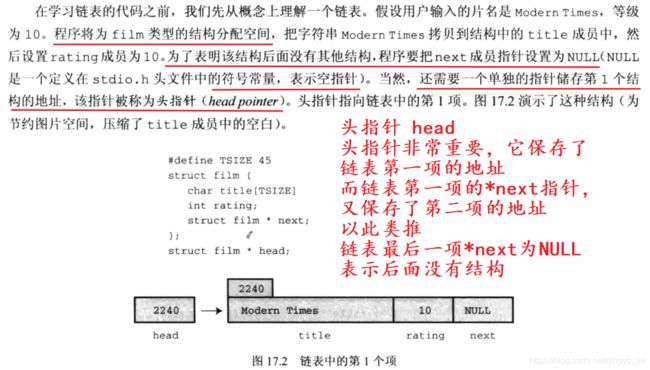
链表的头指针,保存了链表第一项的地址,即头指针指向了链表第一项。
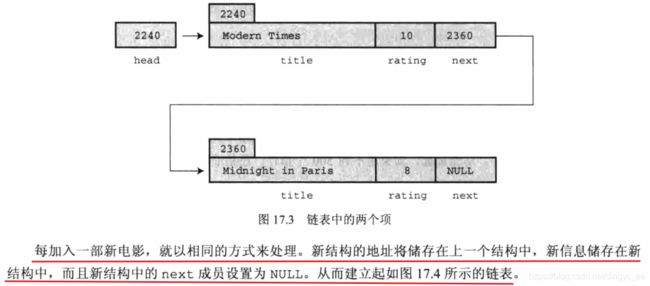
添加链表项
2 使用链表
#include
#include /* 提供 malloc() 函数原型 */
#include
char * s_gets(char * st, int n);
#define TSIZE 45
struct film {
char title[TSIZE];
int rating;
struct film * next; /* 指向链表的下一个结构体 */
};
int main(void)
{
struct film * head = NULL; /* 头指针 */
struct film * tail = NULL; /* 尾指针 */
struct film *current = NULL;
char input[TSIZE];
/* 收集并存储信息 */
puts("Enter first movie title:");
while (s_gets(input, TSIZE) != NULL && input[0] != '\0')
{
current = (struct film *)malloc(sizeof(struct film)); /* 为新结构体申请内存 */
if (head == NULL) /* 链表的第一个结构体 */
head = current;
else
tail->next = current; /* 让链表的尾指针记录当前项的地址 */
current->next = NULL; /* 当前新增的链表项 *next 指向NULL */
strcpy(current->title, input);
puts("Enter your rating <0 - 10> :");
scanf("%d", ¤t->rating);
while (getchar() != '\n') /* 清除缓冲区 */
continue;
puts("Enter next movie title (empty line to quit) :");
tail = current; /* 当前项设置为链表的尾指针 */
}
/* 显示电影链表 */
if (head == NULL)
puts("No data entered!");
else
puts("Here is the movie list:");
current = head; /* 除释放内存外,要保持 head 头指针不能变,否则找不到链表 */
while (current != NULL)
{
printf("Movie: %s Rating: %d\n", current->title, current->rating);
current = current->next;
}
/* 完成任务,释放链表所有结构体的内存 */
puts("\nReady to free memory...");
current = head;
while (head != NULL) /* 从头指针开始,逐项往下释放内存 */
{
current = head;
head = head->next;
free(current);
}
puts("All done!");
return 0;
}
char * s_gets(char * st, int n)
{
char * find;
char * ret_val;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n');
if (find)
*find = '\0';
else
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
return ret_val;
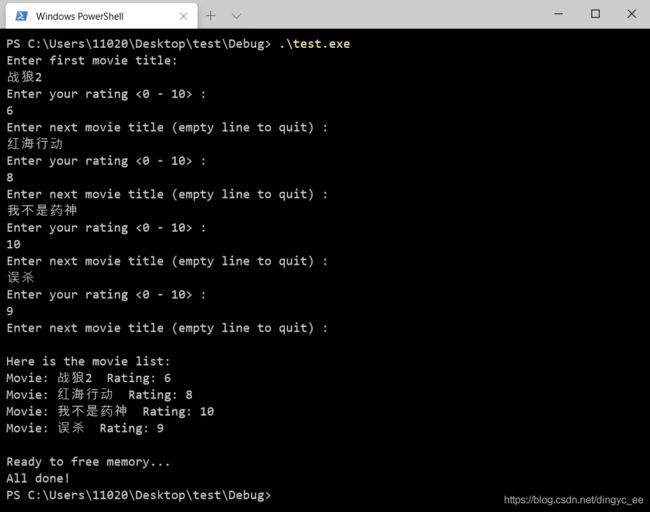
} 程序执行结果
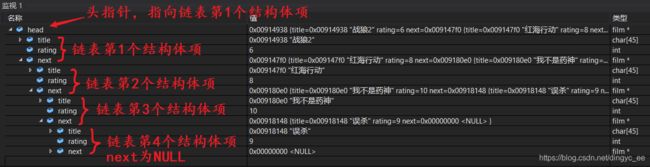
链表的状态:
程序分析:
1 显示链表
为什么不直接使用 head 指针遍历?
2 创建链表
3 释放链表
3 抽象数据类型
1 建立抽象
2 建立接口
描述链表的接口
3 使用接口
list.h
/* list.h -- 简单链表类型的头文件 */
#ifndef __LIST_H
#define __LIST_H
#include
/* 特定程序的说明 */
#define TSIZE 45 /* 存储数组电影名的数组大小 */
struct film {
char title[TSIZE];
int rating;
};
/* 一般类型定义 */
typedef struct film Item; /* 节点数据域 */
struct node {
Item item;
struct node * next; /* 节点结构体 */
};
typedef struct node Node;
typedef Node * List;
/* 函数原型 */
/* 操作: 初始化一个链表 */
/* 前提条件: plist 指向一个链表 */
/* 后置条件: 该链表初始化为空 */
void InitializeList(List * plist);
/* 操作: 确定链表是否为空定义,plist 指向一个已初始化的链表 */
/* 后置条件: 如果链表为空,该函数返回 true;否则返回 false */
bool ListIsEmpty(const List * plist);
/* 操作: 确定链表是否已满,plist 指向一个已初始化的链表 */
/* 后置条件: 如果链表已满,该函数返回 true;否则返回 false */
bool ListIsFull(const List * plist);
/* 操作: 确定链表中的项数,plist 指向一个已初始化的链表 */
/* 后置条件: 该函数返回链表的项数 */
unsigned int ListItemCount(const List * plist);
/* 操作: 在链表的末尾添加项 */
/* 前提条件: Item 是一个待添加至链表的项,plist 指向一个已初始化的链表 */
/* 后置条件: 如果可以,该函数在链表末尾添加一个项,且返回 true;否则返回 false */
bool AddItem(Item item, List * plist);
/* 操作: 把函数作用与链表的每一个项 */
/* plist 指向一个已初始化的链表 */
/* pfun 指向一个函数,该函数接受一个 Item 类型的参数,且无返回值 */
/* 后置条件: pfun 指向的函数作用于链表中的每一项一次 */
void Traverse(const List * plist, void(*pfun)(Item item));
/* 操作: 释放已分配的内存(如果有的话) */
/* plist 指向一个已初始化的链表 */
/* 后置条件: 释放了为链表分配的所有内存,链表设置为空 */
void EmptyTheList(List * plist);
#endif /* __LIST_H */
main.c
#include
#include /* 提供 exit() 函数原型 */
#include
#include "list.h"
void showmovies(Item item);
char * s_gets(char * st, int n);
int main(void)
{
List movies;
Item temp;
/* 初始化链表 */
InitializeList(&movies);
if (ListIsFull(&movies))
{
fprintf(stderr, "No memory avaliable, Bye!\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
/* 获取用户输入并存储 */
puts("Enter first movie title:");
while (s_gets(temp.title, TSIZE) != NULL && temp.title[0] != '\0')
{
puts("Enter your rating <0 - 10> :");
scanf("%d", &temp.rating); /* 读取输入完成,清空缓冲区 */
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
if (AddItem(temp, &movies) != true)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Problem allocating memory!\n");
break;
}
if (ListIsFull(&movies))
{
puts("The list is now full");
break;
}
puts("Enter next movie title (empty line to quit) :");
}
/* 显示 */
if (ListIsEmpty(&movies))
puts("No data entered.");
else
{
puts("Here is the movie list:");
Traverse(&movies, showmovies); /* 调用回调函数打印链表 */
}
printf("You entered %d movies.\n", ListItemCount(&movies));
/* 释放内存 */
EmptyTheList(&movies);
puts("All done.");
return 0;
}
void showmovies(Item item)
{
printf("Movie: %s Rating: %d\n", item.title, item.rating);
}
char * s_gets(char * st, int n)
{
char * find;
char * ret_val;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n');
if (find)
*find = '\0';
else
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
return ret_val;
} 4 实现接口
list.c
#include
#include
#include "list.h"
static void CopyToNode(Item item, Node * node);
void InitializeList(List * plist)
{
*plist = NULL;
}
bool ListIsEmpty(const List * plist)
{
if (*plist == NULL)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool ListIsFull(const List * plist)
{
Node * pt;
bool full;
pt = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (pt == NULL)
full = true;
else
full = false;
free(pt);
return full;
}
unsigned int ListItemCount(const List * plist)
{
unsigned int count = 0;
Node * pnode = *plist; /* 设置链表的开始 */
while (pnode != NULL)
{
count++;
pnode = pnode->next; /* 设置下一个节点 */
}
return count;
}
bool AddItem(Item item, List * plist)
{
Node * pnew;
Node * scan = *plist;
pnew = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node)); /* 为新节点分配内存 */
if (pnew == NULL)
return false;
CopyToNode(item, pnew); /* 新节点拷贝至新内存 */
pnew->next = NULL;
if (scan == NULL) /* 空链表,所以把 */
*plist = pnew; /* pnew 放在链表的开头 */
else
{
while (scan->next != NULL) /* 找到链表的尾节点 */
scan = scan->next;
scan->next = pnew;
}
return true;
}
void Traverse(const List * plist, void(*pfun)(Item item))
{
Node * pnode = *plist; /* 其实是找到头指针 */
while (pnode != NULL)
{
pfun(pnode->item); /* 把函数应用于链表中的项 */
pnode = pnode->next;
}
}
void EmptyTheList(List * plist)
{
Node * phead = *plist;
Node * pnode;
while (phead != NULL)
{
pnode = phead;
phead = phead->next;
free(pnode);
}
}
static void CopyToNode(Item item, Node * node)
{
node->item = item; /* 拷贝结构体 */
} 4 队列
指针的关键点:头指针和头节点。使用头节点,能方便链表的操作。
1 定义队列抽象数据类型
2 定义接口
3 实现接口数据表示
队列的尾部插入操作
bool EnQueue(Item item, Queue * pq)
{
Node * pnew; // 创建节点指针,malloc内存,然后将数据项拷贝至内存
if (QueueIsFull(pq)) // 队列已满
return false;
pnew = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node)); // 申请内存
if (pnew == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Unable to allocate memory!\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
CopyToNode(item, pnew); // 拷贝节点数据项至内存
pnew->next = NULL;
if (QueueIsEmpty(pq)) // 如果队列为空,则设为队列头
pq->front = pnew;
else // 队列不为空,则添加至当前队列尾的尾部
pq->rear->next = pnew;
pq->rear = pnew; // 重新设置队列尾
pq->count++; // 队列计数 + 1
return true;
}队列的头部删除操作
bool DeQueue(Item * pitem, Queue * pq)
{
Node * pt;
if (QueueIsEmpty(pq))
return false;
CopyToItem(pq->front, pitem); // 队列头部链表项,拷贝至
pt = pq->front; // 获取要删除的链表项
pq->front = pt->next; // 队列头指向下一个链表项
free(pt);
pq->count--;
if (pq->count == 0)
pq->rear = NULL;
return true;
}队列实现如下
queue.h
#ifndef __QUEUE_H
#define __QUEUE_H
#include
#define MAX_QUEUE 10 /* 队列最大长度 */
typedef int Item;
struct node
{
Item item;
struct node *next;
};
typedef struct node Node;
struct queue
{
Node * front; // 指向队列头的指针
Node * rear; // 指向队列尾的指针
int count; // 队列中的项数
};
typedef struct queue Queue;
// 初始化队列
void InitializeQueue(Queue * pq);
// 检查队列是否已满
bool QueueIsFull(const Queue * pq);
// 检查队列是否为空
bool QueueIsEmpty(const Queue * pq);
// 确定队列中的项数
int QueueItemCount(const Queue * pq);
// 在队列末尾插入项
bool EnQueue(Item item, Queue * pq);
// 从队列开头删除项
bool DeQueue(Item * pitem, Queue * pq);
// 清空队列
void EmptyTheQueue(Queue * pq);
#endif /* __QUEUE_H */ queue.c
#include
#include
#include "queue.h"
static void CopyToNode(Item item, Node * pnode);
static void CopyToItem(Node * pnode, Item * pitem);
void InitializeQueue(Queue * pq)
{
pq->front = NULL;
pq->rear = NULL;
pq->count = 0;
}
bool QueueIsFull(const Queue * pq)
{
return pq->count == MAX_QUEUE;
}
bool QueueIsEmpty(const Queue * pq)
{
return pq->count == 0;
}
int QueueItemCount(const Queue * pq)
{
return pq->count;
}
bool EnQueue(Item item, Queue * pq)
{
Node * pnew; // 创建节点指针,malloc内存,然后将数据项拷贝至内存
if (QueueIsFull(pq)) // 队列已满
return false;
pnew = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node)); // 申请内存
if (pnew == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Unable to allocate memory!\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
CopyToNode(item, pnew); // 拷贝节点数据项至内存
pnew->next = NULL;
if (QueueIsEmpty(pq)) // 如果队列为空,则设为队列头
pq->front = pnew;
else // 队列不为空,则添加至当前队列尾的尾部
pq->rear->next = pnew;
pq->rear = pnew; // 重新设置队列尾
pq->count++; // 队列计数 + 1
return true;
}
bool DeQueue(Item * pitem, Queue * pq)
{
Node * pt;
if (QueueIsEmpty(pq))
return false;
CopyToItem(pq->front, pitem); // 拷贝数据
pt = pq->front; // 获取要删除的链表项
pq->front = pt->next; // 队列头指向下一个链表项
free(pt);
pq->count--;
if (pq->count == 0)
pq->rear = NULL;
return true;
}
// 通过循环调用队列头部删除函数来实现
void EmptyTheQueue(Queue * pq)
{
Item temp;
while (!QueueIsEmpty(pq))
DeQueue(&temp, pq);
}
static void CopyToNode(Item item, Node * pnode)
{
pnode->item = item;
}
static void CopyToItem(Node * pnode, Item * pitem)
{
*pitem = pnode->item;
} 测试队列功能的驱动程序:
#include
#include "queue/queue.h"
int main(void)
{
Queue line; // 创建队列
Item temp;
int ch;
InitializeQueue(&line);
puts("Test the queue interface. Type a to add a value,");
puts("Type d to delete a value, and type q to quit.");
while ((ch = getchar()) != 'q')
{
if (ch != 'a' && ch != 'd') // 忽略其他输出
continue;
if (ch == 'a')
{
puts("Integer to add:");
scanf("%d", &temp);
if (QueueIsFull(&line))
puts("The queue is full!");
else
{
printf("Putting %d into queue.\n", temp);
EnQueue(temp, &line);
}
}
else
{
if (QueueIsEmpty(&line))
puts("The queue is empty!");
else
{
DeQueue(&temp, &line);
printf("Removing %d from queue.\n", temp);
}
}
printf("%d items in queue\n", QueueItemCount(&line));
puts("a to add, d to delete, q to quit");
}
puts("Now free the queue...");
EmptyTheQueue(&line);
puts("All done!");
return 0;
} 程序执行结果如下
1 数据进入队列
2 队列读出数据