Python服务器运维笔记:第一章数据库精讲 - 1.1.5 mysql查询语句
前言:本文是学习网易微专业的《python全栈工程师》 中的《服务器运维开发工程师》专题的课程笔记,欢迎学习交流。同时感谢老师们的精彩传授!
一、课程目标
select语句结构where条件查询- 组合条件
二、详情解读
2.1.select语句
select语句可使用如下的形式执行:
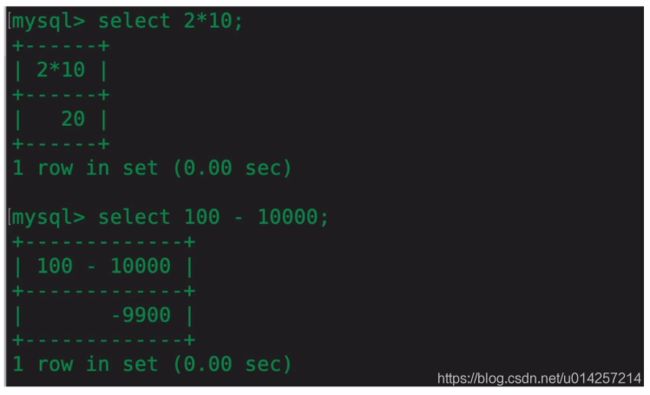
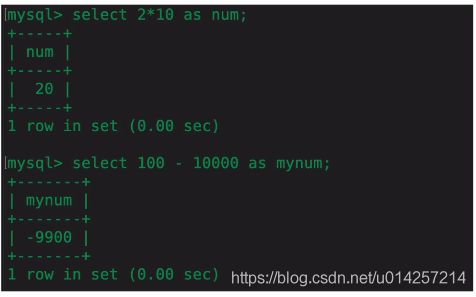
但是列名2*10或者100-10000使用不方便,因此可用as关键字:
2.2.从表中检索数据
从表中检索所有字段:
select * from table
从表中检索特定字段:
select field1, fiedl2, field3 from table
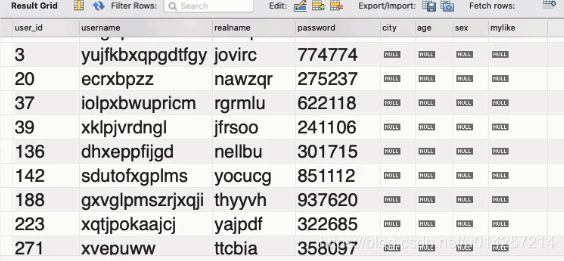
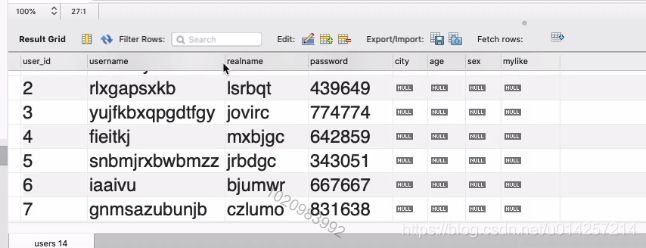
实操演示一:查询所有字段
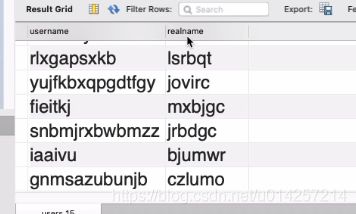
SELECT * FROM `mycms`.`users`
获得如下结果,其中表中字段作为列名:
实操演示二:查询特定字段
SELECT `username`, `realname` FROM `mycms`.`users`
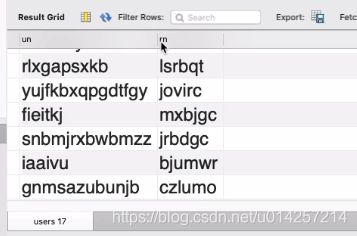
SELECT `username` as un, `realname` as rn FROM `mycms`.`users` as u
2.3.where条件语句
where根据一定的条件condition进行查询:
select * from table where condition
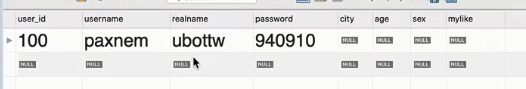
示例:
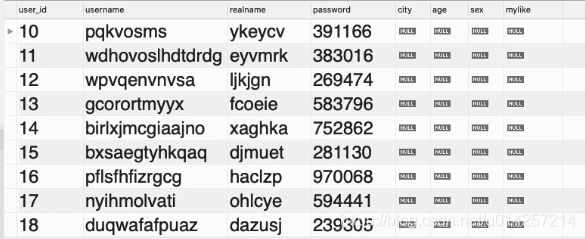
select * from `mycms`.`users` where user_id=100
运行结果:
在SQLAlchemy中,就是使用filter或者filter_by方法
2.3.1.condition表达式
=,>,<,>=,<=,<>,!=,<=> null值相等,is null,is not null
select * from users where user_id > 100;
select * from users where user_id <> 100;
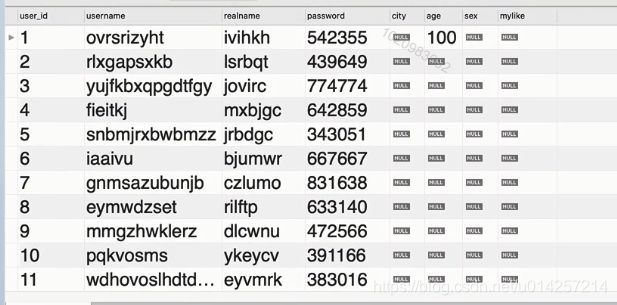
示例一:
select * from `mycms`.`users` where city is null
查询结果:
between - 区间查询(是闭区间,查询结果会包含区间)
select * from table where field between min and max;
select * from `users` where `age` between 18 and 25;
示例二:
select * from `mycms`.`users` where `user_id` between 10 and 20;
select * from users where user_id in (100, 110, 112);
select * from users where age in (20, 23);
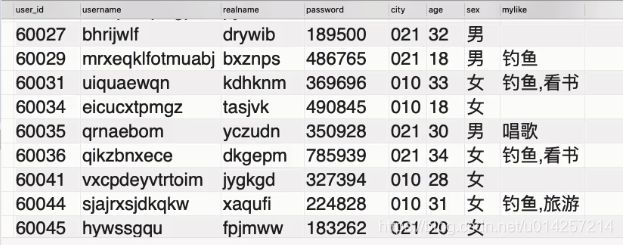
示例三:
select * from `mycms`.`users` where `city` in ("021", "010");
查询结果:
like - 通配符%匹配,%表示任意个字符,_表示一个字符
select * from users where username like "%luxp%";
select * from users where username like "_xp%";
select * from users where username not like "_xp%";
示例四:
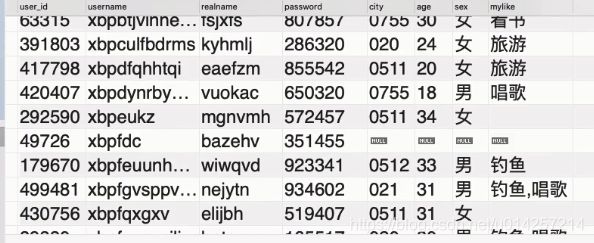
select * from `mycms`.`users` where `username` like "x_p%";
regexp - 正则匹配
select * from users where username regexp "[a-z]+x";
示例五:
select * from `mycms`.`users` where `username` regexp "x[a-z]{1,3}p";
2.4.组合条件
2.4.1.可以通过and或者or进行条件组合
select * from users where (username like "%luxp%") and (age > 20);
select * from users where (username like "_xp%") or (username like '_uxp%');
select * from users where (age > 20) or (age < 18);
2.5.sqlalchemy查询
2.5.1.sqlalchemy
flask-sqlalchemy是在sqlalchemy基础上开发的flask扩展,我们可以在自己的程序中直接使用sqlalchemy
实操一:
新建文件04_select_mysql_connector.py,写入以下代码:
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
import mysql.connector as connector
cnx = connector.connect(user='root', password='root', host='localhost', database='mycms')
cursor = cnx.cursor()
sql = "select * from users where age=20"
cursor.execute(sql)
res = cursor.fetchone() # 返回第一条符合条件的结果
print(res)
res2 = cursor.fetchmany(3) # 返回三符合条件的记录,如果少于3条,则全部返回。
print(res2)
res3 = cursor.fetchall() # 返回所有的查询结果
print(res3)
fetchone()的查询结果:
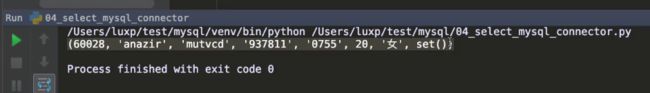
fetchmany(3)的查询结果:

fetchall()的查询结果:
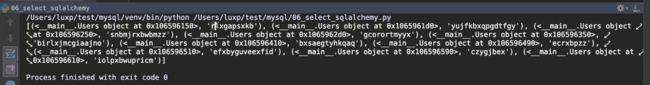
实操二: 通过sqlalchemy进行查询
新建文件06_select_sqlalchemy.py,写入如下代码:
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
# 需要安装sqlalchemy
# pip install sqlalchemy -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
# pip install pymysql
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String, Enum
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
# 创建数据库引擎
engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://root:root@localhost/mycms")
# 创建会话对象,根据不同的数据库引擎创建对应的会话对象
Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
# 创建会话对象实例
session = Session()
# Base为映射基类
Base = declarative_base()
# 数据表模型
class Users(Base):
__tablename__ = "users"
user_id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
username = Column(String(25))
realname = Column(String(25))
password = Column(String(25))
# 查询
res = session.query(Users, Users.username).filter(Users.username.like("%x%")).limit(10).all()
print(res)
import mysql.connector as connector
import random
cnx = connector.connect(user='root', password='123456',
host='localhost',database='mycms')
cursor = cnx.cursor()
#批量插入
# 通过insert into table values(...),(....),(....)格式,只向数据库提交一次插入
#
users=[]
words = list("abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz")
mylikes = ["钓鱼","旅游", "看书", "唱歌"]
citys = ["010", "021", "0512", "020", "0755", "0511"]
def createBatchUsers():
sql_list = []
sql = "INSERT INTO `mycms`.`users` VALUES "
# 批量创建1万条数据
for i in range(0,10000):
username = createUserName()
user = {
"id":i,
"realname" :"".join(random.choices(words,k=6)),
"username" :username,
"password": random.randint(111111, 999999),
"city": random.choice(citys),
"age": random.randint(18,35),
"sex" : random.choice(["男", "女"]),
"mylike" : ",".join(random.choices(mylikes,k=random.randint(0, 2))),
}
values = "(null, '{username}', '{realname}', '{password}', '{city}', '{age}','{sex}', '{mylike}')".format(**user)
sql_list.append(values.format(**user))
try:
sql += ",".join(sql_list)
print(sql)
cursor.execute(sql)
cnx.commit()
except connector.Error as e:
print("error:",e)
cursor.close()
cnx.close()
# 批量创建用户的时候,随机产生的用户名可能会发生重复,必须检测是否重复
# 只有检测可用的才会返回
def createUserName():
while True:
random.shuffle(words)
username = "".join(random.choices(words,k=random.randint(6,15)))
if not checkUser(username) and username not in users:
users.append(username)
break
print(">"*5, username)
return username
# 查询用户名是否存在
def checkUser(username):
sql = "select * from users where username='{username}'"
try:
cursor.execute(sql.format(**{"username": username}))
except connector.Error as e:
print(e)
res = cursor.fetchone()
print(res)
return res
for i in range(50):
createBatchUsers()
2.6.查询练习
1.查找特定城市的会员,比如上海的会员,北京的会员。
2.查找名字中包含特定字母组合的会员
3.查找年龄在18~20岁之间的会员
4.查找年龄在20~25岁之间并且是某个城市的会员
5.查找某个城市的男性会员。
三、课程小结
select语句结构- 条件语句
- 条件表达式
- 条件组合