黑客攻击-木马免杀之PE文件
当你好不容易弄出来一个木马(具体可参考这里)的时候,却被杀毒软件轻易的就检测出来了,那一切岂不是白费了。Win10中的windows defender基于流量检测很容易把常见的木马程序检测出来,那怎么绕过这些检测?
对于此问题,打算开一个专题进行木马免杀的分析,先从最最重要的PE文件说起,要攻击Windows系统,如果不懂PE文件,面对杀毒软件,则只能束手就擒了。
PE文件
PE(Portable Execute)文件是Windows下可执行文件的总称,常见的有DLL,EXE,OCX,SYS等,事实上,一个文件是否是PE文件与其扩展名无关,PE文件可以是任何扩展名
PE全称是Portable Execute,实际上,这种文件格式没有做到Portable Execute,只能用在Windwos。
基本结构
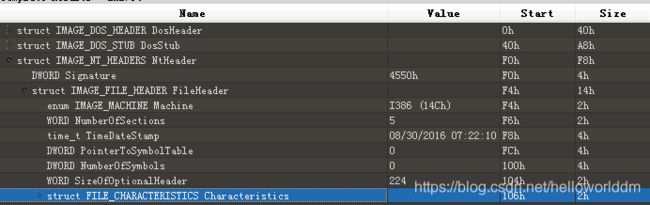
32位PE的基本结构如下,64位的大同小异。
 如下是qq的16进制打开后解析出相应的字段,和上图是匹配的。
如下是qq的16进制打开后解析出相应的字段,和上图是匹配的。
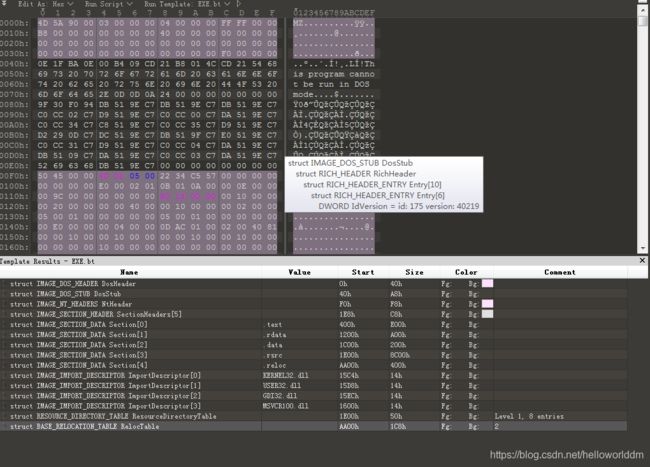
Dos文件头和Dos块
typedef struct _IMAGE_DOS_HEADER { // DOS .EXE header
WORD e_magic; // Magic number
WORD e_cblp; // Bytes on last page of file
WORD e_cp; // Pages in file
WORD e_crlc; // Relocations
WORD e_cparhdr; // Size of header in paragraphs
WORD e_minalloc; // Minimum extra paragraphs needed
WORD e_maxalloc; // Maximum extra paragraphs needed
WORD e_ss; // Initial (relative) SS value
WORD e_sp; // Initial SP value
WORD e_csum; // Checksum
WORD e_ip; // Initial IP value
WORD e_cs; // Initial (relative) CS value
WORD e_lfarlc; // File address of relocation table
WORD e_ovno; // Overlay number
WORD e_res[4]; // Reserved words
WORD e_oemid; // OEM identifier (for e_oeminfo)
WORD e_oeminfo; // OEM information; e_oemid specific
WORD e_res2[10]; // Reserved words
LONG e_lfanew; // File address of new exe header
} IMAGE_DOS_HEADER, *PIMAGE_DOS_HEADER;
对于PE文件来说,有用的是最后一个字段,这个字段指出了真正的PE头在文件中的位置。

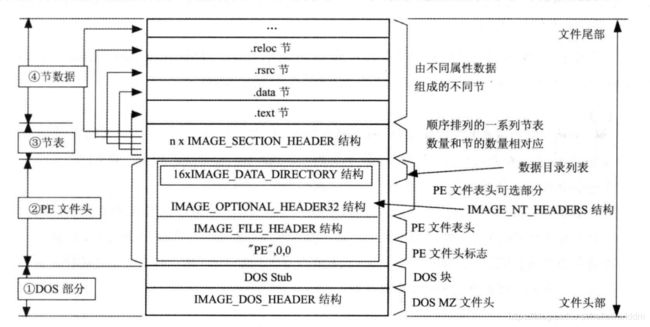
PE文件头
typedef struct _IMAGE_NT_HEADERS {
DWORD Signature;
IMAGE_FILE_HEADER FileHeader;
IMAGE_OPTIONAL_HEADER32 OptionalHeader;
} IMAGE_NT_HEADERS32, *PIMAGE_NT_HEADERS32;
Signature是00004550h,也就是字符’P’和’E’。对于OptionalHeader尽管按照字面的理解是可选的,实际上在每一个PE文件中都是需要的。
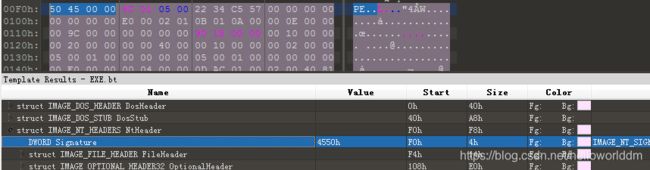 每个结构体的具体信息如下:
每个结构体的具体信息如下:
- AddressOfEntryPoint指出文件被执行时的入口地址,这个地址是RVA(稍后会介绍)。如果像在程序运行前执行一段程序,那么可以把这个入口地址指向你想执行的程序。
- ImageBase指出文件优先载入的地址,一般exe默认优先装入的地址是400000h,而dll是10000000h
- SectionAlignment指定了节被装入内存后的对齐单位,FileAlignment指定了节存储在磁盘文件时的对齐单位
- DataDirectory
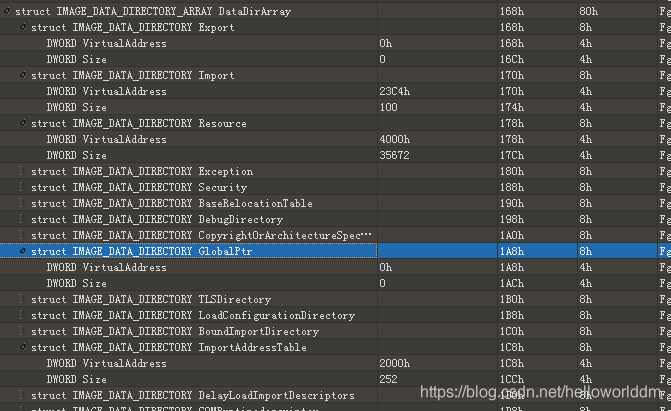 很重要的结构,由16个相同的IMAGE_DATA_DIRECTORY结构组成。其中有导入表、导出表、资源表数据块。
很重要的结构,由16个相同的IMAGE_DATA_DIRECTORY结构组成。其中有导入表、导出表、资源表数据块。
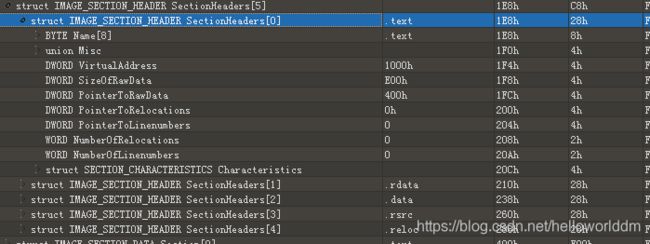
节表和节
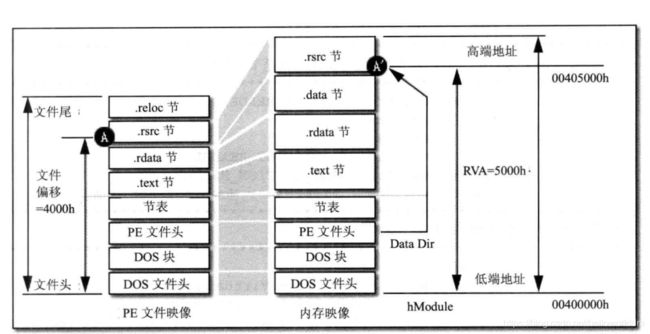
Windows装载器在装载DOS部分,PE文件头部分和节表头部分不进行任何处理,而装载节的时候根据节的属性做不同的处理。下图展示了PE文件到内存的映射。
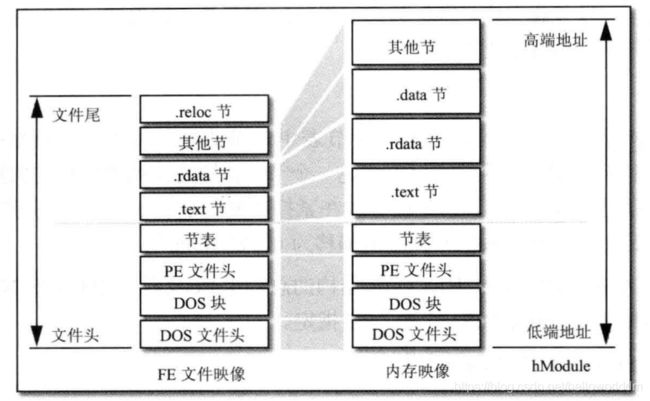
- VirtualAddress指出节被装载到内存后的偏移位置
- PointerToRawData指出节在磁盘文件中所处的位置
RVA和文件偏移的转换
RVA应该时PE文件相关最重要的概念了,导入表导出表等的定位都需要用到RVA。
msf中巧妙调用ReflectiveLoader
在msf中,反射dll注入使用的非常普遍。这段代码后续会详细讲解,这是msf远程控制最核心的一段代码,“小马”(stager)拉"大马"(stage)得以实现,基于的就是这段代码。
def asm_invoke_dll(opts={})
asm = %Q^
; prologue
dec ebp ; 'M'
pop edx ; 'Z'
call $+5 ; call next instruction
pop ebx ; get the current location (+7 bytes)
push edx ; restore edx
inc ebp ; restore ebp
push ebp ; save ebp for later
mov ebp, esp ; set up a new stack frame
; Invoke ReflectiveLoader()
; add the offset to ReflectiveLoader() (0x????????)
add ebx, #{"0x%.8x" % (opts[:rdi_offset] - 7)}
call ebx ; invoke ReflectiveLoader()
; Invoke DllMain(hInstance, DLL_METASPLOIT_ATTACH, config_ptr)
push edi ; push the socket handle
push 4 ; indicate that we have attached
push eax ; push some arbitrary value for hInstance
mov ebx, eax ; save DllMain for another call
call ebx ; call DllMain(hInstance, DLL_METASPLOIT_ATTACH, socket)
; Invoke DllMain(hInstance, DLL_METASPLOIT_DETACH, exitfunk)
; push the exitfunk value onto the stack
push #{"0x%.8x" % Msf::Payload::Windows.exit_types[opts[:exitfunk]]}
push 5 ; indicate that we have detached
push eax ; push some arbitrary value for hInstance
call ebx ; call DllMain(hInstance, DLL_METASPLOIT_DETACH, exitfunk)
^
end
其中 add ebx, #{"0x%.8x" % (opts[:rdi_offset] - 7)} 用来获取ReflectiveLoader的虚拟地址。rdi_offset获取的是ReflectiveLoader的RVA地址。这段代码翻译过来就是ebx-7 = 基址,然后再加上RVA就得到了ReflectiveLoader的虚拟地址。