不会真的学不会kotlin吧?(四)高阶函数
本文是根据慕课网kotlin相关课程本人笔记和个人理解所作
代码部分参考慕课网新kotlin入门课程
文章目录
- 本章简介
- 结构导图
- 高阶函数
- 参数包含函数或者返回函数类型
- 内联函数
- inline
- 常见高阶函数
- let run alse apply use
- 集合变换及序列
- 变化及聚合
- SAM转换
- SAM转换对比
- 正确的添加删除SAM
- Demo
本章简介
这一章主要是kotlin的高阶函数,主要对let,also的使用和内联函数的定义了解
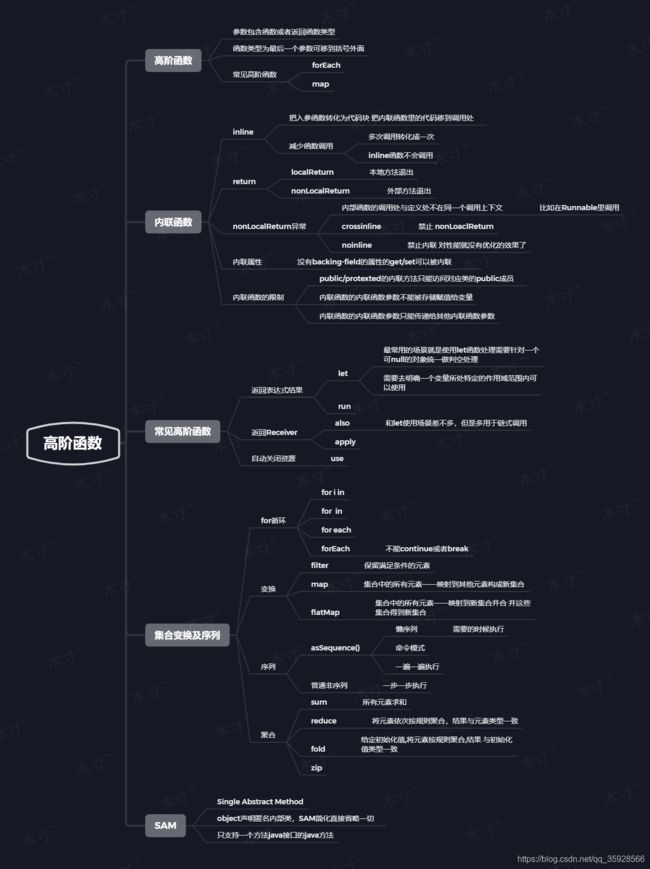
结构导图
高阶函数
参数包含函数或者返回函数类型
kotlin
fun main() {
cost {
val fibonacciNext = fibonacci()
for (i in 0..10) {
println(fibonacciNext())
}
}
// region +折叠
val intArray = IntArray(5){ it + 1 }
intArray.forEach {
println(it)
}
intArray.forEach(::println)
intArray.forEach {
println("Hello $it")
}
//endregion
}
//region +折叠
fun needsFunction(block: () -> Unit) {
block()
}
fun returnsFunction(): () -> Long {
return { System.currentTimeMillis() }
}
//endregion
fun cost(block: () -> Unit) {
val start = System.currentTimeMillis()
block()
println("${System.currentTimeMillis() - start}ms")
}
fun fibonacci(): () -> Long {
var first = 0L
var second = 1L
return {
val next = first + second
val current = first
first = second
second = next
current
}
}
内联函数
inline
kotlin
fun main() {
//region local return
val ints = intArrayOf(1, 2, 3, 4)
ints.forEach {
if(it == 3) return@forEach
println("Hello $it")
}
for (element in ints) {
if(element == 3) continue
println("Hello $element")
}
//endregion
//region non-local return
nonLocalReturn {
//return
}
Runnable {
println("xxx")
println("yyy")
}
//endregion
//region cost
cost {
println("Hello")
}
//endregion
//region inline property
money = 5.0
//endregion
}
inline fun Runnable(noinline block: () -> Unit): Runnable {
return object : Runnable {
override fun run() {
block()
}
}
}
public inline fun IntArray.forEach(crossinline action: (Int) -> Unit): Unit {
for (element in this) action(element)
}
inline fun nonLocalReturn(block: () -> Unit){
block()
}
inline fun hello(){
println("Hello")
}
inline fun cost(block: () -> Unit) {
val start = System.currentTimeMillis()
block()
println(System.currentTimeMillis() - start)
}
var pocket: Double = 0.0
var money: Double
inline get() = pocket
inline set(value) {
pocket = value
}
常见高阶函数
let run alse apply use
| 函数名 | 介绍 | 推荐指数 |
|---|---|---|
| let | val r=X.let{x->R} | 3 |
| run | val r=X.run{this:X->R} | 1 |
| also | val x=X.also{x->Unit} | 3 |
| apply | val x=X.apply{this:X->Unit} | 1 |
| use | val r=Closeable.use{c->R} | 3 |
kotlin
fun main() {
val person = Person("benny", 20)
person.let(::println)
person.run(::println)
val person2 = person.also {
it.name = "hhh"
}
val person3 = person.apply {
name = "xxx"
}
File("build.gradle").inputStream().reader().buffered()
.use {
println(it.readLines())
}
}
集合变换及序列
变化及聚合
| 函数名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| filter | 保留满足条件的元素 |
| map | 集合中的所有元素一一映射到其他元素构成新集合 |
| flatMap | 集合中的所有元素一一映射到新集合并合 并这些集合得到新集合 |
| 函数名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| sum | 所有元素求和 |
| reduce | 将元素依次按规则聚合,结果与元素类型一致 |
| fold | 给定初始化值,将元素按规则聚合,结果 与初始化值类型一致 |
kotlin
fun main() {
val list = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4)
//region sequence
list.asSequence()
.filter {
println("filter: $it")
it % 2 == 0
}.map {
println("map: $it")
it * 2 + 1
}.forEach {
println("forEach: $it")
}
//rxjava
//endregion
list.asSequence()
.flatMap {
(0 until it).asSequence()
}
.joinToString().let(::println)
//rxjava
region
for (i in 0..10) {
println(i)
}
for (e in list) {
println(e)
}
var i = 0
while (i++ < 10) {
println(i)
}
do {
println("Hello")
} while (false)
//endregion
//region for each
list.forEach {
if (it == 2) {
return@forEach
}
println(it)
}
list.forEach {
if (it == 2) return@forEach
println(it)
}
//region
val newList = list.flatMap {
ArrayList<String>(it)
}
list.filter { it % 2 == 0 }
list.asSequence()
.filter { it % 2 == 0 }
list.asSequence()
.map { it * 2 + 1 }
list.asSequence()
.flatMap {
(0 until it).asSequence()
}
.joinToString().let(::println)
list.fold(StringBuilder()) { acc, i ->
acc.append(i)
}
list.asSequence()
.filter {
it % 2 == 0
}.map {
it * 2 + 1
}.flatMap {
(0 until it).asSequence()
}.forEach(::println)
endregion
}
SAM转换
SAM转换对比
| Java | Kotlin | |
|---|---|---|
| Java接口 | 支持 | 支持 |
| Kotlin接口 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| Java方法 | 支持 | 支持 |
| Kotlin函数(方法) | 支持 | 不支持 |
| 抽象类 | 不支持 | 不支持 |
kotlin
fun main() {
val executor: ExecutorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor()
executor.submit(object : Runnable {
override fun run() {
println("run in executor.")
}
})
executor.submit(Runnable {
println("run in executor.")
})
executor.submit { println("run in executor.") }
println("run in main thread.")
submitRunnable {
println("Hello")
}
submit { }
}
fun Runnable(block: () -> Unit): Runnable {
return object : Runnable {
override fun run() {
block()
}
}
}
fun submitRunnable(runnable: Runnable){
runnable.run()
}
fun submit(invokable: Invokable) {
invokable.invoke()
}
typealias FunctionX = ()->Unit
fun submit(lambda: FunctionX){
}
interface Invokable {
fun invoke()
}
正确的添加删除SAM
kotlin
fun main() {
val eventManager = EventManager()
val onEvent = object : EventManager.OnEventListener {
override fun onEvent(event: Int) {
println("onEvent $event")
}
}
val onEvent2 = EventManager.OnEventListener{
println("onEvent $it")
}
// DO NOT use this.
// val onEvent3 = { event: Int ->
// println("onEvent $event")
// }
eventManager.addOnEventListener(onEvent)
eventManager.removeOnEventListener(onEvent)
}
Demo
kotlin
fun main() {
File("build.gradle").readText() // 1. read file
.toCharArray() // 2.
.filter{ !it.isWhitespace() } // 3. filter white space
.groupBy { it }
.map {
it.key to it.value.size
}.let {
println(it)
}
}
kotlin
interface Node {
fun render(): String
}
class StringNode(val content: String): Node {
override fun render(): String {
return content
}
}
class BlockNode(val name: String): Node {
val children = ArrayList<Node>()
val properties = HashMap<String, Any>()
override fun render(): String {
return """<$name ${properties.map { "${it.key}='${it.value}'" }.joinToString(" ")}>${children.joinToString(""){ it.render() }}$name>"""
}
operator fun String.invoke(block: BlockNode.()-> Unit): BlockNode {
val node = BlockNode(this)
node.block()
this@BlockNode.children += node
return node
}
operator fun String.invoke(value: Any) {
this@BlockNode.properties[this] = value
}
operator fun String.unaryPlus(){
this@BlockNode.children += StringNode(this)
}
}
fun html(block: BlockNode.() -> Unit): BlockNode {
val html = BlockNode("html")
html.block()
return html
}
fun BlockNode.head(block: BlockNode.()-> Unit): BlockNode {
val head = BlockNode("head")
head.block()
this.children += head
return head
}
fun BlockNode.body(block: BlockNode.()-> Unit): BlockNode {
val head = BlockNode("body")
head.block()
this.children += head
return head
}
fun main() {
val htmlContent = html {
head {
"meta" { "charset"("UTF-8") }
}
body {
"div" {
"style"(
"""
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
line-height: 200px;
background-color: #C9394A;
text-align: center
""".trimIndent()
)
"span" {
"style"(
"""
color: white;
font-family: Microsoft YaHei
""".trimIndent()
)
+"Hello HTML DSL!!"
}
}
}
}.render()
File("Kotlin.html").writeText(htmlContent)
}
interface Node {
fun render(): String
}
class StringNode(val content: String): Node {
override fun render(): String {
return content
}
}
class BlockNode(val name: String): Node {
val children = ArrayList<Node>()
val properties = HashMap<String, Any>()
override fun render(): String {
return """<$name ${properties.map { "${it.key}='${it.value}'" }.joinToString(" ")}>${children.joinToString(""){ it.render() }}$name>"""
}
operator fun String.invoke(block: BlockNode.()-> Unit): BlockNode {
val node = BlockNode(this)
node.block()
this@BlockNode.children += node
return node
}
operator fun String.invoke(value: Any) {
this@BlockNode.properties[this] = value
}
operator fun String.unaryPlus(){
this@BlockNode.children += StringNode(this)
}
}
fun html(block: BlockNode.() -> Unit): BlockNode {
val html = BlockNode("html")
html.block()
return html
}
fun BlockNode.head(block: BlockNode.()-> Unit): BlockNode {
val head = BlockNode("head")
head.block()
this.children += head
return head
}
fun BlockNode.body(block: BlockNode.()-> Unit): BlockNode {
val head = BlockNode("body")
head.block()
this.children += head
return head
}
fun main() {
val htmlContent = html {
head {
"meta" { "charset"("UTF-8") }
}
body {
"div" {
"style"(
"""
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
line-height: 200px;
background-color: #C9394A;
text-align: center
""".trimIndent()
)
"span" {
"style"(
"""
color: white;
font-family: Microsoft YaHei
""".trimIndent()
)
+"Hello HTML DSL!!"
}
}
}
}.render()
File("Kotlin.html").writeText(htmlContent)
}
kotlin
import java.util.*
fun main(args : Array<String>){
println("Hello World!")
val day = 1.days().ago()
val day1 = 3.days.ago
println(day)
println(day1)
}
fun Int.days(): Pair<Int, Int> {
return Pair(this, Calendar.getInstance().get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR))
}
fun Pair<Int, Int>.ago(): Int {
return this.second - this.first
}
val Int.days: Pair<Int, Int>
get() {
return Pair(this, Calendar.getInstance().get(Calendar.DAY_OF_YEAR))
}
val Pair<Int, Int>.ago: Int
get(){
return this.second - this.first
}