iOS LRU学习参考
1.简介
LRU (英文:Least Recently Used), 意为最近最少使用,这个算法的精髓在于如果一块数据最近被访问,那么它将来被访问的几率也很高,根据数据的历史访问来淘汰长时间未使用的数据。
这篇文章主要分享一下关于内存缓存在iOS 中运用,主要分析一下第三方框架中LRU的运用,包括 Lottie 和 YYCache.
2.算法实现
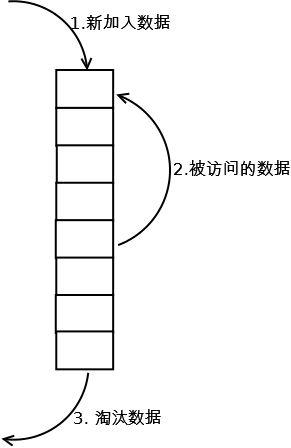
缓存淘汰算法
1.新添加的数据放在头部
2.被访问到的数据放在头部
3.超过最大缓存量的数据将被移除。
3.运用
1.Lottie
Lottie
LOTAnimationCache 这个类是LRU的最简单的使用,主要是缓存动画,分别看一下 .h .m 文件的实现。
/// Global Cache 单例类
+ (instancetype)sharedCache;
/// Adds animation to the cache 主要添加对象API
- (void)addAnimation:(LOTComposition *)animation forKey:(NSString *)key;
/// Returns animation from cache. 获取缓存
- (LOTComposition * _Nullable)animationForKey:(NSString *)key;
/// Removes a specific animation from the cache 移除缓存
- (void)removeAnimationForKey:(NSString *)key;
/// Clears Everything from the Cache 清除缓存
- (void)clearCache;
/// Disables Caching Animation Model Objects 销毁缓存模型
- (void)disableCaching;
通过上面主要接口的API,我们可以发现 一个缓存类的实现无非以上这几个接口,主要实现起来也特别简单。
//首先这是定义一个最大的缓存数量
static const NSInteger kLOTCacheSize = 50;
//类实现中主要维护两张表,字典通过key-value pair存储动画,用数组存储key
@implementation LOTAnimationCache {
NSMutableDictionary *animationsCache_;// 储存动画
NSMutableArray *lruOrderArray_; //保存key
}
//单例的实现,会iOS 的都会写
+ (instancetype)sharedCache {
static LOTAnimationCache *sharedCache = nil;
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
sharedCache = [[self alloc] init];
});
return sharedCache;
}
//本类初始化的时候,初始化数组和字典
- (instancetype)init {
self = [super init];
if (self) {
animationsCache_ = [[NSMutableDictionary alloc] init];
lruOrderArray_ = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
}
return self;
}
//这是最主要的方法
- (void)addAnimation:(LOTComposition *)animation forKey:(NSString *)key{
//清除超过最大缓存量的值
if (lruOrderArray_.count >= kLOTCacheSize) {
//数组第一个key就是最早存入数组
NSString *oldKey = lruOrderArray_.firstObject;
//移除旧key
[lruOrderArray_ removeObject:oldKey];
//移除值
[animationsCache_ removeObjectForKey:oldKey];
}
//移除旧key
[lruOrderArray_ removeObject:key];
//添加新key
[lruOrderArray_ addObject:key];
//存储值
[animationsCache_ setObject:animation forKey:key];
}
//通过key 获取 value
- (LOTComposition *)animationForKey:(NSString *)key {
if (!key) {
return nil;
}
//从 字典中获取 value
LOTComposition *animation = [animationsCache_ objectForKey:key];
//更新数组key
[lruOrderArray_ removeObject:key];
[lruOrderArray_ addObject:key];
return animation;
}
//清除缓存 ,一般在收到内存警告的时候执行此操作,也是一个缓存类必须提供的接口
- (void)clearCache {
[animationsCache_ removeAllObjects];
[lruOrderArray_ removeAllObjects];
}
// 移除对应key 的缓存
- (void)removeAnimationForKey:(NSString *)key {
[lruOrderArray_ removeObject:key];
[animationsCache_ removeObjectForKey:key];
}
// 销毁整个缓存
- (void)disableCaching {
[self clearCache];
animationsCache_ = nil;
lruOrderArray_ = nil;
}
Lottie 可能是我遇到最简单的缓存类了,也是最容易入门LRU的缓存类,实现起来也是很容易的。
2.YYCache
YYCache 中主要使用双向链表来实现内存缓存,主要分析一下主要实现思路,首先看一下简介
YYMemoryCache is a fast in-memory cache that stores key-value pairs.
In contrast to NSDictionary, keys are retained and not copied.
The API and performance is similar to `NSCache`, all methods are thread-safe.
YYMemoryCache 是一个用来key-value 键值对。
与NSDictionary 形成对比的的是keys 会被持有 但是不会被拷贝。
API 和性能类似于NSCache,所有的方法都是线程安全的。
YYMemoryCache objects differ from NSCache in a few ways:
* It uses LRU (least-recently-used) to remove objects; NSCache's eviction method
is non-deterministic.
* It can be controlled by cost, count and age; NSCache's limits are imprecise.
* It can be configured to automatically evict objects when receive memory
warning or app enter background.
The time of `Access Methods` in YYMemoryCache is typically in constant time (O(1)).
YYMemoryCache 有以下几点不同于NSCache:
1.使用LRU(最近最少使用) 来移除对象, NSCache 是不确定的
2.可以被 数量,消耗 和日期来控制,NSCache 是不明确的
3.当收到内存警告或者进入后台的时候自动配置来移除对象。
- YYMemoryCache `Access Methods 时间复杂度是O(1).
主要的方法
#pragma mark - Access Methods
/**
Returns a Boolean value that indicates whether a given key is in cache.
*/
//判断cache 中是否包含key
- (BOOL)containsObjectForKey:(id)key;
/**
Returns the value associated with a given key.
*/
//返回给定的key 对用的值
- (nullable id)objectForKey:(id)key;
/**
Sets the value of the specified key in the cache (0 cost).
*/
//赋值 key-value 0消耗
- (void)setObject:(nullable id)object forKey:(id)key;
/**
Sets the value of the specified key in the cache, and associates the key-value
pair with the specified cost.
*/
//赋值 key-value cost消耗
- (void)setObject:(nullable id)object forKey:(id)key withCost:(NSUInteger)cost;
/**
Removes the value of the specified key in the cache.
*/
// 移除指定key 对应的值
- (void)removeObjectForKey:(id)key;
/**
Empties the cache immediately.
*/
//移除所有的值
- (void)removeAllObjects;
// 淘汰算法
#pragma mark - Trim
/**
Removes objects from the cache with LRU, until the `totalCount` is below or equal to
the specified value.
*/
//对count 数量 移除缓存
- (void)trimToCount:(NSUInteger)count;
/**
Removes objects from the cache with LRU, until the `totalCost` is or equal to
*/
//对cost 移除缓存
- (void)trimToCost:(NSUInteger)cost;
/**
Removes objects from the cache with LRU, until all expiry objects removed by the
specified value.
*/
// 对age(缓存时间) 移除缓存
- (void)trimToAge:(NSTimeInterval)age;
首先看一下底层链表的实现:
1.定义一个节点类
主要包括 前后节点指针,_key 和 _value 以及_cost、 _time
@interface _YYLinkedMapNode : NSObject {
@package
__unsafe_unretained _YYLinkedMapNode *_prev; // retained by dic
__unsafe_unretained _YYLinkedMapNode *_next; // retained by dic
id _key;
id _value;
NSUInteger _cost;
NSTimeInterval _time;
}
@end
@implementation _YYLinkedMapNode
- (void)dealloc{
printf("本类_YYLinkedMapNode已经释放掉了");
}
@end
_YYLinkedMap
接下来看一下双向链表的实现,
主要包括一个字典负责存储,头结点和尾节点,总消耗和总数量
@interface _YYLinkedMap : NSObject {
@package
CFMutableDictionaryRef _dic; // do not set object directly
NSUInteger _totalCost;
NSUInteger _totalCount;
_YYLinkedMapNode *_head; // MRU, do not change it directly
_YYLinkedMapNode *_tail; // LRU, do not change it directly
}
/// Insert a node at head and update the total cost.
// 插入一个节点到头结点
- (void)insertNodeAtHead:(_YYLinkedMapNode *)node;
/// Bring a inner node to header.
//将内部的一个节点放到头部
- (void)bringNodeToHead:(_YYLinkedMapNode *)node;
/// Remove a inner node and update the total cost.
// 移除一个节点并更新总数
- (void)removeNode:(_YYLinkedMapNode *)node;
/// Remove tail node if exist.
//如果存在尾节点 移除
- (_YYLinkedMapNode *)removeTailNode;
/// Remove all node in background queue.
//移除所有
- (void)removeAll;
@end
初始化一个链表,初始化的时候创建一个字典
@implementation _YYLinkedMap
- (instancetype)init {
self = [super init];
//初始化一个字典
_dic = CFDictionaryCreateMutable(CFAllocatorGetDefault(), 0, &kCFTypeDictionaryKeyCallBacks, &kCFTypeDictionaryValueCallBacks);
return self;
}
- (void)dealloc {
CFRelease(_dic);
}
插入一个节点到头部
这个方法等同于第一步 => 添加新数据
- (void)insertNodeAtHead:(_YYLinkedMapNode *)node{
//存入字典表中
CFDictionarySetValue(_dic, (__bridge const void *)(node->_key), (__bridge const void *)(node->_value));
如果存在则将当前node 的置为首位,不存在的话,初始化
if (_head) {
node->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = node;
_head = node;
}
else {
_head = _tail = node;
}
}
将任意一个节点添加到头部
这个方法等同于第二步 => 被访问的数据移到头部
- (void)bringNodeToHead:(_YYLinkedMapNode *)node {
if (_head == node) return; // 如果本身是 head ,return
//如果是尾节点,重新赋值尾节点
if (_tail == node) {
_tail = node->_prev;
_tail->_next = nil;
} else {
//如果是中间的节点,重新赋值 prev next 指针
node->_next->_prev = node->_prev;
node->_prev->_next = node->_next;
}
//将拿到的节点添加到头部
node->_next = _head;
node->_prev = nil;
_head->_prev = node;
_head = node;
}
移除一个节点
用于缓存淘汰算法
- (void)removeNode:(_YYLinkedMapNode *)node {
CFDictionaryRemoveValue(_dic, (__bridge const void *)(node->_key));
_totalCost -= node->_cost;
_totalCount--;
// 源码的作者这一段写的是精华中的精华代码,思路严谨,也是体现使用__unsafe_unretained精华所在,执行效率很高,各位可以好好体会
if (node->_next) node->_next->_prev = node->_prev;
if (node->_prev) node->_prev->_next = node->_next;
if (_head == node) _head = node->_next;
if (_tail == node) _tail = node->_prev;
}
移除尾部节点并返回这个节点,这是很多第三方接口设计之精华
- (_YYLinkedMapNode *)removeTailNode {
if (!_tail) return nil;
_YYLinkedMapNode *tail = _tail;
CFDictionaryRemoveValue(_dic, (__bridge const void *)(_tail->_key));
_totalCost -= _tail->_cost;
_totalCount--;
// 如果只有一个节点 ,直接nil
if (_head == _tail) {
_head = _tail = nil;
} else {
_tail = _tail->_prev;
_tail->_next = nil;
}
return tail;
}
移除所有节点
- (void)removeAll {
_totalCost = 0;
_totalCount = 0;
_head = nil;
_tail = nil;
if (CFDictionaryGetCount(_dic) > 0) {
CFMutableDictionaryRef holder = _dic;
_dic = CFDictionaryCreateMutable(CFAllocatorGetDefault(), 0, &kCFTypeDictionaryKeyCallBacks, &kCFTypeDictionaryValueCallBacks);
//是否异步释放,也就是子线程释放,这里的一个是一个小技巧
if (_releaseAsynchronously) {
dispatch_queue_t queue = _releaseOnMainThread ? dispatch_get_main_queue() : YYMemoryCacheGetReleaseQueue();
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
CFRelease(holder); // hold and release in specified queue
});
} else if (_releaseOnMainThread && !pthread_main_np()) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
CFRelease(holder); // hold and release in specified queue
});
} else {
CFRelease(holder);
}
}
}
接下面看一下缓存淘汰的一些算法
包括 Cost、Count、Age 这三种Limit 来淘汰缓存
- (void)_trimToCost:(NSUInteger)costLimit{
// 判断临界条件 costLimit = 0 全部移除
// 如果 <= 什么也不需要做
BOOL finish = NO;
pthread_mutex_lock(&_lock);
if (costLimit == 0) {
[_lru removeAll];
finish = YES;
} else if (_lru->_totalCost <= costLimit) {
finish = YES;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_lock);
if (finish) return;
//这里采用while 循环的方式移除尾节点,直至满足条件
//这里有一个小技巧是,将移除的节点添加到一个数组中,然后在子线程释放
NSMutableArray *holder = [NSMutableArray new];
while (!finish) {
if (pthread_mutex_trylock(&_lock) == 0) {
if (_lru->_totalCost > costLimit) {
_YYLinkedMapNode *node = [_lru removeTailNode];
if (node) [holder addObject:node];
} else {
finish = YES;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_lock);
} else {
usleep(10 * 1000); //10 ms
}
}
if (holder.count) {
dispatch_queue_t queue = _lru->_releaseOnMainThread ? dispatch_get_main_queue() : YYMemoryCacheGetReleaseQueue();
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
[holder count]; // release in queue
});
}
}
以下两个缓存淘汰一样的思路
- (void)_trimToCount:(NSUInteger)countLimit
- (void)_trimToAge:(NSTimeInterval)ageLimit
- (void)_trimToCount:(NSUInteger)countLimit {
BOOL finish = NO;
pthread_mutex_lock(&_lock);
if (countLimit == 0) {
[_lru removeAll];
finish = YES;
} else if (_lru->_totalCount <= countLimit) {
finish = YES;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_lock);
if (finish) return;
NSMutableArray *holder = [NSMutableArray new];
while (!finish) {
if (pthread_mutex_trylock(&_lock) == 0) {
if (_lru->_totalCount > countLimit) {
_YYLinkedMapNode *node = [_lru removeTailNode];
if (node) [holder addObject:node];
} else {
finish = YES;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_lock);
} else {
usleep(10 * 1000); //10 ms
}
}
if (holder.count) {
dispatch_queue_t queue = _lru->_releaseOnMainThread ? dispatch_get_main_queue() : YYMemoryCacheGetReleaseQueue();
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
[holder count]; // release in queue
});
}
}
- (void)_trimToAge:(NSTimeInterval)ageLimit {
BOOL finish = NO;
NSTimeInterval now = CACurrentMediaTime();
pthread_mutex_lock(&_lock);
if (ageLimit <= 0) {
[_lru removeAll];
finish = YES;
} else if (!_lru->_tail || (now - _lru->_tail->_time) <= ageLimit) {
finish = YES;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_lock);
if (finish) return;
NSMutableArray *holder = [NSMutableArray new];
while (!finish) {
if (pthread_mutex_trylock(&_lock) == 0) {
if (_lru->_tail && (now - _lru->_tail->_time) > ageLimit) {
_YYLinkedMapNode *node = [_lru removeTailNode];
if (node) [holder addObject:node];
} else {
finish = YES;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_lock);
} else {
usleep(10 * 1000); //10 ms
}
}
if (holder.count) {
dispatch_queue_t queue = _lru->_releaseOnMainThread ? dispatch_get_main_queue() : YYMemoryCacheGetReleaseQueue();
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
[holder count]; // release in queue
});
}
}
接下来看一下YYMemoryCache 主要的缓存API 接口的实现,主要是基于底层链表的实现
存储方法key - value pair
- (void)setObject:(id)object forKey:(id)key withCost:(NSUInteger)cost {
//容错判断
if (!key) return;
if (!object) {
[self removeObjectForKey:key];
return;
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&_lock);
// 拿到一个节点
_YYLinkedMapNode *node = CFDictionaryGetValue(_lru->_dic, (__bridge const void *)(key));
NSTimeInterval now = CACurrentMediaTime();
if (node) {
//节点存在
_lru->_totalCost -= node->_cost;
_lru->_totalCost += cost;
node->_cost = cost;
node->_time = now;
node->_value = object;
[_lru bringNodeToHead:node];
} else {
// 节点不存在 -> 直接添加到头部
node = [_YYLinkedMapNode new];
node->_cost = cost;
node->_time = now;
node->_key = key;
node->_value = object;
[_lru insertNodeAtHead:node];
}
//做一次数据的剪枝
// 超过最大容量,清理内存
if (_lru->_totalCost > _costLimit) {
dispatch_async(_queue, ^{
[self trimToCost:_costLimit];
});
}
// 超过最大数量,清理内存
// 小技巧同样是异步释放内存
if (_lru->_totalCount > _countLimit) {
_YYLinkedMapNode *node = [_lru removeTailNode];
if (_lru->_releaseAsynchronously) {
dispatch_queue_t queue = _lru->_releaseOnMainThread ? dispatch_get_main_queue() : YYMemoryCacheGetReleaseQueue();
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
[node class]; //hold and release in queue
});
} else if (_lru->_releaseOnMainThread && !pthread_main_np()) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
[node class]; //hold and release in queue
});
}
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_lock);
}
接下来是获取值
- (id)objectForKey:(id)key {
if (!key) return nil;
pthread_mutex_lock(&_lock);
_YYLinkedMapNode *node = CFDictionaryGetValue(_lru->_dic, (__bridge const void *)(key));
//获取到该节点更新时间 并放置于链表的头部
if (node) {
node->_time = CACurrentMediaTime();
[_lru bringNodeToHead:node];
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_lock);
return node ? node->_value : nil;
}
移除key 对应的 value
- (void)removeObjectForKey:(id)key {
if (!key) return;
pthread_mutex_lock(&_lock);
//思路跟上面一样
_YYLinkedMapNode *node = CFDictionaryGetValue(_lru->_dic, (__bridge const void *)(key));
if (node) {
[_lru removeNode:node];
if (_lru->_releaseAsynchronously) {
dispatch_queue_t queue = _lru->_releaseOnMainThread ? dispatch_get_main_queue() : YYMemoryCacheGetReleaseQueue();
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
[node class]; //hold and release in queue
});
} else if (_lru->_releaseOnMainThread && !pthread_main_np()) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
[node class]; //hold and release in queue
});
}
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_lock);
}
移除所有的数据
- (void)removeAllObjects {
pthread_mutex_lock(&_lock);
[_lru removeAll];
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_lock);
}
以上是YYMemoryCache 利用 LRU 缓存淘汰算法实现的内存缓存,当然源码作者使用了很多方法来处理性能,例如在YYMemoryCache 在初始的时候,便开始5s递归剪枝,存储的时候也检查变量进行剪枝,个人认为在存储的时候可以不用,这方面也可提升性能,没必要频繁的去剪枝缓存淘汰数据。
在YYDiskCache 存储中也使用了LRU缓存淘汰算法,基本的原理和实现都是一样的,YYDiskCache 主要是使用 SQLite 和 File System来进行缓存。
还有一点需要注意的是
// release in queue 的实现
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
[holder count]; // release in queue
});
//hold and release in queue 的实现
dispatch_async(queue, ^{
[node class]; //hold and release in queue
});