mybatis系列总结1
目录
- mybatis 简介
- mybatis 与 hibernate 区别
- 缓存
- Hibernate缓存
- MyBatis缓存
- 对比
- com.mysql.jdbc.MysqlDataTruncation: Data truncation: Data too long for column ‘*’ at row 1
- mybatis mapper xml 特殊符号转义写法
mybatis 简介
Hibernate是当前最流行的 O/R mapping框架。mybatis 是一种"Sql Mapping"的ORM实现。
Hibernate对数据库结构提供较为完整的封装,实现POJO和数据库表之间的映射,以及SQL的自动生成和执行。只需定义好POJO到数据库表的映射关系,即可通过 Hibernate 提供的方法完成持久层操作。甚至不需要对SQL的熟练掌握,Hibernate/OJB会根据制定的存储逻辑,自动生成对应的 SQL并调用JDBC接口加以执行。
mybatis的着力点,则在于POJO与SQL之间的映射关系。iBATIS并不会在运行期自动生成SQL执行。具体的SQL需要程序员编写,然后通过映射配置文件,将SQL所需的参数,以及返回的结果字段映射到指定POJO。使用mybatis提供的ORM机制,对业务逻辑实现人员而言,面对的是纯粹的Java对象,这一层与通过Hibernate 实现ORM而言基本一致,而对于具体的数据操作,Hibernate会自动生成SQL语句。相对 Hibernate而言,mybatis以SQL开发的工作量和数据库移植性上的让步,为系统设计提供更大的自由空间。
mybatis 与 hibernate 区别
相同点:
Hibernate与MyBatis都是通过SessionFactoryBuider由XML配置文件生成SessionFactory,然后由SessionFactory 生成Session,最后由Session来开启执行事务和SQL语句。其中SessionFactoryBuider,SessionFactory,Session的生命周期都是差不多的。都支持JDBC和JTA事务处理。
- mybatis 简单易学,轻量;Hibernate相对较复杂,门槛较高,设计O/R映射,在性能和对象模型之间如何权衡取得平衡。Hibernate功能强大,数据库无关性好,O/R映射能力强。
- 当系统属于二次开发,无法对数据库结构做到控制和修改,那mybatis的灵活性将比Hibernate更适合。
- 系统数据处理量巨大,性能要求极为苛刻,这往往意味着必须通过经过高度优化的SQL语句(或存储过程)才能达到系统性能设计指标。在这种情况下mybatis会有更好的可控性和表现。mybatis比Hibernate更容易进行sql的优化。鉴于一般系统性能的瓶颈都在数据库上,所以这一点是mybatis非常重要的一个优势。
- mybatis 需要手写sql语句,也可以生成,MyBatis可以进行更为细致的SQL优化,可以减少查询字段。Hibernate则基本上可以自动生成,偶尔会写一些Hql。同样的需求,mybatis 的工作量比Hibernate要大很多。类似的,如果涉及到数据库字段的修改,Hibernate修改的地方很少,而mybatis 要把那些sql mapping的地方一一修改。
- 运行效率:在不考虑cache的情况下,mybatis 应该会比hibernate快一些或者很多(根据实际情况会有所不同)。
- 缓存:细节很多,单独另说;
hibernate 优势:
- Hibernate的DAO层开发比MyBatis简单,Mybatis需要维护SQL和结果映射。
- Hibernate对对象的维护和缓存要比MyBatis好,对增删改查的对象的维护要方便。
- Hibernate数据库移植性很好,MyBatis的数据库移植性不好,不同的数据库需要写不同SQL。
- Hibernate有更好的二级缓存机制,可以使用第三方缓存。MyBatis本身提供的缓存机制不佳。
参考:
Hibernate3和MyBatis(iBatis)的执行效率比较
缓存
Hibernate缓存
Hibernate一级缓存是Session缓存,利用好一级缓存就需要对Session的生命周期进行管理好。建议在一个Action操作中使用一个Session。一级缓存需要对Session进行严格管理。
Hibernate二级缓存是SessionFactory级的缓存。 SessionFactory的缓存分为内置缓存和外置缓存。内置缓存中存放的是SessionFactory对象的一些集合属性包含的数据(映射元素据及预定SQL语句等),对于应用程序来说,它是只读的。外置缓存中存放的是数据库数据的副本,其作用和一级缓存类似.二级缓存除了以内存作为存储介质外,还可以选用硬盘等外部存储设备。二级缓存称为进程级缓存或SessionFactory级缓存,它可以被所有session共享,它的生命周期伴随着SessionFactory的生命周期存在和消亡。
MyBatis缓存
包括一级和二级。Mybatis默认查询顺序:二级缓存>一级缓存>数据库。
一级缓存:局部的Session会话级别的数据缓存。是为了短时间的一样的查询带来的资源浪费,MyBatis会在SqlSession对象中建立一个简单的缓存,将每次查询到的结果结果缓存起来,当下次查询时,如果判断先前有个完全一样的查询,会直接从缓存中直接将结果取出,返回给用户,不需要再进行一次数据库查询。默认开启。
二级缓存:默认关闭。需要手动在SQL映射文件中,如UserMapper.xml配置cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));。作用:
- 映射语句文件中的所有 select 语句将会被缓存。
- 映射语句文件中的所有 insert,update 和 delete 语句会刷新缓存。
- 缓存会使用 Least Recently Used(LRU,最近最少使用的)算法来回收。
- 根据时间表(比如 no Flush Interval,没有刷新间隔),缓存不会以任何时间顺序来刷新。
- 缓存会存储列表集合或对象(无论查询方法返回什么)的 1024 个引用。
- 缓存会被视为是 read/write(可读/可写)的缓存,意味着对象检索不是共享的,而且可以安全地被调用者修改,而不干扰其他调用者或线程所做的潜在修改。
所有的这些属性都可以通过缓存元素的属性来修改。
比如:
这个更高级的配置创建了一个 FIFO 缓存,并每隔 60 秒刷新,存数结果对象或列表的 512 个引用,而且返回的对象被认为是只读的,因此在不同线程中的调用者之间修改它们会导致冲突。可用的收回策略有, 默认的是 LRU:
LRU – 最近最少使用的:移除最长时间不被使用的对象。
FIFO – 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。
SOFT – 软引用:移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。
WEAK – 弱引用:更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。
flushInterval(刷新间隔)可以被设置为任意的正整数,而且它们代表一个合理的毫秒形式的时间段。默认情况是不设置,也就是没有刷新间隔,缓存仅仅调用语句时刷新。
size(引用数目)可以被设置为任意正整数,要记住你缓存的对象数目和你运行环境的可用内存资源数目。默认值是1024。
readOnly(只读)属性可以被设置为 true 或 false。只读的缓存会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例。因此这些对象不能被修改。这提供了很重要的性能优势。可读写的缓存会返回缓存对象的拷贝(通过序列化) 。这会慢一些,但是安全,因此默认是 false。
对比
相同点
Hibernate和Mybatis的二级缓存除了采用系统默认的缓存机制外,都可以通过实现你自己的缓存或为其他第三方缓存方案,创建适配器来完全覆盖缓存行为。
不同点
Hibernate的二级缓存配置在SessionFactory生成的配置文件中进行详细配置,然后再在具体的表-对象映射中配置是那种缓存。
MyBatis的二级缓存配置都是在每个具体的表-对象映射中进行详细配置,这样针对不同的表可以自定义不同的缓存机制。并且Mybatis可以在命名空间中共享相同的缓存配置和实例,通过Cache-ref来实现。
Hibernate对查询对象有着良好的管理机制,用户无需关心SQL。所以在使用二级缓存时如果出现脏数据,系统会报出错误并提示;MyBatis使用二级缓存时需要特别小心。如果不能完全确定数据更新操作的波及范围,避免Cache的盲目使用,否则会有脏数据。
参考:
Hibernate与MyBatis的对比
com.mysql.jdbc.MysqlDataTruncation: Data truncation: Data too long for column ‘*’ at row 1
mybatis + MySQL 存储数据时遇到上面的报错,第一反应是去检查数据库表的DDL语句,以及查看待执行的 SQL 语句,但是两者都没有问题。最后才发现 mybatis 的 mapper.xml 文件里面的需要严格对应起来,即顺序。
<insert id="insert" parameterType="SomePO">
INSERT INTO order_data (
DemandOrderId, OrderFromWeight, OtherRequirementWeight, InterceptWeight)
VALUES (
#{po.demandOrderId},
#{po.orderFromWeight},
#{po.interceptWeight},
#{po.otherRequirementWeight})
insert>
比如上面的sampleMapper.xml 文件的写法有问题,
mybatis mapper xml 特殊符号转义写法
| 特殊符号 | 符号 | 意义 |
|---|---|---|
< |
< | 小于 |
<= |
<= | 小于或等于 |
> |
> | 大于 |
>= |
>= | 大于或等于 |
<> |
<> | 不等于 |
& |
& | 逻辑与 |
' |
’ | 单引号 |
" |
" | 双引号 |
也可以使用<[CDATA[ ]]>符号进行说明,将此类符号不进行解析,比如写 < > = 等:
MySQL like的写法
like concat('%',#{param},'%') 或者 like '%${param}%',推荐使用前者,可以避免SQL注入。
mybatis配置多个typeAliase
在mybatis-config.xml文件里面配置:
<typeAliases>
<package name="cn.caijiajia.campaign.common.domain" />
<package name="cn.caijiajia.campaign.common.form" />
<package name="cn.caijiajia.campaign.common.domain.vo" />
typeAliases>
mybatis + MySQL 实现分页
方式一:
<sql id="Base_Column_List">
TargetID, UID, UName, UserId
sql>
<select id="searchByCondition" resultType="com.johnny.user.entity.CfgOrgUserTargetGmv">
SELECT
<include refid="Base_Column_List"/>
FROM cfg_orguser_targetgmv where 1=1
<if test="name != null and name !='' ">
and (UName like concat(concat("%", #{name}), "%") or UID like concat(concat("%", #{name}), "%") or
UserId like concat(concat("%", #{name}), "%"))
if>
<if test="pageIndex != null and pageSize != null ">
limit #{pageIndex}, #{pageSize}
if>
select>
对应的 Java mapper接口:
List
mybatis注解@MapKey使用
适用场景:
从数据库查询得到两个数据,是一一对应的k-v对形式的数据,现在希望把结果直接用Map接收,然后通过map.get(id)方便地获取name的值。
示例代码:
Map<String, SomeInfo> selectedSomeInfoMap = mgmContactsInfoMapper.getSelectedSomeInfoMap("csdn", uid);
对应的 mapper 文件的写法,这里面的mobile得是数据库的字段,SomeInfo的信息也得是直接或间接来自于数据库,查询条件可以有多个:
@MapKey("mobile")
Map<String, SomeInfo> getSelectedSomeInfoMap(@Param("appName") String appName, @Param("uid") String uid);
使用,注意这里需要对结果info做一下判空处理:
SomeInfo info = selectedSomeInfoMap.get(mobile);
mybatis 返回 list
Java 代码即 mapper 接口里面有一个接口需要返回一个 list 数据:
List
对应的 mapper.xml 文件:
<select id="getParentPathByPoid" resultMap="parentPathList">
SELECT ParentPath FROM BaoTuan_POI WHERE Poid = #{poid} AND DataStatus = 1 AND DataType='D'
select>
<resultMap id="parentPathList" type="java.lang.String">
<result column="ParentPath" property="parentPath" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
resultMap>
注意到上面的 jdbcType="VARCHAR" 如果写成 jdbcType="STRING",则会抛异常:
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: No enum constant org.apache.ibatis.type.JdbcType.STRING
遇到这种问题时,打开源码即可。根本就不需要像无头苍蝇一样去Google,需要学会去看源码,看error stack trace。
mapper.xml 文件可以配置有多个
列名和bean属性名不一样导致获取不到数据
如下,parent_path是数据表的字段名,即列名;property是表实体POJO的属性名,一般在Java中属性名使用驼峰命名方式,但是MySQL表的字段名建议是下划线。这样mybatis通过反射得到 bean时,无法将查询到的表字段数据 set 到 bean 属性中。通过下面配置实现一一对应。
<resultMap id="parentPathList" type="java.lang.String">
<result column="parent_path" property="parentPath" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
resultMap>
mybatis 实现插入或者更新
CRUD 开发中,经常遇到一种场景就是依据待保存的数据的情况,实现插入新纪录或者更新记录。mybatis 模版代码如下:
<insert id="insertUpdate" parameterType="com.johnny.online.entity.User">
<selectKey keyProperty="count" resultType="int" order="BEFORE">
select count(*) from user where user_id= #{userId}
selectKey>
<if test="count > 0">
update user
set username= #{username}
where user_id= #{userId}
if>
<if test="count==0">
insert into user (user_id,username,userpass) values(#{userId},#{username},#{userpass})
if>
insert>
待进一步研究,不能实现:
<update id="insertUpdate" parameterType="CfgOrgUserTargetGmv">
insert into cfg_orguser_targetgmv(TargetID, UID, UName, PlatformUserId, PlatformProviderId, GMVQuarter1Target, GMVQuarter2Target,
GMVQuarter3Target, GMVQuarter4Target, GMVAnnualTarget, CreateUser, ModifyUser, UserGroupId, UserGroupName)
VALUES
(#{po.targetId}, #{po.uid}, #{po.saleName}, #{po.platformUserId}, #{po.platformProviderId}, #{po.gmvQuarter1Target}, #{po.gmvQuarter2Target},
#{po.gmvQuarter3Target}, #{po.gmvQuarter4Target}, #{po.gmvAnnualTarget}, #{po.createUser}, #{po.modifyUser}, #{po.userGroupId}, #{po.userGroupName})
on duplicate key UPDATE targetId = VALUES(TargetID)
update>
Mybatis 模糊查询 MySQL 中记录的三种常用方法
以MySQL数据库为例(不同的数据库,有些可能不支持)
常用的模糊查询有三种方法:
- 直接使用 % 拼接字符串,如
'%'#{name}'%'或"%"#{name}"%",单引号或双引号都可以。 - 使用concat(str1,str2)函数拼接
- 使用mybatis的bind标签
示例:在userMapper.xml文件中新建映射sql的标签:
<select id="getUsersByFuzzyQuery" parameterType="User" resultType="User">
select <include refid="columns"/> from users
<where>
<if test="name != null">
name like "%"#{name}"%"
if>
<if test="phone != null">
and phone like concat(concat("%",#{phone}),"%")
if>
<if test="email != null">
<bind name="pattern" value="'%'+email+'%'"/>
and email like #{pattern}
if>
where>
select>
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Result Maps collection already contains value for *
常规的SSM应用启动失败,报错:
Cause: org.apache.ibatis.builder.BuilderException: Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: java.lang.RuntimeException: Error parsing Mapper XML. Cause: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Mapped Statements collection already contains value for GeographyMapper.getByCode.
定位原因是在 mybatis 的 mapper.xml 文件里面有重复的 id 定义。
<select id="getByCode" resultType="Geography"
parameterType="java.lang.String">
select * from Geography where code = ${code}
select>
<select id="getByCode" resultType="Geography"
parameterType="java.lang.String">
select * from Geography where fullName = ${fullName}
select>
org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.TooManyResultsException: Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: 2
如下一条简单的 SQL 语句,期望返回一条记录,即一个 poid 最多有一条记录,但是现在测试环境的脏数据有两个记录(没有添加唯一索引),导致这个报错:
<select id="getParentPathByPoid" resultType="string">
SELECT ParentPath FROM POI WHERE Poid = #{poid} AND DataStatus = 1
select>
解决方法:
- 删除测试环境的脏数据;
- 在末尾加上
limit 1,如果是 SQL server 数据源,则改为SELECT top 1 ParentPath FROM POI WHERE Poid = #{poid} AND DataStatus = 1; - 改写 mapper 的 SQL 语句,获取
list,然后过滤;
The entity name must immediately follow the ‘&’ in the entity reference
mybatis 解析不了&&,mapper.xml 文件如下:
<update id="update" parameterType="Geography">
update Geography
<trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="code != null && code !=''">
code=#{code},
if>
<if test="name != null && name != ''">
name=#{name},
if>
trim>
where id= #{id}
update>
解决方法:使用正确的语法,用and替换&&
mybatis调用存储过程
非常不建议。不过作为示例,还是记录一下。
<select id="archiveCoupons" statementType="CALLABLE">
CALL sp_coupon_archive(#{reserveDays});
select>
对应的 mapper 接口:
void archiveCoupons(@Param("reserveDays") int reserveDays);
mybatis自定义标签
定义一个sql标签:
<sql id="restrict_app">
(app_name = 'all' OR app_name LIKE CONCAT('%', #{appName}, '%'))
sql>
使用:
UPDATE user_task
SET status = 'VIEWED', updated_at = now()
WHERE `type` = #{type} AND
@Param注解
用于给mapper接口方法的参数指定一个别名,若接口只有一个参数则可以不用指定别名,List 参数除外。当有多个参数时一定要指定,否则 mybatis 映射不到对应的字段。另外:
使用@Param注解来声明参数时,使用 #{} 或 ${} 的方式都可以。
不使用@Param注解来声明参数时,必须使用 #{}方式。使用 ${} 会报错:org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ReflectionException: There is no getter for property named 'day' in 'class java.lang.String'
@Select("select column from table where userid = #{userid} ")
public int selectColumn(int userid);
那么#{}和${}有什么区别呢?
#{} 表示一个占位符,通过 #{} 可以实现preparedStatement 向占位符中设置值,自动进行java 类型和 JDBC 类型转换;${}将传入的数据直接显示生成在sql中。#{} 可以有效防止 SQL 注入。
Mybatis 传递多个参数的几种方式
方法1:顺序传参法
public User selectUser(String name, int deptId);
<select id="selectUser" resultMap="UserResultMap">
select * from user
where user_name = #{0} and dept_id = #{1}
select>
#{}里面的数字代表你传入参数的顺序。
不建议使用,1. 参考上文,只能使用#{},且易导致SQL 注入;2. 顺序需要严格控制;3. 参数过大,影响阅读代码,不符合编码规范。
方法2:@Param注解传参法
public User selectUser(@Param("name") String name, @Param("deptId") int deptId);
略,有效防止 SQL 注入,但是仅仅推荐在参数不多的情况使用。
方法3:Java Bean传参法
public User selectUser(Map
<select id="selectUser" parameterType="com.johnny.demo.domain.User" resultMap="UserResultMap">
select * from user
where user_name = #{User.userName} and dept_id = #{User.deptId}
select>
#{}里面的名称对应的是 User类里面的成员属性。直观。
方法4:Map 传参法
public User selectUser(Map
<select id="selectUser" parameterType="java.util.Map" resultMap="UserResultMap">
select * from user
where user_name = #{userName} and dept_id = #{deptId}
select>
#{}里面的名称对应的是 Map里面的key名称。
这种方法适合传递多个参数,且参数易变能灵活传递的情况。但是 HashMap 的 key 存在 hard code 的问题。
批量更新以及单个更新
实现批量更新on duplicate key UPDATE :
<insert id="duplicateUpdate" parameterType="User">
insert into user(id, uid, name, certificate_type, certificate_no, from_app_name, mobile, mobile_id_md5)
VALUES
<foreach collection="list" item="user" separator=",">
(#{user.id}, #{user.uid}, #{user.name}, #{user.certificateType}, #{user.certificateNo},#{user.fromAppName}, #{user.mobile}, #{user.mobileAndCertificateNoMD5})
foreach>
on duplicate key UPDATE
id = VALUES (id)
insert>
单个记录的更新on duplicate key UPDATE:
<update id="insertUpdate" parameterType="User">
insert into user(id, uid, name, certificate_type, certificate_no, from_app_name, mobile, mobile_id_md5)
VALUES
(#{id}, #{uid},#{name}, #{certificateType}, #{certificateNo}, #{fromAppName}, #{mobile}, #{mobileAndCertificateNoMD5})
on duplicate key UPDATE
id = VALUES (id)
update>
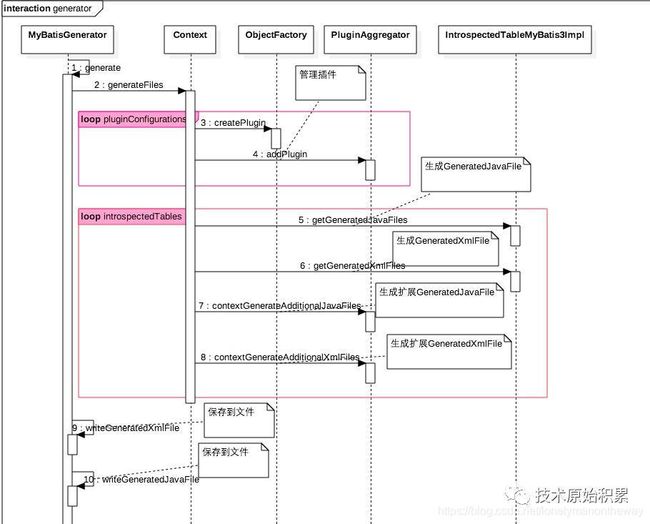
generatorConfig
使用Mybatis Generator 这个maven插件来快速生成Dao类,mapper 配置文件和 Model 类。MyBatis Generator是MyBatis的代码生成器.可以自动查询数据库中的所有表,然后生成可以访问表的基础对象类型.解决了对数据库操作有最大影响的一些简单的CRUD增删改查操作,但是仍需要对联合查询和存储过程手写SQL语句和对象。
使用 mybatis-generator 步骤:
- pom.xml 文件新增配置:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generatorgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-maven-pluginartifactId>
<version>1.3.7version>
<configuration>
<configurationFile>${basedir}/src/main/resources/mybatis/generatorConfig.xmlconfigurationFile>
<verbose>trueverbose>
<overwrite>trueoverwrite>
configuration>
plugin>
如果不使用maven配置的话,也可以使用单元测试或者main入口函数的形式:
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, IOException, InterruptedException, XMLParserException, InvalidConfigurationException {
List<String> warnings = new ArrayList<>();
boolean overwrite = true;
// 配置文件
File configFile = new File("generatorConfig.xml");
ConfigurationParser cp = new ConfigurationParser(warnings);
Configuration config = cp.parseConfiguration(configFile);
DefaultShellCallback callback = new DefaultShellCallback(overwrite);
MyBatisGenerator myBatisGenerator = new MyBatisGenerator(config, callback, warnings);
myBatisGenerator.generate(null);
}
- 新增 generatorConfig.xml:
<generatorConfiguration>
<classPathEntry location="mysql-connector-java-5.1.45-bin.jar"/>
<context id="default" targetRuntime="MyBatis3">
<property name="beginningDelimiter" value="`"/>
<property name="endingDelimiter" value="`"/>
<commentGenerator>
<property name="suppressDate" value="true"/>
<property name="suppressAllComments" value="false"/>
commentGenerator>
<jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://:3306/?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8" userId="me" password="myPass">
jdbcConnection>
<javaTypeResolver>
<property name="forceBigDecimals" value="false"/>
javaTypeResolver>
<javaModelGenerator targetPackage="com.johnny.onlinemall.domain" targetProject="../src/main/java">
<property name="constructorBased" value="false"/>
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false"/>
<property name="immutable" value="false"/>
<property name="trimStrings" value="true"/>
javaModelGenerator>
<sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="com.johnny.onlinemall.mapper" targetProject="../src/main/resources">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false"/>
sqlMapGenerator>
<javaClientGenerator targetPackage="com.johnny.onlinemall.mapper" targetProject="../src/main/java" type="MIXEDMAPPER">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value=""/>
<property name="exampleMethodVisibility" value=""/>
<property name="methodNameCalculator" value=""/>
<property name="rootInterface" value=""/>
javaClientGenerator>
<table tableName="trans_log" delimitIdentifiers="true" delimitAllColumns="true"/>
context>
generatorConfiguration>
- 命令行:
mvn mybatis-generator:generate -e,-e参数是为了输出错误信息,方便排查问题。看到“BUILD SUCCESS”表示成功生成。
原理
mybatis-config.xml配置文件
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="multipleResultSetsEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="REUSE"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="false"/>
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="true"/>
<setting name="defaultStatementTimeout" value="25000"/>
settings>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/basessm/dao/UserMapper.xml"/>
mappers>
configuration>
Mybatis缓存
MyBatis-Plus
官网:http://mp.baomidou.com/
简称MP,Mybatis增强工具,在 Mybatis 的基础上只做增强不做改变,为简化开发、提高效率而生。
功能:
提供Mapper接口与配置文件中对应SQL的导航
编辑XML文件时自动补全
根据Mapper接口, 使用快捷键生成xml文件及SQL标签
ResultMap中的property支持自动补全,支持级联(属性A.属性B.属性C)
快捷键生成@Param注解
XML中编辑SQL时, 括号自动补全
XML中编辑SQL时, 支持参数自动补全(基于@Param注解识别参数)
自动检查Mapper XML文件中ID冲突
自动检查Mapper XML文件中错误的属性值
支持Find Usage
支持重构从命名
支持别名
自动生成ResultMap属性