不会真的学不会kotlin吧?(三)表达式
本文是根据慕课网kotlin相关课程本人笔记和个人理解所作
代码部分参考慕课网新kotlin入门课程
文章目录
- 本章简介
- 结构导图
- 常量和变量
- 变量 var
- 只读变量 val
- 常量const
- 常量引用
- 分支表达式
- if else
- when
- try catch表达式
- 运算符和中缀表达式
- 中缀表达式
- Infix 方法的中缀表达
- Lambda表达式
- 匿名函数
- EG
本章简介
这一章主要是kotlin的表达式相关的东西,我的理解就是kotlin中的 + - * / 其实都是函数,也可以重写这些函数和操作符,还有中缀操作符,不过代码的阅读性会有所下降
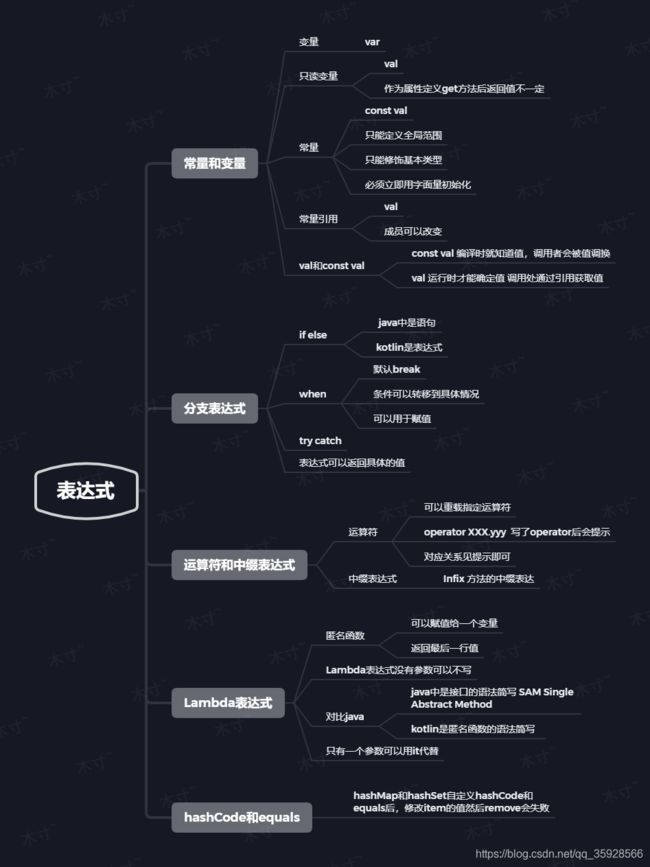
结构导图
常量和变量
变量 var
java
int a;
kotlin
var a:Int
只读变量 val
java
final int a;
kotlin
val a:Int
class X {
val b: Int
get() {
return (Math.random() * 100).toInt()
}
}
作为属性定义get后可以返回不同值
常量const
java
final static int a = 3;
kotlin
object KotlinVars2 {
const val b = 3
}
class KotlinVars {
companion object {
const val b = 3
}
}
第二种可以通过类名访问,伴生对象
只能定义全局范围 只能修饰基本类型 必须立即用字面量初始化
常量引用
java
final Person a = new Person(18);
a.setAge(19);
kotlin
val person = Person(18, "Bennyhuo")
person.age = 19
分支表达式
if else
java
int a = 2;
int c;
if (a == 3) {
c = 4;
} else {
c = 5;
}
c = a == 3 ? 4 : 5;
kotlin
var a = 2
var c: Int
if (a == 3) {
c = 4
} else {
c = 5
}
c = if (a == 3) 4 else 5
when
java
switch (a) {
case 0:
c = 5;
break;
case 1:
c = 100;
break;
default:
c = 20;
}
kotlin
c = when (a) {
0 -> 5
1 -> 100
else -> 20
}
var x: Any = Any()
c = when {
x is String -> x.length
x == 1 -> 100
else -> 20
}
c = when(val input = readLine()){
null -> 0
else -> input.length
}
try catch表达式
java
int b = 0;
try {
c = a / b;
} catch (ArithmeticException | NullPointerException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
c = 0;
}
kotlin
val b = 0
try {
c = a / b
}catch (e: Exception){
e.printStackTrace()
c = 0
}
c = try {
a / b
} catch (e: ArithmeticException){
2
} catch (e: Exception) {
e.printStackTrace()
0
}
c = try {
a / b
} catch (e: ArithmeticException){
2
} catch (e: Exception) {
e.printStackTrace()
0
}
运算符和中缀表达式
中缀表达式
kotlin
infix fun String.rotate(count: Int): String {
val index = count % length
return this.substring(index) + this.substring(0, index)
}
class Book
class Desk
infix fun Book.on(desk: Desk) {
}
fun main() {
//https://kotlinlang.org/docs/reference/operator-overloading.html
"Hello" == "World"
"Hello".equals("World")
2 + 3
2.plus(3)
val list = listOf(1, 2, 3, 4)
2 in list
list.contains(2)
val map = mutableMapOf(
"Hello" to 2,
"World" to 3
)
val value = map["Hello"]
// val value = map.get("Hello")
map["World"] = 4
map.set("World", 4)
val func = fun() {
println("Hello")
}
2 > 3
2.compareTo(3) > 0
func.invoke()
func()
2 to 3
2.to(3)
println("HelloWorld" rotate 5)
val book = Book()
val desk = Desk()
book on desk
}
Infix 方法的中缀表达
kotlin
//复数
class Complex(var real: Double, var image: Double){
override fun toString() = "$real + ${image}i"
}
operator fun Complex.plus(other: Complex): Complex {
return Complex(this.real + other.real, this.image + other.image)
}
operator fun Complex.plus(other: Double): Complex {
return Complex(this.real + other, this.image)
}
operator fun Complex.plus(other: Int): Complex {
return Complex(this.real + other, this.image)
}
operator fun Complex.minus(real: Double): Complex {
return Complex(this.real - real, this.image)
}
operator fun Complex.get(index: Int): Double = when(index){
0 -> this.real
1 -> this.image
else -> throw IndexOutOfBoundsException()
}
fun main() {
val c1 = Complex(3.0, 4.0)
val c2 = Complex(2.0, 2.0)
println(c1 + 2.0)
println(c1 + c2)
println(c1 + 3)
println(c1 - 3.0)
println(c1[0])
println(c1[1])
println(c1[2])
}
Lambda表达式
匿名函数
java
interface Function1 {
String invoke(int p);
}
interface Function2 {
String apply(int p0, long p1);
}
Runnable lambda = () -> {
System.out.println("Hello");
};
// var lambda2 = () -> {
// System.out.println("Hello");
// };
Function1 f1 = (p) -> {
System.out.println(p);
return "Hello";
};
Function2 f2 = (p0, p1) -> {
System.out.println(p0 + p1);
return "World";
};
String result = f1.invoke(2);
f2.apply(1, 2);
kotlin
val func: () -> Unit = fun() {
println("Hello")
}
val lambda: () -> Unit = {
println("Hello")
}
val f1 = { p: Int ->
println(p)
"Hello"
}
println(f1(1))
IntArray(5) { it + 1 }
EG
kotlin
class Person(val age: Int, val name: String){
override fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean {
val other = (other as? Person)?: return false
return other.age == age && other.name == name
}
override fun hashCode(): Int {
return 1 + 7 * age + 13 * name.hashCode()
}
}
fun main() {
val persons = HashSet<Person>()
// (0..5).forEach {
// persons += Person(20, "Benny")
// }
val person = Person(20, "Benny")
persons += person
// a moment later
println(persons.size)
val person2 = Person(person.age+1, person.name)
persons -= person
println(persons.size)
}
kotlin
operator fun String.minus(right: Any?)
= this.replaceFirst(right.toString(), "")
operator fun String.times(right: Int): String {
return (1..right).joinToString(""){ this }
}
operator fun String.div(right: Any?): Int {
val right = right.toString()
return this.windowed(right.length, 1, transform = {
it == right
}) // [false, false, false, false ... false, true, ..., true]
.count { it }
}
fun main() {
val value = "HelloWorld World"
println(value - "World")
println(value * 2)
val star = "*"
println("*" * 20)
println(value / 3)
println(value / "l")
println(value / "ld")
}