Lombok 使用(maven+idea的环境下)
Lombok 使用(maven+idea的环境下)
官网对Lombok的解释:
Project Lombok是一个java库,可以自动插入编辑器并构建工具,为您的java增添色彩。
永远不要再写另一个getter或equals方法,使用一个注解,您的类具有一个功能齐全的构建器,自动化您的日志记录变量等等。
官网网址为:https://projectlombok.org/
一、编译 javac(https://projectlombok.org/)
在使用任何javac(版本1.6 - 1.8)编译时,只需将lombok放在类路径上:javac -cp lombok.jar ....
JDK 9
对于JDK9的支持,如果你尚未模块化自己的项目(还没有module-info.java),则从版本1.16.20开始包含在lombok中。 正常使用lombok:javac -cp lombok.jar ...
如果你模块化自己的项目(你已经编写了一个module-info.java文件),那么在边缘版本中可以获得对JDK9的支持。 使用它:javac -cp lombok.jar -p lombok.jar ...
请注意,您必须将lombok添加到module-info.java文件中:
module myapp {
requires static lombok;
}确保'static'部分不会在运行时出现lombok。
二、maven依赖(https://projectlombok.org/setup/maven)
1、添加Maven依赖
为了能在工程中使用Lombok,工程中需要引入Lombok的Maven依赖
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.18.6
provided
2、Delomboking:Lombok Maven插件
官方推荐使用这个maven插件来delombok。 如果要在应用lombok之后在源上运行源分析工具,或者如果要生成javadoc,这个插件很有用。
三、idea(https://projectlombok.org/setup/intellij)
Jetbrains IntelliJ IDEA编辑器与lombok兼容。
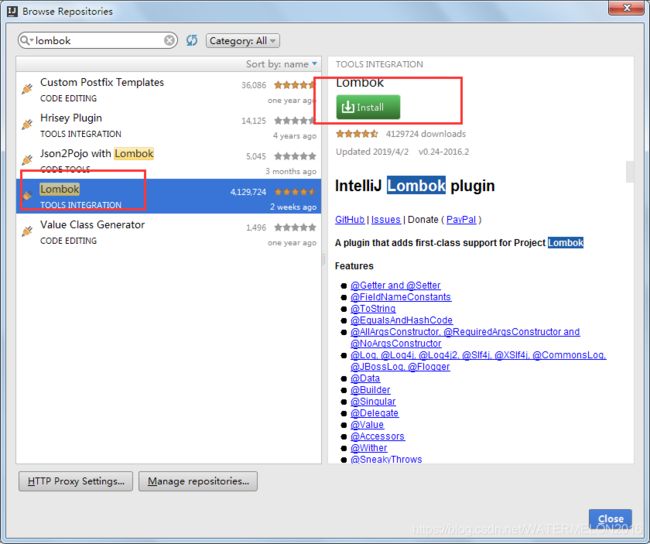
添加Lombok IntelliJ插件以添加对IntelliJ的lombok支持:
(1)转到File > Settings > Plugins
(2)单击Browse repositories ...
(3)搜索Lombok插件
(4)单击“Install plugin”
(5)重启IntelliJ IDEA
四、使用(https://projectlombok.org/features/all)
详细使用教程可以看上面网址,这里简单介绍一下常见注解的使用。
1、@Data
这个注解的功能:
1) @ToString: 涉及类字段的相应 toString实现
2) @EqualsAndHashCode:涉及类字段的相应 equals和hashCode实现
3) @Getter:所有字段的getter
4) @Setter: 所有非final字段的setter
5) @RequiredArgsConstructor: 初始化所有final字段的构造函数,所有非final字段并没有使用@NonNull标记。(构造函数只包含final字段,不包含非final字段)
-
访问级别
使用生成的@Getter和@Setter都是public的。 要覆盖访问级别,请使用显式的@Setter和/或@Getter批注对字段或类进行批注。您还可以使用此批注(通过将其与AccessLevel.NONE组合)来完全禁止生成getter和/或setter。
-
存在方法则不会产生
如果类已经包含与通常生成的任何方法具有相同名称和参数计数的方法,则不会生成该方法,也不会发出警告或错误。例如,如果您已经有一个签名为equals(AnyType param)的方法,则不会生成equals方法,即使从技术上讲,由于具有不同的参数类型,它可能是完全不同的方法。同样的规则适用于构造函数(任何显式构造函数都会阻止@Data生成一个),以及toString,equals和所有getter和setter。您可以使用@ lombok.experimental.Tolerate标记任何构造函数或方法,以将它们隐藏在lombok中。
-
staticConstructor参数
@Data可以很好地处理字段的泛型参数。为了在为具有泛型的类构造对象时减少样板,可以使用staticConstructor参数来调用私有构造函数,以及返回新实例的静态方法。这样,javac将推断变量名称。因此,通过这样声明:@Data(staticConstructor =“of”)类Foo
Lombok写法
import lombok.AccessLevel;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.ToString;
@Data public class DataExample {
private final String name;
@Setter(AccessLevel.PACKAGE) private int age;
private double score;
private String[] tags;
@ToString(includeFieldNames=true)
@Data(staticConstructor="of")
public static class Exercise {
private final String name;
private final T value;
}
} 普通java写法
import java.util.Arrays;
public class DataExample {
private final String name;
private int age;
private double score;
private String[] tags;
public DataExample(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
public double getScore() {
return this.score;
}
public String[] getTags() {
return this.tags;
}
public void setTags(String[] tags) {
this.tags = tags;
}
@Override public String toString() {
return "DataExample(" + this.getName() + ", " + this.getAge() + ", " + this.getScore() + ", " + Arrays.deepToString(this.getTags()) + ")";
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof DataExample;
}
@Override public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) return true;
if (!(o instanceof DataExample)) return false;
DataExample other = (DataExample) o;
if (!other.canEqual((Object)this)) return false;
if (this.getName() == null ? other.getName() != null : !this.getName().equals(other.getName())) return false;
if (this.getAge() != other.getAge()) return false;
if (Double.compare(this.getScore(), other.getScore()) != 0) return false;
if (!Arrays.deepEquals(this.getTags(), other.getTags())) return false;
return true;
}
@Override public int hashCode() {
final int PRIME = 59;
int result = 1;
final long temp1 = Double.doubleToLongBits(this.getScore());
result = (result*PRIME) + (this.getName() == null ? 43 : this.getName().hashCode());
result = (result*PRIME) + this.getAge();
result = (result*PRIME) + (int)(temp1 ^ (temp1 >>> 32));
result = (result*PRIME) + Arrays.deepHashCode(this.getTags());
return result;
}
public static class Exercise {
private final String name;
private final T value;
private Exercise(String name, T value) {
this.name = name;
this.value = value;
}
public static Exercise of(String name, T value) {
return new Exercise(name, value);
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public T getValue() {
return this.value;
}
@Override public String toString() {
return "Exercise(name=" + this.getName() + ", value=" + this.getValue() + ")";
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof Exercise;
}
@Override public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Exercise)) return false;
Exercise other = (Exercise) o;
if (!other.canEqual((Object)this)) return false;
if (this.getName() == null ? other.getValue() != null : !this.getName().equals(other.getName())) return false;
if (this.getValue() == null ? other.getValue() != null : !this.getValue().equals(other.getValue())) return false;
return true;
}
@Override public int hashCode() {
final int PRIME = 59;
int result = 1;
result = (result*PRIME) + (this.getName() == null ? 43 : this.getName().hashCode());
result = (result*PRIME) + (this.getValue() == null ? 43 : this.getValue().hashCode());
return result;
}
}
} 支持的配置键:
lombok.data.flagUsage = [warning | error] (default: not set)(默认:未设置)
如果已配置,Lombok会将@Data的任何用法标记为警告或错误。
2、@Getter/@Setter
不用再写public int getFoo(){return foo;}。
可以使用@Getter和/或@Setter注释任何字段,让lombok自动生成默认的getter / setter。自动生成的getter/setter方法和idea自动生成的是一样的。
除非明确指定AccessLevel,否则生成的getter / setter方法将是公共的,如下面的示例所示。合法访问级别为PUBLIC,PROTECTED,PACKAGE和PRIVATE。
还可以在类上放置@Getter和/或@Setter注解。在这种情况下,就像使用注解注释该类中的所有非静态字段。
可以使用特殊的AccessLevel.NONE访问级别手动禁用任何字段的getter / setter生成。这可以覆盖类上@Getter,@ Setter或@Data注解的行为。
使用Lombok表达式
import lombok.AccessLevel;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
public class GetterSetterExample {
/**
* Age of the person. Water is wet.
*
* @param age New value for this person's age. Sky is blue.
* @return The current value of this person's age. Circles are round.
*/
@Getter @Setter private int age = 10;
/**
* Name of the person.
* -- SETTER --
* Changes the name of this person.
*
* @param name The new value.
*/
@Setter(AccessLevel.PROTECTED) private String name;
@Override public String toString() {
return String.format("%s (age: %d)", name, age);
}
}
不使用Lombok
public class GetterSetterExample {
/**
* Age of the person. Water is wet.
*/
private int age = 10;
/**
* Name of the person.
*/
private String name;
@Override public String toString() {
return String.format("%s (age: %d)", name, age);
}
/**
* Age of the person. Water is wet.
*
* @return The current value of this person's age. Circles are round.
*/
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
/**
* Age of the person. Water is wet.
*
* @param age New value for this person's age. Sky is blue.
*/
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
/**
* Changes the name of this person.
*
* @param name The new value.
*/
protected void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}支持的配置项:
lombok.accessors.chain = [true | false](默认值:false)
如果设置为true,则生成的setter将返回此值(而不是void)。 @Accessors批注的显式配置链参数优先于此设置。
lombok.accessors.fluent = [true | false](默认值:false)
如果设置为true,则生成的getter和setter将不会以bean标准'get,is或set;为前缀;相反,这些方法将使用与字段相同的名称(减去前缀)。 @Accessors批注的显式配置链参数优先于此设置。
lombok.accessors.prefix += a field prefix (default: empty list) (默认值:空列表)
这是一个列表属性;可以使用+ =运算符添加条目。可以使用 - =运算符删除父配置文件中的继承前缀。 Lombok将从字段名称中删除任何匹配的字段前缀,以确定要生成的getter / setter的名称。 例如,ombok.accessors.prefix -= m,如果m是此设置中列出的前缀之一,则名为mFoobar的字段将生成名为getFoobar()的getter,而不是getMFoobar()。 @Accessors批注的显式配置前缀参数优先于此设置。
lombok.getter.noIsPrefix = [true | false](默认值:false)
如果设置为true,则为布尔字段生成的getter将使用get前缀而不是defaultis前缀,并且任何调用getter的生成代码(如@ToString)也将使用get而不是is
lombok.setter.flagUsage = [警告|错误](默认:未设置)
如果已配置,Lombok会将@Setter的任何用法标记为警告或错误。
lombok.getter.flagUsage = [警告|错误](默认:未设置)
如果已配置,Lombok会将@Getter的任何用法标记为警告或错误。
lombok.copyableAnnotations = [完全限定类型列表](默认值:空列表)
Lombok会将任何这些注释从字段复制到setter参数和getter方法。请注意,lombok附带了一堆“开箱即用”的注释,这些注释已知是可复制的:所有流行的可空/非空注释。
3、@ToString
默认情况下,将打印所有非静态字段。如果要跳过某些字段,可以使用@ ToString.Exclude注释这些字段。或者,您可以使用@ToString(onlyExplicitlyIncluded = true)准确指定要使用的字段,然后使用@ToString.Include标记要包含的每个字段。
-
打印内容
通过将callSuper设置为true,可以将toString的超类实现的输出包含到输出中。请注意,java.lang.Object中toString()的默认实现几乎没有意义,因此除非您扩展另一个类,否则您可能不希望这样做。
-
打印顺序
您可以使用@ ToString.Include(name =“some other name”)更改用于标识成员的名称,并且可以通过@ ToString.Include(rank = -1)更改成员的打印顺序。没有等级的成员被认为具有等级0,更高等级的成员被首先打印,并且相同等级的成员以它们在源文件中出现的相同顺序被打印。
使用Lombok
import lombok.ToString;
@ToString
public class ToStringExample {
private static final int STATIC_VAR = 10;
private String name;
private Shape shape = new Square(5, 10);
private String[] tags;
@ToString.Exclude private int id;
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@ToString(callSuper=true, includeFieldNames=true)
public static class Square extends Shape {
private final int width, height;
public Square(int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
}
}
不使用Lombok
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ToStringExample {
private static final int STATIC_VAR = 10;
private String name;
private Shape shape = new Square(5, 10);
private String[] tags;
private int id;
public String getName() {
return this.getName();
}
public static class Square extends Shape {
private final int width, height;
public Square(int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
@Override public String toString() {
return "Square(super=" + super.toString() + ", width=" + this.width + ", height=" + this.height + ")";
}
}
@Override public String toString() {
return "ToStringExample(" + this.getName() + ", " + this.shape + ", " + Arrays.deepToString(this.tags) + ")";
}
}支持的配置项:
lombok.toString.includeFieldNames = [true | false](默认值:true)
通常,lombok以fieldName = fieldValue的形式为每个字段生成toString响应的片段。如果此设置设置为false,则lombok将省略该字段的名称,只需部署所有字段值的逗号分隔列表。如果明确指定,注释参数“includeFieldNames”优先于此设置。
lombok.toString.doNotUseGetters = [true | false](默认值:false)
如果设置为true,则在生成toString方法时,lombok将直接访问字段,而不是使用getter(如果可用)。如果明确指定,注释参数“doNotUseGetters”优先于此设置。
lombok.toString.callSuper = [call | skip | warn] (default: skip)(默认:跳过)
如果设置为call,如果你的类扩展了某些内容,lombok将生成对toString的超类实现的调用。如果设置为跳过,则不会生成此类呼叫。如果设置为警告,则不会生成此类调用,但是lombok会生成警告以告知您。
ombok.toString.flagUsage = [warning | error] (default: not set)(默认:未设置)
如果已配置,Lombok会将@ToString的任何用法标记为警告或错误。
3、 @EqualsAndHashCode
使用@EqualsAndHashCode进行标记,Lombok会自动生成equals(Object other)和hashCode()方法。可以在成员变量上标记{@EqualsAndHashCode.Include和 @EqualsAndHashCode(onlyExplicitlyIncluded = true)}或者@EqualsAndHashCode.Exclude,来明确指定是否使用指定字段。
当把@EqualsAndHashCode注解在有父类的接口中时,子类中生成的equals方法以及hashCode方法不会带有父类字段。可以将callSuper设置成true,显示指定生成的方法中包含父类的equals以及hashCode方法。如果不继承除Object外的其他类中将callSuper设置成true,将会报编译错误。
使用Lombok
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class EqualsAndHashCodeExample {
private transient int transientVar = 10;
private String name;
private double score;
@EqualsAndHashCode.Exclude private Shape shape = new Square(5, 10);
private String[] tags;
@EqualsAndHashCode.Exclude private int id;
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper=true)
public static class Square extends Shape {
private final int width, height;
public Square(int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
}
}不使用Lombok
import java.util.Arrays;
public class EqualsAndHashCodeExample {
private transient int transientVar = 10;
private String name;
private double score;
private Shape shape = new Square(5, 10);
private String[] tags;
private int id;
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@Override public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) return true;
if (!(o instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample)) return false;
EqualsAndHashCodeExample other = (EqualsAndHashCodeExample) o;
if (!other.canEqual((Object)this)) return false;
if (this.getName() == null ? other.getName() != null : !this.getName().equals(other.getName())) return false;
if (Double.compare(this.score, other.score) != 0) return false;
if (!Arrays.deepEquals(this.tags, other.tags)) return false;
return true;
}
@Override public int hashCode() {
final int PRIME = 59;
int result = 1;
final long temp1 = Double.doubleToLongBits(this.score);
result = (result*PRIME) + (this.name == null ? 43 : this.name.hashCode());
result = (result*PRIME) + (int)(temp1 ^ (temp1 >>> 32));
result = (result*PRIME) + Arrays.deepHashCode(this.tags);
return result;
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample;
}
public static class Square extends Shape {
private final int width, height;
public Square(int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
@Override public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) return true;
if (!(o instanceof Square)) return false;
Square other = (Square) o;
if (!other.canEqual((Object)this)) return false;
if (!super.equals(o)) return false;
if (this.width != other.width) return false;
if (this.height != other.height) return false;
return true;
}
@Override public int hashCode() {
final int PRIME = 59;
int result = 1;
result = (result*PRIME) + super.hashCode();
result = (result*PRIME) + this.width;
result = (result*PRIME) + this.height;
return result;
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof Square;
}
}
}支持配置项:
lombok.equalsAndHashCode.doNotUseGetters = [true | false](默认值:false)
如果设置为true,则在生成equals和hashCode方法时,lombok将直接访问字段而不是使用getter(如果可用)。 如果明确指定,注释参数“doNotUseGetters”优先于此设置。
lombok.equalsAndHashCode.callSuper = [call | 跳过| 警告](默认:警告)
如果设置为call,则lombok将生成对hashCode的超类实现的调用,并且如果您的类扩展了某些内容则等于。 如果设置为skip,则不会生成此类调用。 默认行为类似于skip,还有一个警告。
lombok.equalsAndHashCode.flagUsage = [warning | error](默认:未设置)
如果已配置,Lombok会将@EqualsAndHashCode的任何用法标记为警告或错误。
4、@NoArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor, @AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor:
生成一个无参的构造方法。如果当前的类中存在final类型的字段,则会抛出异常。要想避免上述的异常,就需要使用 @NoArgsConstructor(force = true),然后所有final字段都会被初始化成0或false或null。
@RequiredArgsConstructor:
生成一个带有参数的构造方法,构造方法中的参数为所有final类型的字段以及被@NonNull标记的字段。
@AllArgsConstructor:
生成一个带有所有字段的构造方法,构造方法也会对标记有@NonNull的字段进行参数检查。
这些注释中的每一个都允许使用替代形式,其中生成的构造函数始终是私有的,并且生成包围私有构造函数的附加静态工厂方法。通过为注释提供staticName值来启用此模式,如下所示:@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName =“of”)。与普通构造函数不同,这种静态工厂方法将推断泛型。这意味着您的API用户可以编写MapEntry.of(“foo”,5)而不是更长的新MapEntry
与大多数其他lombok注释不同,显式构造函数的存在不会阻止这些注释生成自己的构造函数。这意味着您可以编写自己的专用构造函数,并让lombok生成样板文件。如果出现冲突(您的一个构造函数最终使用与lombok生成的签名相同的签名),则会发生编译器错误。
使用Lombok
import lombok.AccessLevel;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.NonNull;
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "of")
@AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
public class ConstructorExample {
private int x, y;
@NonNull private T description;
@NoArgsConstructor
public static class NoArgsExample {
@NonNull private String field;
}
} 不使用Lombok
public class ConstructorExample {
private int x, y;
@NonNull private T description;
private ConstructorExample(T description) {
if (description == null) throw new NullPointerException("description");
this.description = description;
}
public static ConstructorExample of(T description) {
return new ConstructorExample(description);
}
@java.beans.ConstructorProperties({"x", "y", "description"})
protected ConstructorExample(int x, int y, T description) {
if (description == null) throw new NullPointerException("description");
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.description = description;
}
public static class NoArgsExample {
@NonNull private String field;
public NoArgsExample() {
}
}
} 5、@NonNull
被@NonNull注解标上的参数,会判断是否等于null,如果等于null就抛出如下异常: if (param == null) throw new NullPointerException("param is marked @NonNull but is null");
使用Lombok
import lombok.NonNull;
public class NonNullExample extends Something {
private String name;
public NonNullExample(@NonNull Person person) {
super("Hello");
this.name = person.getName();
}
}不使用Lombok
import lombok.NonNull;
public class NonNullExample extends Something {
private String name;
public NonNullExample(@NonNull Person person) {
super("Hello");
if (person == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("person is marked @NonNull but is null");
}
this.name = person.getName();
}
}支持配置项:
lombok.nonNull.exceptionType = [NullPointerException | IllegalArgumentException](默认值:NullPointerException)。
当lombok生成一个null-check if语句时,默认情况下会抛出一个java.lang.NullPointerException,并将'field name标记为@NonNull但为null'作为异常消息。 但是,您可以在此配置键中使用IllegalArgumentException,以使lombok使用此消息抛出该异常。
lombok.nonNull.flagUsage = [warning | error] (default: not set)(默认:未设置)
如果已配置,Lombok会将@NonNull的任何用法标记为警告或错误。
6、 @Value
@Value是简写:final @ToString @EqualsAndHashCode @AllArgsConstructor @FieldDefaults(makeFinal = true,level = AccessLevel.PRIVATE)@Getter。他和@Data相似,但是他生成的字段都是final类型的。可以使用 @NonFinal或@PackagePrivate注解来覆盖默认的final和默认的访问级别。
使用Lombok
import lombok.AccessLevel;
import lombok.experimental.NonFinal;
import lombok.experimental.Value;
import lombok.experimental.Wither;
import lombok.ToString;
@Value public class ValueExample {
String name;
@Wither(AccessLevel.PACKAGE) @NonFinal int age;
double score;
protected String[] tags;
@ToString(includeFieldNames=true)
@Value(staticConstructor="of")
public static class Exercise {
String name;
T value;
}
} 不使用Lombok
import java.util.Arrays;
public final class ValueExample {
private final String name;
private int age;
private final double score;
protected final String[] tags;
@java.beans.ConstructorProperties({"name", "age", "score", "tags"})
public ValueExample(String name, int age, double score, String[] tags) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
this.tags = tags;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public double getScore() {
return this.score;
}
public String[] getTags() {
return this.tags;
}
@java.lang.Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) return true;
if (!(o instanceof ValueExample)) return false;
final ValueExample other = (ValueExample)o;
final Object this$name = this.getName();
final Object other$name = other.getName();
if (this$name == null ? other$name != null : !this$name.equals(other$name)) return false;
if (this.getAge() != other.getAge()) return false;
if (Double.compare(this.getScore(), other.getScore()) != 0) return false;
if (!Arrays.deepEquals(this.getTags(), other.getTags())) return false;
return true;
}
@java.lang.Override
public int hashCode() {
final int PRIME = 59;
int result = 1;
final Object $name = this.getName();
result = result * PRIME + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode());
result = result * PRIME + this.getAge();
final long $score = Double.doubleToLongBits(this.getScore());
result = result * PRIME + (int)($score >>> 32 ^ $score);
result = result * PRIME + Arrays.deepHashCode(this.getTags());
return result;
}
@java.lang.Override
public String toString() {
return "ValueExample(name=" + getName() + ", age=" + getAge() + ", score=" + getScore() + ", tags=" + Arrays.deepToString(getTags()) + ")";
}
ValueExample withAge(int age) {
return this.age == age ? this : new ValueExample(name, age, score, tags);
}
public static final class Exercise {
private final String name;
private final T value;
private Exercise(String name, T value) {
this.name = name;
this.value = value;
}
public static Exercise of(String name, T value) {
return new Exercise(name, value);
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public T getValue() {
return this.value;
}
@java.lang.Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) return true;
if (!(o instanceof ValueExample.Exercise)) return false;
final Exercise other = (Exercise)o;
final Object this$name = this.getName();
final Object other$name = other.getName();
if (this$name == null ? other$name != null : !this$name.equals(other$name)) return false;
final Object this$value = this.getValue();
final Object other$value = other.getValue();
if (this$value == null ? other$value != null : !this$value.equals(other$value)) return false;
return true;
}
@java.lang.Override
public int hashCode() {
final int PRIME = 59;
int result = 1;
final Object $name = this.getName();
result = result * PRIME + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode());
final Object $value = this.getValue();
result = result * PRIME + ($value == null ? 43 : $value.hashCode());
return result;
}
@java.lang.Override
public String toString() {
return "ValueExample.Exercise(name=" + getName() + ", value=" + getValue() + ")";
}
}
} 支持配置项:
lombok.value.flagUsage = [warning | error] (default: not set)(默认:未设置)
如果已配置,Lombok会将@Value的任何用法标记为警告或错误。
lombok.val.flagUsage = [warning | error] (default: not set)(默认:未设置)
如果已配置,Lombok会将val的任何用法标记为警告或错误。
7、@Cleanup
使用@Cleanup确保在代码执行路径退出当前作用域之前自动清除给定资源。
使用Lombok
import lombok.Cleanup;
import java.io.*;
public class CleanupExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
@Cleanup InputStream in = new FileInputStream(args[0]);
@Cleanup OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(args[1]);
byte[] b = new byte[10000];
while (true) {
int r = in.read(b);
if (r == -1) break;
out.write(b, 0, r);
}
}
}不使用Lombok
import java.io.*;
public class CleanupExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(args[0]);
try {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(args[1]);
try {
byte[] b = new byte[10000];
while (true) {
int r = in.read(b);
if (r == -1) break;
out.write(b, 0, r);
}
} finally {
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
} finally {
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
}
}
}支持配置项:
lombok.cleanup.flagUsage = [warning | error] (default: not set)(默认:未设置)
如果已配置,Lombok会将@Cleanup的任何用法标记为警告或错误。
8、val/var、@Builder、@Log、@SneakyThrows、@Synchronized、@Getter(lazy=true)这里就不介绍了,详情见官网文档