Android动画TimeInterpolator(插值器)和TypeEvaluator(估值器)分析
跟上之前的三篇文章
Android属性动画ValueAnimator源码简单分析
Android属性动画ObjectAnimator源码简单分析
Android属性动画AnimatorSet源码简单分析
这篇文章继续分析Android动画的TimeInterpolator(插值器)和TypeEvaluator(估值器)的简单实现,以及分别去自定义插值器和估值器。
一,TimeInterpolator(插值器)
在动画的播放过程中Android中提供插值器来改变动画的播放速率,采用不用的插值器来实现不同的播放效果。
所有的插值器都要去实现TimeInterpolator接口,TimeInterpolator接口代码如下。
public interface TimeInterpolator {
/**
* Maps a value representing the elapsed fraction of an animation to a value that represents
* the interpolated fraction. This interpolated value is then multiplied by the change in
* value of an animation to derive the animated value at the current elapsed animation time.
*
* @param input A value between 0 and 1.0 indicating our current point
* in the animation where 0 represents the start and 1.0 represents
* the end
* @return The interpolation value. This value can be more than 1.0 for
* interpolators which overshoot their targets, or less than 0 for
* interpolators that undershoot their targets.
*/
float getInterpolation(float input);
}从代码中可以看到这里只需要实现getInterpolation()函数就好了,参数input是一个0到1之间的数。但是返回的值是可以大于1,也是可以小于0的,对于返回值倒是没什么特定的要求。
TimeInterpolator接口里面getInterpolation函数的参数input,那我们肯定好奇这个参数是怎么来的,为什么他会是一个0-1之间的数值呢。到底表示的而是什么呢。接下来就得简单的来看下这个参数是怎么来的了。
有了 Android属性动画ValueAnimator源码简单分析文章的分析,我们知道插值器的使用是在ValueAnimator类的animateValue()函数中使用的。animateValue()函数源码如下。
void animateValue(float fraction) {
fraction = mInterpolator.getInterpolation(fraction);
mCurrentFraction = fraction;
int numValues = mValues.length;
for (int i = 0; i < numValues; ++i) {
mValues[i].calculateValue(fraction);
}
if (mUpdateListeners != null) {
int numListeners = mUpdateListeners.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) {
mUpdateListeners.get(i).onAnimationUpdate(this);
}
}
}看到第二行插值器的使用了哦。那接了下就得去知道animateValue()函数是在哪里调用的了。 继续看ValueAnimator类中的animationFrame()函数
boolean animationFrame(long currentTime) {
boolean done = false;
switch (mPlayingState) {
case RUNNING:
case SEEKED:
float fraction = mDuration > 0 ? (float)(currentTime - mStartTime) / mDuration : 1f;
if (mDuration == 0 && mRepeatCount != INFINITE) {
// Skip to the end
mCurrentIteration = mRepeatCount;
if (!mReversing) {
mPlayingBackwards = false;
}
}
if (fraction >= 1f) {
if (mCurrentIteration < mRepeatCount || mRepeatCount == INFINITE) {
// Time to repeat
if (mListeners != null) {
int numListeners = mListeners.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) {
mListeners.get(i).onAnimationRepeat(this);
}
}
if (mRepeatMode == REVERSE) {
mPlayingBackwards = !mPlayingBackwards;
}
mCurrentIteration += (int) fraction;
fraction = fraction % 1f;
mStartTime += mDuration;
// Note: We do not need to update the value of mStartTimeCommitted here
// since we just added a duration offset.
} else {
done = true;
fraction = Math.min(fraction, 1.0f);
}
}
if (mPlayingBackwards) {
fraction = 1f - fraction;
}
animateValue(fraction);
break;
}
return done;
}6行先拿到了一个fraction,float fraction = mDuration > 0 ? (float)(currentTime - mStartTime) / mDuration : 1f; 这个也好理解就是用动画的当前时间减去动画的开始时间在除以每次动画的持续时间。得到了fraction。
14-35行 fraction>1 动画多次播放了,并且播放的次数还没完。27行 fraction = fraction % 1f; 多次播放也是分解从一次一次来看的,这个时候fraction就相当于是每次动画过程中的线性速率0-1之间值的。
36-38行 如果是反向播放 1-fraction 这个好说。
39行 调用animateValue(fraction);
到这里我们也就知道了TimeInterpolator接口里面getInterpolation函数的参数input就是动画每一次播放过程中的时间比例值确实是0-1之间的值。
提示:上面函数的调用过程大部分都是直接给出了结论,直接给出了在哪里哪里调用了 都是在 Android属性动画ValueAnimator源码简单分析的分析基础之上给出来的。
接下来就该是TimeInterpolator(插值器)的使用了,两种方式使用Android已经帮我们实现的插值器,使用自定义插值器。
1. Android已经实现的插值器
Android里面已经默认实现了9种插值器,这9种插值器如下
既然Android已经实现了这么多种的插值器,我们肯定得好奇里面具体的源码是怎么实现的吧。我们就来瞧瞧第一个插值器AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator的源码实现,没啥说的源码先贴上来。
/**
* An interpolator where the rate of change starts and ends slowly but
* accelerates through the middle.
*/
@HasNativeInterpolator
public class AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator extends BaseInterpolator
implements NativeInterpolatorFactory {
public AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator() {
}
@SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"})
public AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
}
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
return (float)(Math.cos((input + 1) * Math.PI) / 2.0f) + 0.5f;
}
/** @hide */
@Override
public long createNativeInterpolator() {
return NativeInterpolatorFactoryHelper.createAccelerateDecelerateInterpolator();
}
}这类看起来还是蛮简单哈,我们就关心两个地方,一个是构造函数一个是getInterpolation()函数。
构造函数两个,第一个是是我们具体JAVA代码中new的时候用到,第二个构造函数是在资源文件里面使用的时候调用的(@android:anim/accelerate_decelerate_interpolator的时候会调用这个构造函数)。
getInterpolation()函数,根据AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator插值器的曲线图得到对应的数学表达式(cos((x + 1) * PI) / 2.0) + 0.5,然后数学表达式转换为代码形式。
AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator的效果展现如下(例子代码底下会给出)
注:Android自带的9种插值器的效果在例子代码里面都有一一的展现。
2. 自定义插值器
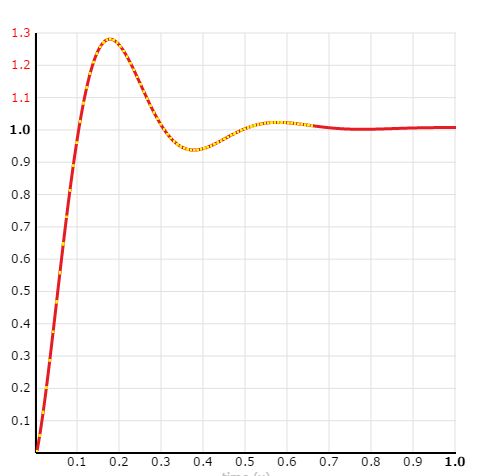
接下来我们就来动手实现一个自定义插值器的例子,我们来实现SpringInterpolator插值器。
第一步,确定我们要实现的插值器的曲线图
第二步,数学表达式
pow(2, -10 * x) * sin((x - factor / 4) * (2 * PI) / factor) + 1
factor = 0.4 这个我们在构造函数的时候指定
第三步 代码实现(把数学表达式转换为代码)
public class SpringInterpolator implements Interpolator {
private static final float DEFAULT_FACTOR = 0.4f;
private float mFactor;
public SpringInterpolator() {
this(DEFAULT_FACTOR);
}
public SpringInterpolator(float factor) {
mFactor = factor;
}
@Override
public float getInterpolation(float input) {
// pow(2, -10 * input) * sin((input - factor / 4) * (2 * PI) / factor) + 1
return (float) (Math.pow(2, -10 * input) * Math.sin((input - mFactor / 4.0d) * (2.0d * Math.PI) / mFactor) + 1);
}
}第四步 具体效果
参照http://www.tuicool.com/articles/3yANji自定义插值器里面还实现了一种CubicHermiteInterpolator的插值器。CubicHermiteInterpolator插值器的两个点可以通过 http://cubic-bezier.com/#.17,.67,.83,.67 来获取想要的数值。具体的效果也可以在例子代码里面看到。
二,TypeEvaluator(估值器)
动画过程中TypeEvaluator(估值器)的作用:当我们ValueAnimator.ofObject()函数来做动画效果的时候就会用到估值器了,估值器说白了就是用来确定在动画过程中每时每刻动画的具体值得换句话说就是确定ValueAnimator.getAnimatedValue()返回的具体对象类型啊。具体分析在下文给出。
所有的估值器都要实现TypeEvaluator接口,TypeEvaluator接口具体代码如下。
public interface TypeEvaluator {
/**
* This function returns the result of linearly interpolating the start and end values, with
* fraction representing the proportion between the start and end values. The
* calculation is a simple parametric calculation: result = x0 + t * (x1 - x0),
* where x0 is startValue, x1 is endValue,
* and t is fraction.
*
* @param fraction The fraction from the starting to the ending values
* @param startValue The start value.
* @param endValue The end value.
* @return A linear interpolation between the start and end values, given the
* fraction parameter.
*/
public T evaluate(float fraction, T startValue, T endValue);
} TypeEvaluator接口只需要实现一个evaluate()函数就好了,这个函数有三个参数,fraction: 表示当前这段数值变化值得比例,startValue:表示当前这段数值变化的开始值,endValue: 表示当前这段数据变化的结束值。
看到这里我们肯定的好奇TypeEvaluator(估值器)在哪里用到了,估值出来的值去哪里了呢。继续在前面文章 Android属性动画ValueAnimator源码简单分析的基础之上来看这个问题。
有了 Android属性动画ValueAnimator源码简单分析的分析我们知道估值器的使用是在KeyframeSet类里面的getValue()函数里面。
那就进KeyframeSet类里面的getValue()代码里面去看看
public Object getValue(float fraction) {
// Special-case optimization for the common case of only two keyframes
if (mNumKeyframes == 2) {
if (mInterpolator != null) {
fraction = mInterpolator.getInterpolation(fraction);
}
return mEvaluator.evaluate(fraction, mFirstKeyframe.getValue(),
mLastKeyframe.getValue());
}
if (fraction <= 0f) {
final Keyframe nextKeyframe = mKeyframes.get(1);
final TimeInterpolator interpolator = nextKeyframe.getInterpolator();
if (interpolator != null) {
fraction = interpolator.getInterpolation(fraction);
}
final float prevFraction = mFirstKeyframe.getFraction();
float intervalFraction = (fraction - prevFraction) /
(nextKeyframe.getFraction() - prevFraction);
return mEvaluator.evaluate(intervalFraction, mFirstKeyframe.getValue(),
nextKeyframe.getValue());
} else if (fraction >= 1f) {
final Keyframe prevKeyframe = mKeyframes.get(mNumKeyframes - 2);
final TimeInterpolator interpolator = mLastKeyframe.getInterpolator();
if (interpolator != null) {
fraction = interpolator.getInterpolation(fraction);
}
final float prevFraction = prevKeyframe.getFraction();
float intervalFraction = (fraction - prevFraction) /
(mLastKeyframe.getFraction() - prevFraction);
return mEvaluator.evaluate(intervalFraction, prevKeyframe.getValue(),
mLastKeyframe.getValue());
}
Keyframe prevKeyframe = mFirstKeyframe;
for (int i = 1; i < mNumKeyframes; ++i) {
Keyframe nextKeyframe = mKeyframes.get(i);
if (fraction < nextKeyframe.getFraction()) {
final TimeInterpolator interpolator = nextKeyframe.getInterpolator();
final float prevFraction = prevKeyframe.getFraction();
float intervalFraction = (fraction - prevFraction) /
(nextKeyframe.getFraction() - prevFraction);
// Apply interpolator on the proportional duration.
if (interpolator != null) {
intervalFraction = interpolator.getInterpolation(intervalFraction);
}
return mEvaluator.evaluate(intervalFraction, prevKeyframe.getValue(),
nextKeyframe.getValue());
}
prevKeyframe = nextKeyframe;
}
// shouldn't reach here
return mLastKeyframe.getValue();
}对于这个函数的具体分析可以参考 Android属性动画ValueAnimator源码简单分析里面对这个函数详细的分析,这里是想在多扯一点,当我们使用ValueAnimator.ofObject()的时候,是一定要去设置估值器的,其实从代码的侧面也是可以看出来得这个函数里面使用的mEvaluator都是没有null值判断的。他不像IntKeyframeSet类里面的getIntValue()函数的mEvaluator,IntKeyframeSet类里面的getIntValue()函数的mEvaluator是有一个为null判断的如果没指定mEvaluator的时候会调用类似于IntEvaluator类的具体实现的。
估值器的使用地方我们知道了是KeyframeSet类里面的getValue(),接下来我们就得知道KeyframeSet类里面的getValue()在哪里调用了吧。是在PropertyValuesHolder类的calculateValue()函数里面使用了。
void calculateValue(float fraction) {
Object value = mKeyframes.getValue(fraction);
mAnimatedValue = mConverter == null ? value : mConverter.convert(value);
}第二行的 mKeyframes.getValue(fraction);调用到了getValue(),得到的值放在了mAnimatedValue里面,要通过PropertyValuesHolder类的getAnimatedValue()函数来得这个值,接着我们的知道PropertyValuesHolder类的calculateValue()函数在哪里用到了吧。ValueAnimator类的animateValue函数中调用了 看代码
void animateValue(float fraction) {
fraction = mInterpolator.getInterpolation(fraction);
mCurrentFraction = fraction;
int numValues = mValues.length;
for (int i = 0; i < numValues; ++i) {
mValues[i].calculateValue(fraction);
}
if (mUpdateListeners != null) {
int numListeners = mUpdateListeners.size();
for (int i = 0; i < numListeners; ++i) {
mUpdateListeners.get(i).onAnimationUpdate(this);
}
}
}第6行 调用到了哦。mValues[i].calculateValue(fraction);
animateValue()这个函数在动画的过程中一直会调用到的。所以PropertyValuesHolder类的getAnimatedValue函数得到的值随着动画的进行是会改变的。
PropertyValuesHolder类的getAnimatedValue()函数的返回值最最直观的表现就是在ValueAnimator类的getAnimatedValue()函数中用到了。
ValueAnimator类的getAnimatedValue函数
public Object getAnimatedValue() {
if (mValues != null && mValues.length > 0) {
return mValues[0].getAnimatedValue();
}
// Shouldn't get here; should always have values unless ValueAnimator was set up wrong
return null;
}上面稀里糊涂的扯了一堆总的来说呢就是想说明一点,最后通过估值器计算出来的值呢,最直接反映到的地方就是ValueAnimator类的getAnimatedValue()函数得到的值。(函数的正好是我们在ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener接口的onAnimationUpdate()函数里面使用)。
提示:上面函数的调用过程大部分都是直接给出了结论,直接给出了某某函数在哪里哪里调用了 都是在 Android属性动画ValueAnimator源码简单分析的分析基础之上给出来的。
接下来就该是TypeEvaluator(估值器)的使用了,两种方式使用Android内部实现的估值器,使用自定义的估值器。
1. Android系统内置的估值器
Android里面默认提供了如下几种估值器 ArgbEvaluator, FloatArrayEvaluator, FloatEvaluator, IntArrayEvaluator, IntEvaluator, PointFEvaluator, RectEvaluator。
我们同样挑一个来看看具体的源码实现就挑ArgbEvaluator,具体源码如下
public class ArgbEvaluator implements TypeEvaluator {
private static final ArgbEvaluator sInstance = new ArgbEvaluator();
/**
* Returns an instance of ArgbEvaluator that may be used in
* {@link ValueAnimator#setEvaluator(TypeEvaluator)}. The same instance may
* be used in multiple Animators because it holds no state.
* @return An instance of ArgbEvalutor.
*
* @hide
*/
public static ArgbEvaluator getInstance() {
return sInstance;
}
/**
* This function returns the calculated in-between value for a color
* given integers that represent the start and end values in the four
* bytes of the 32-bit int. Each channel is separately linearly interpolated
* and the resulting calculated values are recombined into the return value.
*
* @param fraction The fraction from the starting to the ending values
* @param startValue A 32-bit int value representing colors in the
* separate bytes of the parameter
* @param endValue A 32-bit int value representing colors in the
* separate bytes of the parameter
* @return A value that is calculated to be the linearly interpolated
* result, derived by separating the start and end values into separate
* color channels and interpolating each one separately, recombining the
* resulting values in the same way.
*/
public Object evaluate(float fraction, Object startValue, Object endValue) {
int startInt = (Integer) startValue;
int startA = (startInt >> 24) & 0xff;
int startR = (startInt >> 16) & 0xff;
int startG = (startInt >> 8) & 0xff;
int startB = startInt & 0xff;
int endInt = (Integer) endValue;
int endA = (endInt >> 24) & 0xff;
int endR = (endInt >> 16) & 0xff;
int endG = (endInt >> 8) & 0xff;
int endB = endInt & 0xff;
return (int)((startA + (int)(fraction * (endA - startA))) << 24) |
(int)((startR + (int)(fraction * (endR - startR))) << 16) |
(int)((startG + (int)(fraction * (endG - startG))) << 8) |
(int)((startB + (int)(fraction * (endB - startB))));
}
}看起来也是蛮简单的,ArgbEvaluator和颜色有关系的,evaluate函数里面分别对startValue和endValue做了拆分。int总共32位,8位8位的去拆分,分别对应A,R,G,B。 然后对A,R,G,B每个都做fraction转换,在组合到一起形成一个int值。
2. 自定义估值器
自定义一个CharEvaluator的估值器,实现A-Z的变化,也是网上参考的别人的例子。
具体代码如下
public class CharEvaluator implements TypeEvaluator<Character> {
@Override
public Character evaluate(float fraction, Character startValue, Character endValue) {
int startInt = (int) startValue;
int endInt = (int) endValue;
int curInt = (int) (startInt + fraction * (endInt - startInt));
return (char) curInt;
}
}
三,源码
例子代码下载地址