SpringMVC源码解析之HandlerMapping与HandlerAdapter
1. HandlerMapping
SpringMVC的HandlerMapping的作用是根据相应的请求映射到对应的handler,并将 Handler(执行程序)与一堆 HandlerInterceptor(拦截器)封装到 HandlerExecutionChain(处理器执行链) 对象中。
当我们发送一个请求时,DispatcherServlet会拦截请求执行doDispatch方法,并遍历注册的HandlerMapping来处理请求(未指定HandlerMapping时会使用spring-webmvcjar下DispatcherServlet.properties配置文件加载,默认是org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping,Spring 3.1及以上版本,DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping会被RequestMappingHandlerMapping替代,多个HandlerMapping会根据order属性来依次处理直到匹配到handler)。
// doDispatch方法中调用
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
//遍历容器中的HandlerMapping实例,让 HandlerMapping 实例根据自己实现类的方式去尝试查找 Handler
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}HandlerExecutionChain对象中的handler有可能是一个 HandlerMethod(封装了 Controller 中的方法)对象,也有可能是一个 Controller 对象、 HttpRequestHandler 对象或 Servlet 对象,而这个 Handler 具体是什么对象,也是与所使用的 HandlerMapping 实现类有关。 HandlerMapping 实现类有两个分支,分别继承自 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping(得到 HandlerMethod)和 AbstractUrlHandlerMapping(得到 HttpRequestHandler、Controller 或 Servlet),它们又统一继承于 AbstractHandlerMapping:

AbstractHandlerMapping实现了HandlerMapping的getHandler()方法,代码如下:
//获取HandlerExecutionChain
@Override
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//该方法是抽象方法,具体实现由其子类执行获取HandlerExecutionChain实例或HandlerMethod实例
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
//获取默认handler
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// 将 Handler 与一堆拦截器包装到 HandlerExecutionChain 对象中
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.globalCorsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}getHandlerInternal()查看源码可知由AbstractUrlHandlerMapping和AbstractHandlerMethodMapping实现。
1.1 AbstractUrlHandlerMapping及其子类
AbstractUrlHandlerMapping 这个分支获取的 Handler 的类型实际就是一个 Controller 类,因此一个Controller类只能处理一个请求,使用该分支实现类处理的Controller必须实现org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller接口或继承其子类(DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping除外)。AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的getHandlerInternal()方法源码如下:
@Override
protected Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 根据当前请求获取“查找路径”
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
// 根据路径获取 Handler(即Controller),先尝试直接匹配,再尝试模式匹配
Object handler = lookupHandler(lookupPath, request);
if (handler == null) {
// We need to care for the default handler directly, since we need to
// expose the PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE for it as well.
Object rawHandler = null;
if ("/".equals(lookupPath)) {
rawHandler = getRootHandler();
}
if (rawHandler == null) {
rawHandler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (rawHandler != null) {
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (rawHandler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) rawHandler;
rawHandler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
validateHandler(rawHandler, request);
//将Handler对象包装到HandlerExecutionChain对象中
handler = buildPathExposingHandler(rawHandler, lookupPath, lookupPath, null);
}
}
if (handler != null && logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Mapping [" + lookupPath + "] to " + handler);
}
else if (handler == null && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No handler mapping found for [" + lookupPath + "]");
}
return handler;
}上述代码可知handler是通过lookupHandler方法获取的,而查看源码:
Object handler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);
handlerMap是一个Map集合,lookupPath作为key,handler实例作为value,每个AbstractUrlHandlerMapping的实现类对应的handlerMap都有所不同。
1.1.1 ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping
根据类名访问 Controller,this.handlerMap如下格式:
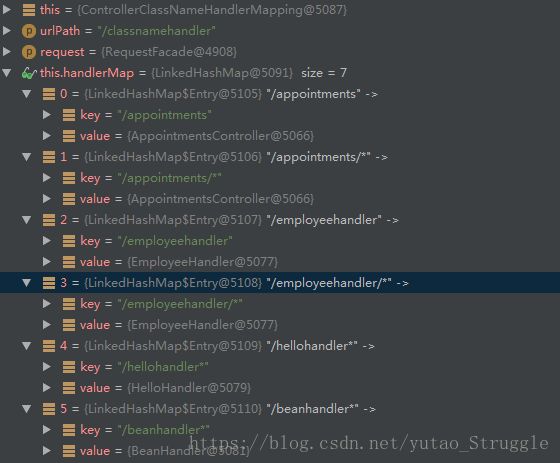
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.ControllerClassNameHandlerMapping">
<property name="order" value="4"/>
<property name="basePackage" value="com.controller"/>
1.1.2 BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
利用 BeanName 来作为 URL 使用:http://localhost/beanHandler
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping">
<property name="order" value="5"/>
bean>
<bean id="/beanHandler" class="com.controller.BeanHandler"/>1.1.3 ControllerBeanNameHandlerMapping
根据 Bean 名访问 Controller,与 BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping 类似,但是bean名称不用遵循URL公约:http://localhost/helloHandler
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.ControllerBeanNameHandlerMapping">
<property name="order" value="0"/>
bean>
<bean id="helloHandler" class="com.controller.HelloHandler"/>1.1.4 SimpleUrlHandlerMapping
可以将 URL 与处理器的定义分离,还可以对 URL 进行统一的映射管理,mappings属性会注入到handlerMap中,通过
Object handler = this.handlerMap.get(urlPath);获取handler。
http://localhost/hello
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleUrlHandlerMapping">
<property name="order" value="2"/>
<property name="mappings">
<props>
<prop key="hello">helloHandlerprop>
props>
property>
bean>
<bean id="helloHandler" class="com.controller.HelloHandler"/>1.1.5 DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping
Spring3.1之前用于处理@ReqeustMapping,this.handlerMap中保存了@RequestMapping的value值和handler实例,具体定位到方法在DefaultAnnotationHandlerAdapter中实现
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping">
<property name="order" value="1"/>
bean>1.2 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping及其子类
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping这个分支获取的 Handler 的类型是 HandlerMethod,即这个 Handler 是一个方法,它保存了方法的信息(如Method),这样一个 Controller 就可以处理多个请求了。
@Override
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//获取请求的路径
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking up handler method for path " + lookupPath);
}
//this.mappingRegistry.registry是一个Map集合,保存了RequestMappingInfo与HandlerMethod的映射关系,开启读锁
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
// 获取当前请求最佳匹配的处理方法(即Controller类的方法中)
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (handlerMethod != null) {
logger.debug("Returning handler method [" + handlerMethod + "]");
}
else {
logger.debug("Did not find handler method for [" + lookupPath + "]");
}
}
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
//解除读锁
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}上述提到this.mappingRegistry.registry是一个Map集合,保存了RequestMappingInfo与HandlerMethod的映射关系,ReqeustMappingInfo保存的时RequestMapping的信息,HandlerMethod是如何获取的呢?
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping实现了InitializingBean接口,在初始化属性赋值之后调用afterPropertiesSet()方法,afterPropertiesSet()调用了initHandlerMethods()方法,源码如下:
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext());
}
//获取容器中所有bean的名称,detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts 默认false,不从父容器中查找
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
//遍历beanName
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
Class beanType = null;
try {
//通过beanName获取该bean的类型
beanType = getApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve target class for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
//该bean非空并且有@Controller或@RequestMapping注解
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
// 利用反射得到 Bean 中的 Method 并包装成 HandlerMethod,然后放入 Map 中
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) {
// 获取这个 Bean 的 Class 对象
Class handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
// 获取被代理前的原始类型
final Class userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
//获取这个bean的所有Method和RequestMappingInfo对象
Map methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
new MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup() {
@Override
public T inspect(Method method) {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
}
});
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(methods.size() + " request handler methods found on " + userType + ": " + methods);
}
for (Map.Entry entry : methods.entrySet()) {
//Method对象
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(entry.getKey(), userType);
//RequestMappingInfo对象
T mapping = entry.getValue();
//将RequestMappingInfo和Method注册,
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
}
}
//通过this.mappingRegistry.register注册
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
} 由此可见this.mappingRegistry用于存取RequestMappingInfo和HandlerMethod,实际上lookupHandlerMethod也是从this.mappingRegistry中获取HandlerMethod。
1.2.1 RequestMappingHandlerMapping
Spring 3.1中新增RequestMappingHandlerMapping用以增强@RequestMapping,替代了Spring 3.1之前的DefaultAnnotationHanlderMapping,可以直接检查类级别和方法级别的请求映射返回HandlerMethod。具体用法见SpringMVC框架基础
2. HandlerAdapter
根据 Handler 来找到支持它的 HandlerAdapter,通过 HandlerAdapter 执行这个 Handler 得到 ModelAndView 对象,源码如下:
//doDispatch中调用,通过handler获取对应的HandlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
//遍历注册的HandlerAdapter
for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]");
}
//通过instanceof判断handler的类型(HandlerMethod/HttpRequestHandler/Controller/Servlet)获取支持handler的HandlerAdapter并返回
if (ha.supports(handler)) {
return ha;
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}DispatcherServlet上述通过getHandlerAdapter()方法获取了HandlerAdapter实例后,再将handler交由对应的HandlerAdapter处理,返回ModelAndView,源码如下:
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());2.1 HttpRequestHandlerAdapter
HttpRequestHandlerAdapter可以执行HttpRequestHandler类型的handler,源码如下:
@Override
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
((HttpRequestHandler) handler).handleRequest(request, response);
return null;
}2.2 SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter
SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter可以执行Controller类型的handler,源码如下:
@Override
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return ((Controller) handler).handleRequest(request, response);
}2.3 SimpleServletHandlerAdapter
SimpleServletHandlerAdapter可以执行Servlet类型的handler,源码如下:
@Override
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
((Servlet) handler).service(request, response);
return null;
}2.5 AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter
AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter在Spring3.1后被RequestMappingHandlerAdapter所替代,源码如下:
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
Class clazz = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handler);
Boolean annotatedWithSessionAttributes = this.sessionAnnotatedClassesCache.get(clazz);
if (annotatedWithSessionAttributes == null) {
annotatedWithSessionAttributes = (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(clazz, SessionAttributes.class) != null);
this.sessionAnnotatedClassesCache.put(clazz, annotatedWithSessionAttributes);
}
if (annotatedWithSessionAttributes) {
checkAndPrepare(request, response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers, true);
}
else {
checkAndPrepare(request, response, true);
}
// Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required.
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
return invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handler);
}
}
}
return invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handler);
}AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter的handler参数实际上是Controller类型,而非HandlerMethod的类型,invokeHandlerMethod()方法才决定执行哪个方法。
2.6 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter

RequestMappingHandlerAdapter是AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter的子类,用于处理HandlerMethod类型的handler,AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter的handle()方法调用了handleInternal()方法,而handleInternal()方法是一个抽象方法,由RequestMappingHandlerAdapter实现,源码如下:
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
// Check whether we should support the request method.
checkRequest(request);
// Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required.synchronizeOnSession默认为false
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No HttpSession available -> no mutex necessary
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No synchronization on session demanded at all...,执行HandlerMethod并返回一个ModelAndView(数据绑定、参数绑定、创建模型和视图容器等)
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
//返回一个ModelAndView,交给后续的ViewResolver
return mav;
}由此可见,虽然SpringMVC提供了灵活的方法返回值,但最后都会被处理成一个ModelAndView。