Android高级-Material Design交互设计
概念
主题
这三个必须要求API 在21以上
如果要兼容21以下的 就要使用兼容包:
兼容主题
主题常用属性
ColorAccent 强调色
常用控件
常用动画
Demo
省略一堆API介绍
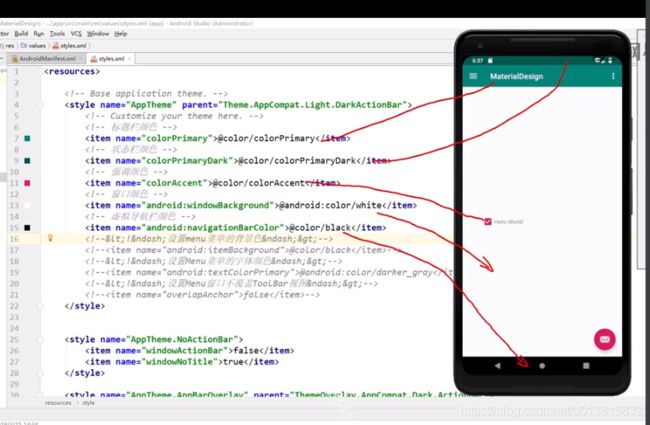
压缩的太狠了,哈哈哈 下面的高45dp的黑色长框就是要实现的效果
app:layout_behavior="@string/hide_bottom_view_on_scroll_behavior"
CoordinatorLayout详解
app:layout_behavior=“@string/hide_bottom_view_on_scroll_behavior"
app:layout_behavior=“@string/hide_bottom_view_on_scroll_behavior" 依赖于滚动事件进行底部视图的隐藏进入源码查看:
android.support.design.behavior.HideBottomViewOnScrollBehavior 表示的类的全路径,他绑定到了LayoutParams上,可以猜测FrameLayout这些自带的类似我们进CoordinatorLayout源码看一下:
看源码的目的:有两种给CoordinatorLayout设置behavior的方式
这个view他一定有他自己的LayoutParams,我们来看一下
第一种方法
通过属性获取是否需要设置behavior,通过反射的技术获取到CoordinatorLayout.Behavior的实例,然后再通过获取到的behavior对象,关联到LayoutParams上
mBehavior.onAttachedToLayoutParams(this);
他的构造方法中,有
这句代码是判断是否需要加载Behavior,如果需要加载,那么就去调用CoordinatorLayout#parseBehavior方法
static CoordinatorLayout.Behavior parseBehavior(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, String name) {
if(TextUtils.isEmpty(name)) {
return null;
} else {
String fullName;
//判断是否有包名
if(name.startsWith(".")) {
//拼接包名
fullName = context.getPackageName() + name;
} else if(name.indexOf(46) >= 0) {
fullName = name;
} else {
fullName = !TextUtils.isEmpty(WIDGET_PACKAGE_NAME)?WIDGET_PACKAGE_NAME + '.' + name:name;
}
try {
Map> constructors = (Map)sConstructors.get();
if(constructors == null) {
constructors = new HashMap();
sConstructors.set(constructors);
}
Constructor c = (Constructor)((Map)constructors).get(fullName);
if(c == null) {
//通过上面的包名,通过反射的技术获取CoordinatorLayout.Behavior 的class对象
Class clazz = context.getClassLoader().loadClass(fullName);
//获取两个参数的构造方法c
c = clazz.getConstructor(CONSTRUCTOR_PARAMS);
c.setAccessible(true);
((Map)constructors).put(fullName, c);
}
//返回 CoordinatorLayout.Behavior 的实例对象
return (CoordinatorLayout.Behavior)c.newInstance(new Object[]{context, attrs});
} catch (Exception var7) {
throw new RuntimeException("Could not inflate Behavior subclass " + fullName, var7);
}
}
} 然后
if(this.mBehavior != null) { this.mBehavior.onAttachedToLayoutParams(this); }
第二种方法:
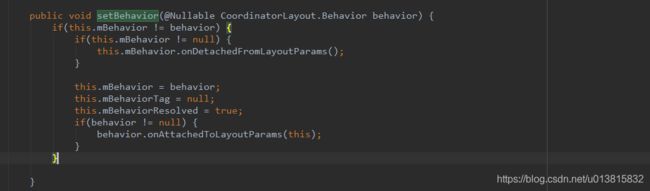
通过代码CoordinatorLayout#LayoutParams 的setBehavior
到这里,给子view设置Behavior的方式和原理我们呢就清楚了
现在看CoordinatorLayout是如何结合Behavior实现对子view的事件响应
CoordinatorLayout采用的是内嵌滑动机制,
内嵌滑动机制提供了一套机制,提供了一套父view和子view的嵌套滑动的交互机制,前提条件是
父view实现NestedScrollingParent接口,
而子view实现NestedScrollingChilid接口,
然后按照接口的要求,他们各自需要实现一个NestedScrolViewHelp的帮助类,来辅助子view和父view的交互
我们看到CoordinatorLayout是实现了
NestedScrollingParent2接口,这个接口所以CoordinatorLayout作为父view的条件是满足的,
我们再来看一下Recyclview
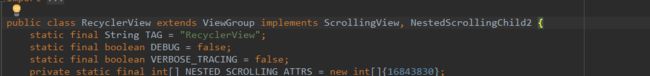
Recyclview同样满足作为子View的条件
上面我们实现了一个效果:上图
我们知道,滑动事件的开始是从Recyclview滑动开始,那我们就从这开始分析:
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent e) {
//省略....
this.mVelocityTracker.addMovement(e);
int action = e.getActionMasked();
int actionIndex = e.getActionIndex();
switch(action) {
case 0://down事件
if(this.mIgnoreMotionEventTillDown) {
this.mIgnoreMotionEventTillDown = false;
}
this.mScrollPointerId = e.getPointerId(0);
this.mInitialTouchX = this.mLastTouchX = (int)(e.getX() + 0.5F);
this.mInitialTouchY = this.mLastTouchY = (int)(e.getY() + 0.5F);
if(this.mScrollState == 2) {
this.getParent().requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true);
this.setScrollState(1);
}
this.mNestedOffsets[0] = this.mNestedOffsets[1] = 0;
int nestedScrollAxis = 0;
if(canScrollHorizontally) {
nestedScrollAxis |= 1;
}
if(canScrollVertically) {
nestedScrollAxis |= 2;
}
//down事件的最后调用
this.startNestedScroll(nestedScrollAxis, 0);
break;
//省略...
return this.mScrollState == 1;
}
}继续追踪
追踪前半部分:
如果它等于空,就将Recyclview作为view传递给NestScrollingChildHelper,然后就可以调用NestScrollingChildHelper#startNestedScroll方法:
public boolean startNestedScroll(int axes, int type) {
if(this.hasNestedScrollingParent(type)) {
return true;
} else {
//表示是否支持内嵌滑动
if(this.isNestedScrollingEnabled()) {
//mView表示的是RecyclView,而,getParent()方法返回的就是CoordinatorLayout
ViewParent p = this.mView.getParent();
//通过for循环调用onStartNestedScroll方法
for(View child = this.mView; p != null; p = p.getParent()) {
if(ViewParentCompat.onStartNestedScroll(p, child, this.mView, axes, type)) {
this.setNestedScrollingParentForType(type, p);
ViewParentCompat.onNestedScrollAccepted(p, child, this.mView, axes, type);
return true;
}
if(p instanceof View) {
child = (View)p;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}继续追踪:
if(ViewParentCompat.onStartNestedScroll(p, child, this.mView, axes, type)) {
public static boolean onStartNestedScroll(ViewParent parent, View child, View target, int nestedScrollAxes, int type) {
//判断是否是NestedScrollingParent2这个接口
if(parent instanceof NestedScrollingParent2) {
//如果是的话 就来到了CoordinatorLayout#onStartNestedScroll的方法中
return ((NestedScrollingParent2)parent).onStartNestedScroll(child, target, nestedScrollAxes, type);
} else {
if(type == 0) {
if(VERSION.SDK_INT >= 21) {
try {
return parent.onStartNestedScroll(child, target, nestedScrollAxes);
} catch (AbstractMethodError var6) {
Log.e("ViewParentCompat", "ViewParent " + parent + " does not implement interface " + "method onStartNestedScroll", var6);
}
} else if(parent instanceof NestedScrollingParent) {
return ((NestedScrollingParent)parent).onStartNestedScroll(child, target, nestedScrollAxes);
}
}
return false;
}
}查看CoordinatorLayout#onStartNestedScroll
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(View child, View target, int nestedScrollAxes) {
return this.onStartNestedScroll(child, target, nestedScrollAxes, 0);
}
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(View child, View target, int axes, int type) {
boolean handled = false;
int childCount = this.getChildCount();
//遍历所有的子view,
for(int i = 0; i < childCount; ++i) {
View view = this.getChildAt(i);
//如果这个view可见
if(view.getVisibility() != 8) {
//进而得到这个view的 CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams
CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams lp = (CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams)view.getLayoutParams();
//然后通过CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams得到Behavior
CoordinatorLayout.Behavior viewBehavior = lp.getBehavior();
if(viewBehavior != null) {
//如果不为null,那么就会执行viewBehavior 的onStartNestedScroll方法
boolean accepted = viewBehavior.onStartNestedScroll(this, view, child, target, axes, type);
handled |= accepted;
lp.setNestedScrollAccepted(type, accepted);
} else {
lp.setNestedScrollAccepted(type, false);
}
}
}
return handled;
}到此到behavior的调用就完成了,简单总结一下:
RecyclerView#onInterceptTouchEvent----->NestScrollingChildHelper#startNestedScroll-------->CoordinatorLayout#onStartNestedScroll ----------->CoordinatorLayout.Behavior#onStartNestedScroll方法
然后我们从布局文件中找到HideBottomViewOnScrollBehavior ,进入源码查看
public class HideBottomViewOnScrollBehavior extends Behavior {
protected static final int ENTER_ANIMATION_DURATION = 225;
protected static final int EXIT_ANIMATION_DURATION = 175;
private static final int STATE_SCROLLED_DOWN = 1;
private static final int STATE_SCROLLED_UP = 2;
private int height = 0;
private int currentState = 2;
private ViewPropertyAnimator currentAnimator;
public HideBottomViewOnScrollBehavior() {
}
//两个参数的构造方法
public HideBottomViewOnScrollBehavior(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public boolean onLayoutChild(CoordinatorLayout parent, V child, int layoutDirection) {
this.height = child.getMeasuredHeight();
return super.onLayoutChild(parent, child, layoutDirection);
}
//重写了这onStartNestedScroll这个方法
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View directTargetChild, View target, int nestedScrollAxes) {
return nestedScrollAxes == 2;
}
//重写了onNestedScroll方法 滑动事件处理view的动画,如果是向下滑动,调用slideDown
public void onNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed) {
if(this.currentState != 1 && dyConsumed > 0) {
this.slideDown(child);
} else if(this.currentState != 2 && dyConsumed < 0) {
this.slideUp(child);
}
}
//通过动画处理了显示与隐藏
protected void slideUp(V child) {
if(this.currentAnimator != null) {
this.currentAnimator.cancel();
child.clearAnimation();
}
this.currentState = 2;
this.animateChildTo(child, 0, 225L, AnimationUtils.LINEAR_OUT_SLOW_IN_INTERPOLATOR);
}
protected void slideDown(V child) {
if(this.currentAnimator != null) {
this.currentAnimator.cancel();
child.clearAnimation();
}
this.currentState = 1;
this.animateChildTo(child, this.height, 175L, AnimationUtils.FAST_OUT_LINEAR_IN_INTERPOLATOR);
}
private void animateChildTo(V child, int targetY, long duration, TimeInterpolator interpolator) {
this.currentAnimator = child.animate().translationY((float)targetY).setInterpolator(interpolator).setDuration(duration).setListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
HideBottomViewOnScrollBehavior.this.currentAnimator = null;
}
});
} 之前我们分析的是 onStartNestedScroll,现在我们分析onNestedScroll ,这个方法是在滑动的时候会被调用,所以我们继续从RecyclerView的滑动事件开始看起:
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent e) {
//省略...
int action = e.getActionMasked();
int actionIndex = e.getActionIndex();
if(action == 0) {
this.mNestedOffsets[0] = this.mNestedOffsets[1] = 0;
}
vtev.offsetLocation((float)this.mNestedOffsets[0], (float)this.mNestedOffsets[1]);
int nestedScrollAxis;
switch(action) {
case 0:
//省略。。
case 1:
this.mVelocityTracker.addMovement(vtev);
eventAddedToVelocityTracker = true;
this.mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000, (float)this.mMaxFlingVelocity);
float xvel = canScrollHorizontally?-this.mVelocityTracker.getXVelocity(this.mScrollPointerId):0.0F;
float yvel = canScrollVertically?-this.mVelocityTracker.getYVelocity(this.mScrollPointerId):0.0F;
if(xvel == 0.0F && yvel == 0.0F || !this.fling((int)xvel, (int)yvel)) {
this.setScrollState(0);
}
this.resetTouch();
break;
case 2://move方法
nestedScrollAxis = e.findPointerIndex(this.mScrollPointerId);
if(nestedScrollAxis < 0) {
Log.e("RecyclerView", "Error processing scroll; pointer index for id " + this.mScrollPointerId + " not found. Did any MotionEvents get skipped?");
return false;
}
int x = (int)(e.getX(nestedScrollAxis) + 0.5F);
int y = (int)(e.getY(nestedScrollAxis) + 0.5F);
int dx = this.mLastTouchX - x;
int dy = this.mLastTouchY - y;
if(this.dispatchNestedPreScroll(dx, dy, this.mScrollConsumed, this.mScrollOffset, 0)) {
dx -= this.mScrollConsumed[0];
dy -= this.mScrollConsumed[1];
vtev.offsetLocation((float)this.mScrollOffset[0], (float)this.mScrollOffset[1]);
this.mNestedOffsets[0] += this.mScrollOffset[0];
this.mNestedOffsets[1] += this.mScrollOffset[1];
}
if(this.mScrollState != 1) {
boolean startScroll = false;
if(canScrollHorizontally && Math.abs(dx) > this.mTouchSlop) {
if(dx > 0) {
dx -= this.mTouchSlop;
} else {
dx += this.mTouchSlop;
}
startScroll = true;
}
if(canScrollVertically && Math.abs(dy) > this.mTouchSlop) {
if(dy > 0) {
dy -= this.mTouchSlop;
} else {
dy += this.mTouchSlop;
}
startScroll = true;
}
if(startScroll) {
this.setScrollState(1);
}
}
if(this.mScrollState == 1) {
this.mLastTouchX = x - this.mScrollOffset[0];
this.mLastTouchY = y - this.mScrollOffset[1];
//找到这个方法scrollByInternal
if(this.scrollByInternal(canScrollHorizontally?dx:0, canScrollVertically?dy:0, vtev)) {
this.getParent().requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true);
}
if(this.mGapWorker != null && (dx != 0 || dy != 0)) {
this.mGapWorker.postFromTraversal(this, dx, dy);
}
}
break;
//省略...
vtev.recycle();
return true;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}查看scrollByInternal方法:
boolean scrollByInternal(int x, int y, MotionEvent ev) {
int unconsumedX = 0;
int unconsumedY = 0;
int consumedX = 0;
int consumedY = 0;
this.consumePendingUpdateOperations();
if(this.mAdapter != null) {
this.scrollStep(x, y, this.mScrollStepConsumed);
consumedX = this.mScrollStepConsumed[0];
consumedY = this.mScrollStepConsumed[1];
unconsumedX = x - consumedX;
unconsumedY = y - consumedY;
}
if(!this.mItemDecorations.isEmpty()) {
this.invalidate();
}
//注意这个方法
if(this.dispatchNestedScroll(consumedX, consumedY, unconsumedX, unconsumedY, this.mScrollOffset, 0)) {
this.mLastTouchX -= this.mScrollOffset[0];
this.mLastTouchY -= this.mScrollOffset[1];
if(ev != null) {
ev.offsetLocation((float)this.mScrollOffset[0], (float)this.mScrollOffset[1]);
}
this.mNestedOffsets[0] += this.mScrollOffset[0];
this.mNestedOffsets[1] += this.mScrollOffset[1];
} else if(this.getOverScrollMode() != 2) {
if(ev != null && !MotionEventCompat.isFromSource(ev, 8194)) {
this.pullGlows(ev.getX(), (float)unconsumedX, ev.getY(), (float)unconsumedY);
}
this.considerReleasingGlowsOnScroll(x, y);
}
if(consumedX != 0 || consumedY != 0) {
this.dispatchOnScrolled(consumedX, consumedY);
}
if(!this.awakenScrollBars()) {
this.invalidate();
}
return consumedX != 0 || consumedY != 0;
}dispatchNestedScroll,我们发现,他跟startNestedScroll方法的流程是一样的,
public boolean dispatchNestedScroll(int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, int[] offsetInWindow, int type) {
return this.getScrollingChildHelper().dispatchNestedScroll(dxConsumed, dyConsumed, dxUnconsumed, dyUnconsumed, offsetInWindow, type);
} private NestedScrollingChildHelper getScrollingChildHelper() {
if(this.mScrollingChildHelper == null) {
this.mScrollingChildHelper = new NestedScrollingChildHelper(this);
}
return this.mScrollingChildHelper;
}
public boolean dispatchNestedScroll(int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, @Nullable int[] offsetInWindow, int type) {
if(this.isNestedScrollingEnabled()) {
ViewParent parent = this.getNestedScrollingParentForType(type);
if(parent == null) {
return false;
}
if(dxConsumed != 0 || dyConsumed != 0 || dxUnconsumed != 0 || dyUnconsumed != 0) {
int startX = 0;
int startY = 0;
if(offsetInWindow != null) {
this.mView.getLocationInWindow(offsetInWindow);
startX = offsetInWindow[0];
startY = offsetInWindow[1];
}
ViewParentCompat.onNestedScroll(parent, this.mView, dxConsumed, dyConsumed, dxUnconsumed, dyUnconsumed, type);
if(offsetInWindow != null) {
this.mView.getLocationInWindow(offsetInWindow);
offsetInWindow[0] -= startX;
offsetInWindow[1] -= startY;
}
return true;
}
if(offsetInWindow != null) {
offsetInWindow[0] = 0;
offsetInWindow[1] = 0;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void onNestedScroll(ViewParent parent, View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, int type) {
//y又去判断类型,如果是NestedScrollingParent2 那么就是去调用CoordinatorLayout的onNestedScroll
if(parent instanceof NestedScrollingParent2) {
((NestedScrollingParent2)parent).onNestedScroll(target, dxConsumed, dyConsumed, dxUnconsumed, dyUnconsumed, type);
} else if(type == 0) {
if(VERSION.SDK_INT >= 21) {
try {
parent.onNestedScroll(target, dxConsumed, dyConsumed, dxUnconsumed, dyUnconsumed);
} catch (AbstractMethodError var8) {
Log.e("ViewParentCompat", "ViewParent " + parent + " does not implement interface " + "method onNestedScroll", var8);
}
} else if(parent instanceof NestedScrollingParent) {
((NestedScrollingParent)parent).onNestedScroll(target, dxConsumed, dyConsumed, dxUnconsumed, dyUnconsumed);
}
}
}所以我们去看
CoordinatorLayout#onNestedScroll方法
public void onNestedScroll(View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed) {
this.onNestedScroll(target, dxConsumed, dyConsumed, dxUnconsumed, dyUnconsumed, 0);
}
public void onNestedScroll(View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, int type) {
int childCount = this.getChildCount();
boolean accepted = false;
//for循环
for(int i = 0; i < childCount; ++i) {
View view = this.getChildAt(i);
if(view.getVisibility() != 8) {
CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams lp = (CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams)view.getLayoutParams();
if(lp.isNestedScrollAccepted(type)) {
//获取 CoordinatorLayout.Behavior对象
CoordinatorLayout.Behavior viewBehavior = lp.getBehavior();
if(viewBehavior != null) {
//调用CoordinatorLayout.Behavior的onNestedScroll方法
viewBehavior.onNestedScroll(this, view, target, dxConsumed, dyConsumed, dxUnconsumed, dyUnconsumed, type);
accepted = true;
}
}
}
}
if(accepted) {
this.onChildViewsChanged(1);
}
}接着我们回来看HideBottomViewOnScrollBehavior的onStartNestedScroll方法
//这个是在down事件 down调用的 返回的是boolean值 表示的是后续的事件是否被接受,
表示的true,后续滑动会被接受,反之不能
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View directTargetChild, View target, int nestedScrollAxes) {
return nestedScrollAxes == 2;
}
//
public void onNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed) {
if(this.currentState != 1 && dyConsumed > 0) {
this.slideDown(child);
} else if(this.currentState != 2 && dyConsumed < 0) {
this.slideUp(child);
}
}然后我们来实现一个自定义的Behavior
public class ScaleBehavior extends CoordinatorLayout.Behavior {
private FastOutLinearInInterpolator mFastOutLinearInInterpolator =new FastOutLinearInInterpolator();
private LinearOutSlowInInterpolator mLinearOutSlowInInterpolator = new LinearOutSlowInInterpolator();
public ScaleBehavior(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, @NonNull V child, @NonNull View directTargetChild, @NonNull View target, int axes, int type) {
return axes == ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL;//垂直滚动
}
@Override
public void onNestedScroll(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, @NonNull V child, @NonNull View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, int type) {
super.onNestedScroll(coordinatorLayout, child, target, dxConsumed, dyConsumed, dxUnconsumed, dyUnconsumed, type);
if (dyConsumed > 0 && child.getVisibility() == View.VISIBLE && !isRuuning ){//向下滑动 我们对控件进行缩放隐藏
scaleHide(child);
}else if (dyConsumed<0 && child.getVisibility() == View.INVISIBLE && !isRuuning ){//向上滑动 缩放显示控件
scaleShow(child);
}
}
private boolean isRuuning;
//通过属性动画来实现动画
private void scaleShow(V child) {
ViewCompat.animate(child)
.scaleX(1)
.scaleY(1)
.setDuration(500)
.setInterpolator(mLinearOutSlowInInterpolator)
.setListener(new ViewPropertyAnimatorListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationStart(View view) {
isRuuning =true;
}
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(View view) {
isRuuning=false;
view.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
@Override
public void onAnimationCancel(View view) {
isRuuning =false;
}
});
}
private void scaleHide(final V child) {
ViewCompat.animate(child)
.scaleX(0)
.scaleY(0)
.setDuration(500)
.setInterpolator(mFastOutLinearInInterpolator)
.setListener(new ViewPropertyAnimatorListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationStart(View view) {
isRuuning =true;
}
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(View view) {
isRuuning = false;
child.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
}
@Override
public void onAnimationCancel(View view) {
isRuuning = false;
}
});
}
} 效果图:
录屏的时候有闪屏,但是模拟器运行的时候是没有闪屏的