Android Input事件APP端流程分析
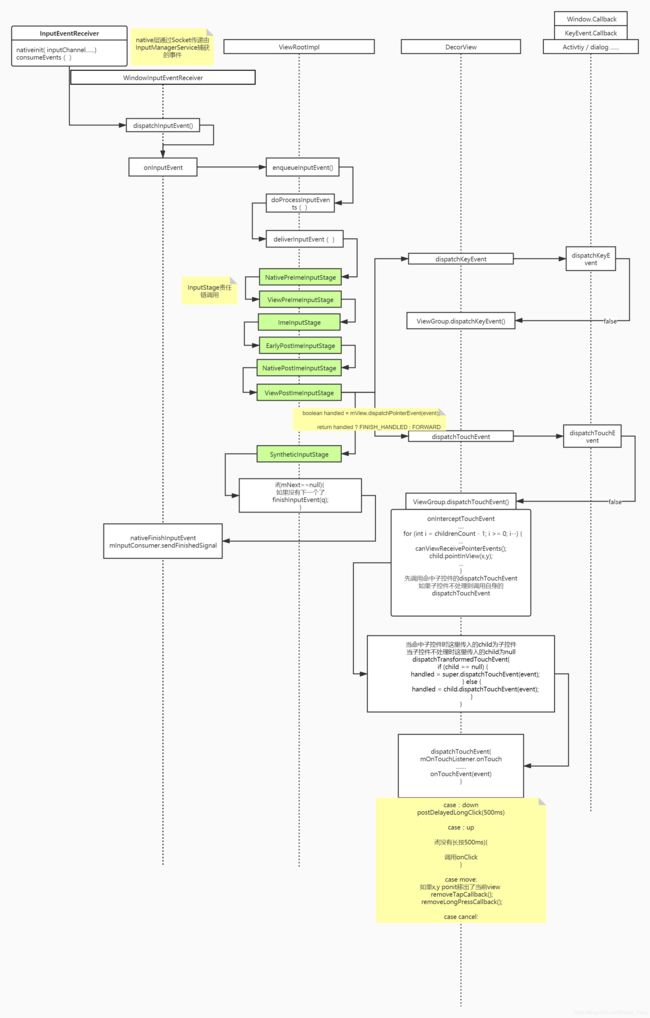
先上流程图
WindowInputEventReceiver WindowInputEventReceiver为InputEventReceiver的子类 是接收InputManagerService派发事件的APP端,在InputEventReceiver.cpp 中可以看到 接收到input事件后回调Java层的dispatchInputEvent 即 InputEventReceiver的dispatchInputEvent 方法,dispatchInputEvent 调用onInputEvent方法, onInputEvent进行重写,即调用WindowInputEventReceiver的onInputEvent
InputEventReceiver.cpp
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::consumeEvents(JNIEnv* env,
bool consumeBatches, nsecs_t frameTime, bool* outConsumedBatch) {
//........
if (inputEventObj) {
if (kDebugDispatchCycle) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Dispatching input event.", getInputChannelName());
}
//回调Java层dispatchInputEvent
env->CallVoidMethod(receiverObj.get(),
gInputEventReceiverClassInfo.dispatchInputEvent, seq, inputEventObj);
//.............
}
}
InputEventReceiver.java
private void dispatchInputEvent(int seq, InputEvent event, int displayId) {
mSeqMap.put(event.getSequenceNumber(), seq);
onInputEvent(event, displayId);
}
WindowInputEventReceiver的onInputEvent调用
ViewRootImpl的enqueueInputEvent -->doProcessInputEvents-->deliverInputEvent
在deliverInputEvent方法内进行 InputStage的链式调用如下
//WindowInputEventReceiver 继承于 InputEventReceiver
final class WindowInputEventReceiver extends InputEventReceiver {
public WindowInputEventReceiver(InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) {
super(inputChannel, looper);
}
@Override
public void onInputEvent(InputEvent event, int displayId) {
enqueueInputEvent(event, this, 0, true);
}
}
void enqueueInputEvent(InputEvent event,
InputEventReceiver receiver, int flags, boolean processImmediately) {
....
doProcessInputEvents();
....
}
void doProcessInputEvents() {
....
deliverInputEvent(q);
....
}
private void deliverInputEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
InputStage stage;
if (q.shouldSendToSynthesizer()) {
stage = mSyntheticInputStage;
} else {
stage = q.shouldSkipIme() ? mFirstPostImeInputStage : mFirstInputStage;
}
if (q.mEvent instanceof KeyEvent) {
mUnhandledKeyManager.preDispatch((KeyEvent) q.mEvent);
}
if (stage != null) {
handleWindowFocusChanged();
//InputStage 进行链式调用
//层层过滤,如果不处理交则给下一个(FORWARD),处理则返回FINISH_HANDLE
stage.deliver(q);
} else {
finishInputEvent(q);
}
}
InputStage
| InputStage | 说明 |
| NativePreImeInputStage | 分发早于IME的InputEvent到NativeActivity中去处理, NativeActivity和普通acitivty的功能一致,不过是在native层实现,这样执行效率会更高,同时NativeActivity在游戏开发中很实用(不支持触摸事件)。 |
| ViewPreIMEInputStage | 分发早于IME的InputEvent到View框架处理,会调用view(输入焦点)的onkeyPreIme方法,同时会给View在输入法处理key事件之前先得到消息并优先处理,View系列控件可以直接复写onKeyPreIme( 不支持触摸事件)。 |
| ImeInputStage | 分发InputEvent到IME处理调用ImeInputStage的onProcess,InputMethodManager的dispatchInputEvent方法处理消息(不支持触摸事件)。 |
| EarlyPostImeInputStage | 与touchmode相关,比如你的手机有方向键,按方向键会退出touchmode,这个事件被消费,有可能会有view的背景变化,但不确定(支持触摸事件)。 |
| NativePostImeInputStage | 分发InputEvent事件到NativeActivity,IME处理完消息后能先于普通Activity处理消息(此时支持触摸事件)。 |
| ViewPostImeInputStage | 分发InputEvent事件到View框架,view的事件分发(支持触摸事件)。最终会调用到输入焦点的3个方法:使用setKeyListener注册的监听器的onKey,之后是onKeyDown和onKeyUp,或者调用activity的onKeyDown和onKeyUp方法,也就是兜底处理无人处理的key事件 |
| SyntheticInputStage | 未处理 InputEvent最后处理。 |
ViewPostImeInputStage是将InputEvent分发到View层的实现所在 onProcess 方法如下
final class ViewPostImeInputStage extends InputStage {
.......
@Override
protected int onProcess(QueuedInputEvent q) {
if (q.mEvent instanceof KeyEvent) {
//处理按键事件
return processKeyEvent(q);
} else {
final int source = q.mEvent.getSource();
if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER) != 0) {
//处理指针事件 (触摸或者鼠标等输入设备)
return processPointerEvent(q);
} else if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_TRACKBALL) != 0) {
//轨迹球事件
return processTrackballEvent(q);
} else {
//其他
return processGenericMotionEvent(q);
}
}
}
......
}
private int processPointerEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
//.....
//调用View层分发 这里的mView 为
boolean handled = mView.dispatchPointerEvent(event);
.....
return handled ? FINISH_HANDLED : FORWARD;
}
processPointerEvent 调用了mView层的dispatchPointerEvent分发, 这里的mView 为DecorView
DecorView 的dispatch方法会先调用Window.CallBack 或者KeyEvent.CallBack在进行View层的分发,
这里的Widow.CallBack的实现有Activity, Dialog等 先回调 Window.CallBack如果 返回false不处理则进行View层分发
DecorView.java
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
final Window.Callback cb = mWindow.getCallback();
return cb != null && !mWindow.isDestroyed() && mFeatureId < 0
? cb.dispatchTouchEvent(ev) : super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}此后就是我们熟悉的View或ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent相关流程了
例如 ViewGroup判断 point的X,Y在那个子控件内,命中子控件后,再调用子控件的dispatchTouchEvent
如果命中的子控件不处理(比如setClickable(false)),或没有命中 则调用自身的dispatchTouchEvent