数据结构Collection-----Vector及其子类Stack源码解析
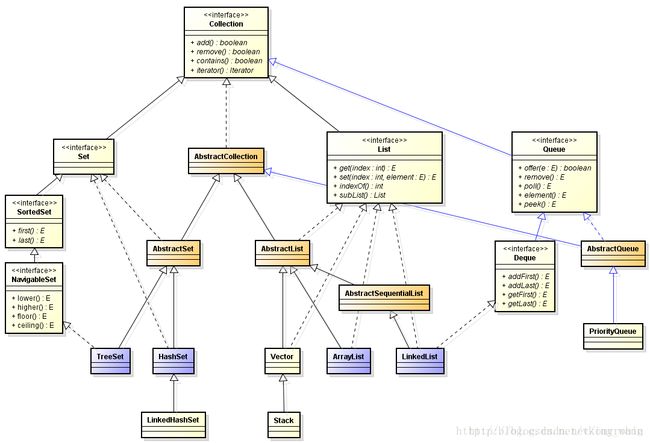
继承关系
通过图片我们能够看出Stack是Vector的子类,Stack就是常说的栈结构
Vector:重要的属性和构造方法
public class Vector<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>,
RandomAccess, Cloneable, Serializable {
/**
* The number of elements or the size of the vector.
* 数据元素数量
*/
protected int elementCount;
/**
* The elements of the vector.
* 底层实现Object数组
*/
protected Object[] elementData;
/**
* How many elements should be added to the vector when it is detected that
* it needs to grow to accommodate extra entries. If this value is zero or
* negative the size will be doubled if an increase is needed.
*
* 扩容因子,扩容量,稍后遇到的时候会介绍
*/
protected int capacityIncrement;
//默认数组长度
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 10;
/**
* Constructs a new vector using the default capacity.
*/
public Vector() {
this(DEFAULT_SIZE, 0);
}
/**
* Constructs a new vector using the specified capacity.
*
* @param capacity
* the initial capacity of the new vector.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* if {@code capacity} is negative.
*/
public Vector(int capacity) {
this(capacity, 0);
}
/**
* Constructs a new vector using the specified capacity and capacity
* increment.
*
* 由于上面两个构造最终调用的都是这个构造函数,我们来看这个构造
*
* @param capacity
* the initial capacity of the new vector.
* @param capacityIncrement
* the amount to increase the capacity when this vector is full.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* if {@code capacity} is negative.
*
*/
public Vector(int capacity, int capacityIncrement) {
//没什么好说的,设定数组长度必须大于0
if (capacity < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("capacity < 0: " + capacity);
}
//初始化数组、数据元素数量和扩容因子(注意这里有扩容因子的初始化操作,前两个构造默认值都是0)
elementData = newElementArray(capacity);
elementCount = 0;
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
- 增加
@Override
public synchronized boolean add(E object) {
//数据元素数量和数组数据量相等,说明数组容量不足需要扩容
if (elementCount == elementData.length) {
growByOne();
}
//数组的增加数据操作,相信都看的懂
elementData[elementCount++] = object;
//计数器++
modCount++;
return true;
}
//接下来我们看看扩容的时候发生了什么,这里就需要扩容因子这个变量了
private void growByOne() {
int adding = 0;
//判断扩容因子是否小于等于0,我们知道使用无参和1个参数构造的时候,都未指定扩容因子的大小,默认值就是0
if (capacityIncrement <= 0) {
//如果未指定capacityIncrement 的值,adding赋值为当前数组的长度,如果数组长度为0,那么
//adding赋值为1
if ((adding = elementData.length) == 0) {
adding = 1;
}
} else {
//如果指定了一个大于0的capacityIncrement ,adding赋值为capacityIncrement扩容因子值
adding = capacityIncrement;
}
//重新构建一个数组,数组长度为elementData.length + adding
//简单理解如果未指定capacityIncrement 的值,原容量*2(0的时候+1)
//指定capacityIncrement 的值,原容量+capacityIncrement
E[] newData = newElementArray(elementData.length + adding);
System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, newData, 0, elementCount);
elementData = newData;
}
@Override
public void add(int location, E object) {
insertElementAt(object, location);
}
public synchronized void insertElementAt(E object, int location) {
if (location >= 0 && location <= elementCount) {
//扩容操作
if (elementCount == elementData.length) {
growByOne();
}
int count = elementCount - location;
if (count > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, location, elementData,
location + 1, count);
}
elementData[location] = object;
//数据元素数量++
elementCount++;
//计数器++
modCount++;
} else {
throw arrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(location, elementCount);
}
}- 删除
/**
* 没什么好说的,就是数组操作
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public synchronized E remove(int location) {
if (location < elementCount) {
E result = (E) elementData[location];
elementCount--;
int size = elementCount - location;
if (size > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, location + 1, elementData,
location, size);
}
elementData[elementCount] = null;
modCount++;
return result;
}
throw arrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(location, elementCount);
}- 修改
/**
* 直接将数组location位置数据,数组操作替换
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public synchronized E set(int location, E object) {
if (location < elementCount) {
E result = (E) elementData[location];
elementData[location] = object;
return result;
}
throw arrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(location, elementCount);
}- 查找
/**
* 不想说话
*/
@Override
public E get(int location) {
return elementAt(location);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized E elementAt(int location) {
if (location < elementCount) {
return (E) elementData[location];
}
throw arrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(location, elementCount);
}总结:基本上除了扩容方式和ArrayList有所区别(可以根据capacityIncrement自行控制扩容数量),还有相关操作函数都带有synchronized 关键字外(线程安全),基本是类似的
Stack:重要的属性和构造方法
public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> {
/**
* Constructs a stack with the default size of {@code Vector}.
* 尴尬,没啥太重要的,Stack毕竟是继承自Vector
*/
public Stack() {
}
}提到栈结构,我们不得不说栈中很重要的概念,出栈和入栈。
- 出栈
/**
* Returns the element at the top of the stack and removes it.
* * @return the element at the top of the stack.
* @throws EmptyStackException
* if the stack is empty.
* @see #peek
* @see #push
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized E pop() {
//elementCount 继承自Vector的属性,如果是0抛出异常
if (elementCount == 0) {
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
//数据元素数量--
final int index = --elementCount;
//获取最后一个元素
final E obj = (E) elementData[index];
//将最后一个元素置空
elementData[index] = null;
//计数器++
modCount++;
return obj;
}栈结构出栈就是置空栈顶(最后一个)元素,所以栈结构是一种后进先出的线性表结构也叫做LIFO(Last in First out)表
这里我们会发下一个很有趣的现象,这里并没有像Vector.remove元素的时候采取的重新构建数组的方式,而是只是将栈顶(最后一个)元素置空,这是为了什么呢,因为在栈中,出栈入栈是最基本也是最普遍的操作相对来说比较频繁,如果我每次出栈都要重新构建数组长度,重新分配内存,每次入栈的时候又要扩容,实在是太小家子气了!
- 入栈
/**
* Pushes the specified object onto the top of the stack.
*
* @param object
* The object to be added on top of the stack.
* @return the object argument.
* @see #peek
* @see #pop
*/
public E push(E object) {
addElement(object);
return object;
}
addElement是Vector中的方法,也就是Stack父类的方法
/**
* Adds the specified object at the end of this vector.
* * @param object
* the object to add to the vector.
*/
public synchronized void addElement(E object) {
//扩容操作,是不是很眼熟和Vector的add区别不大,但是这里需要注意的是,因为上文提到出栈操作中并没有将
//elemetData数组像Vector.remove重新构建数组,所以elementData.length并没有发生变化,只不过出
//栈的元素赋值为null了,所以elementCount表示的是非null元素的数量,只有在栈中非null元素数量和数
//组长度相同时,才进行扩容操作,否则直接入栈进行类似set一样的修改操作,将null元素赋值
if (elementCount == elementData.length) {
growByOne();
}
elementData[elementCount++] = object;
modCount++;
}- 查找
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the object, starting from
* the top of the stack.
*
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the object, assuming that
* the topmost object on the stack has a distance of one.
* @param o
* the object to be searched.
*/
public synchronized int search(Object o) {
final Object[] dumpArray = elementData;
final int size = elementCount;
if (o != null) {
//从数组elementData的栈顶(elementData)开始查找,返回找到的第一个对象所在的下标位置
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (o.equals(dumpArray[i])) {
return size - i;
}
}
} else {
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (dumpArray[i] == null) {
return size - i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}栈结构在查找元素的时候也是先从栈顶(最后一个)元素开始向栈底(第一个元素)进行遍历。
我们做Android都对Activity不陌生,Activity就是一个标准的使用栈这种数据结构来存储的,还有一种标准的栈结构,就是波兰表达式,也是后缀表达式,我们数学课堂上学的四则运算称之为中缀表达式,但是计算机是无法理解的,而计算机采用的就是后缀表达式来处理,而中缀向后缀的转换过程就使用的栈这种数据结构。
中缀表达式 :
9+(3-1)*3+10/2 = 20
后缀表达式 :
931-3*+10 2/+
923*+10 2/ +
96+10 2/ +
15 10 2/ +
15 5 +
20
具体如何转换的不在本章讨论范围,而且连表达式都是抄的,我就不班门弄斧了。