Jupyter notebook交互输入方法(ipywidgets控件),包括文本框text input box,按钮button等
交互式输入用到的包是ipywidgets,如果还未安装,可以在终端中使用pip install ipywidgets安装。
引用:
import ipywidgets as widgets # 控件库
from IPython.display import display # 显示控件的方法
官方文档:https://ipywidgets.readthedocs.io/en/stable/index.html
Github项目地址:https://github.com/jupyter-widgets/ipywidgets
widgets中的控件包括两部分:
- UI/HTML element,这是显示在output cell中的部分,通常是实例化后将其作为
display函数的实参传递 - event handler,控件的注册事件,通常做法是将一个定义好的python函数作为实参传递到控件的事件中
例子 - TextBox
import ipywidgets as widgets # 控件库
from IPython.display import display # 显示控件的方法
text = widgets.Text()
display(text)
def print_value(sender):
print(sender.value)
text.on_submit(print_value) # 回车以提交内容
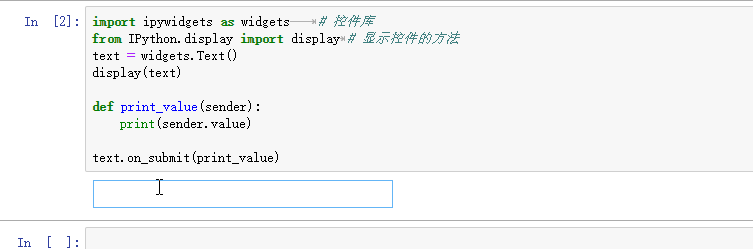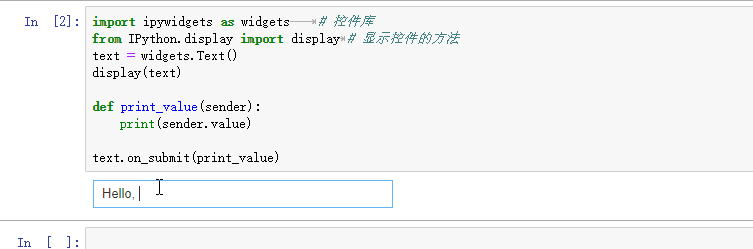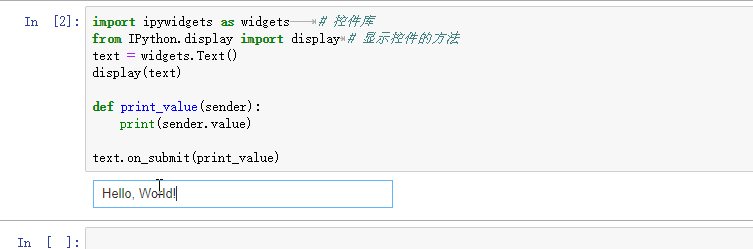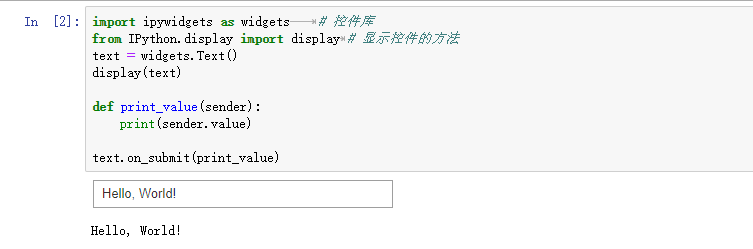
在jupyter notebook中输入以上代码,运行后会在输出区显示一个文本框,在文本框中输入内容并回车后,会触发on_submit事件,并输出文本框中的内容。
再次输入并回车,不会清除上一次的输出,而是换行重新输出(图中未展示)。
常用控件
-
widgets.Text():文本框,构造函数没有形参,常用事件.on_submit(callback),使用示例见上文 -
widgets.Button(**kwages):按钮,构造函数的形参包括:- description:显示在按钮上的文字
- tooltip:鼠标悬浮时显示的提示文字
- icon:图标(没有成功使用过)
- disabled:bool值,是否禁止交互
常用事件:
.on_click(callback)。例子:btn = widgets.Button(description = "OK", tooltip = 'this is a button') def btn_click(sender): print('Button %s clicked!' % sender.description) btn.on_click(btn_click) display(btn)
widgets.Box():容器,将其它控件组合在一起的控件,类似.Net中的Panel,在构造时传入一个其它控件的数组,没有常用事件。除此外还有HBox()、VBox()等容器。box = widgets.Box([text,btn]) display(box)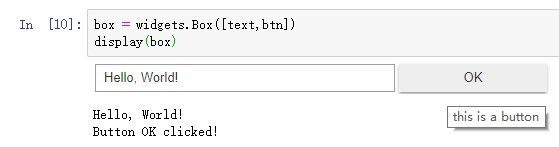
如果觉得使用
Box比较麻烦,可以直接在display()里传入多个控件,也能达到组合效果,但是布局就比较随机了。比如上面的例子也可以直接使用display(text,btn)。

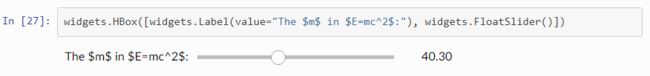
widgets.Label(value:str):普通文本标签,通常与其它控件共同组合在Box中以显示说明文本,在构造时传入实参value作为要显示的文本,没有常用事件。widgets.HBox([widgets.Label(value="The $m$ in $E=mc^2$:"), widgets.FloatSlider()])
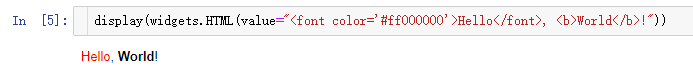
widgets.HTML(value:str):HTML文本标签,支持HTML特性,例如粗体、斜体、彩色字体等。如:
display(widgets.HTML(value="Hello, World!"))
选项类控件
可以用于选取的控件有下拉菜单DropDown、单选列表Select、单选按钮RadioButtons、多选列表SelectMultiple、并列开关ToggleButtons、滑动选取SelectionSlider、范围选取SelectionRangeSlider等。
选取控件有共同的基类_Selection,其初始化参数(也是其属性)有:
options:是一个列表list,表示可以选取的选项,其元素既可以是简单的str值,也可以是形如(label, value)的键值对;label:是当前选项在页面上显示的值value:是当前选项在控件内部使用的值index:是当前选项在options中的索引值
- 如果
options元素不是键值对而是str,则label与value相等- 如果在初始化时同时指定
value、label与index,则以最后指定的值为准
例如widgets.DropDown:
drpbx = Dropdown(options=[("first", 1), ("second", 2), ("third", 3)], index=0, value=1, label="second")
def chosen(_):
print("Selected index:{}, value:{}, label:{}".format(drpbx.index, drpbx.value, drpbx.label))
drpbx.observe(chosen, names="value")
display(drpbx)
observe的含义与用法见下文
其它选项类控件的例子请查阅官方文档
不常用控件与observe事件
上述控件属于比较常用的几个,包含有特殊事件。以下的控件通常不再包含特殊事件,而是将所有事件整合到
observe(handler:callable, names:list, type:str='change')中,用法见下文。
先看一下observe的文档:
print(ipywidgets.Widget.observe.__doc__)
Setup a handler to be called when a trait changes.
This is used to setup dynamic notifications of trait changes.
Parameters
----------
handler : callable
A callable that is called when a trait changes. Its
signature should be ``handler(change)``, where ``change`` is a
dictionary. The change dictionary at least holds a 'type' key.
* ``type``: the type of notification.
Other keys may be passed depending on the value of 'type'. In the
case where type is 'change', we also have the following keys:
* ``owner`` : the HasTraits instance
* ``old`` : the old value of the modified trait attribute
* ``new`` : the new value of the modified trait attribute
* ``name`` : the name of the modified trait attribute.
names : list, str, All
If names is All, the handler will apply to all traits. If a list
of str, handler will apply to all names in the list. If a
str, the handler will apply just to that name.
type : str, All (default: 'change')
The type of notification to filter by. If equal to All, then all
notifications are passed to the observe handler.
意思就是,observe可以关注控件的一些属性,当这些属性的值变化时,就会调用handler方法,并传递一组字典作为handler的实参。字典的内容包括{'name','old','new','owner','type'},分别是:属性名、旧属性值、新属性值、属性所属的控件、事件类型。示例如下:
slt = widgets.Select(options=['first','second','third'])
display(slt)
def attr_event_handler(attrs):
print(attrs)
print('attribute {name} of {owner} {type} from {old} to {new}'.format(
name=attrs['name'],owner=type(attrs['owner']),type=attrs['type'],old=attrs['old'],new=attrs['new']))
slt.observe(attr_event_handler, names='value')
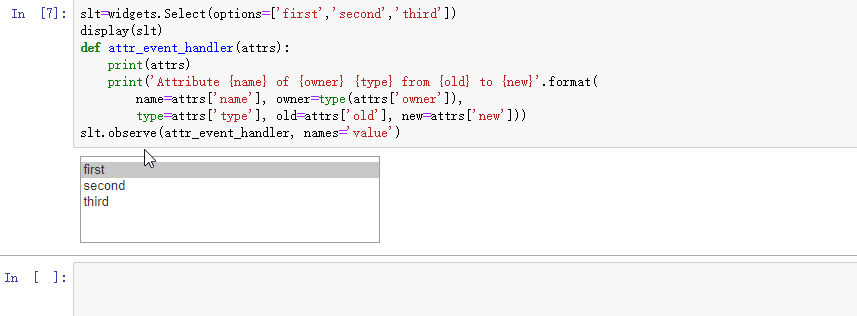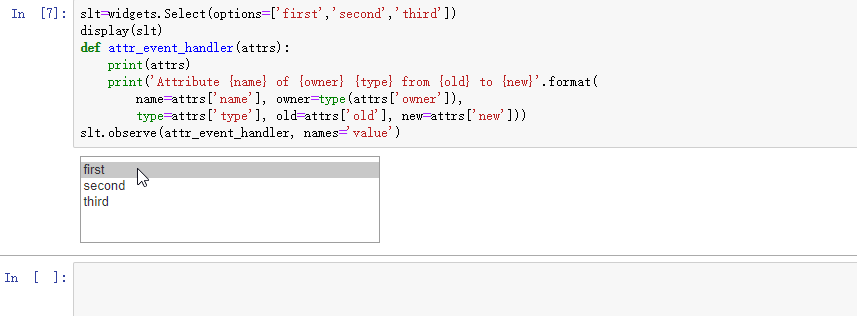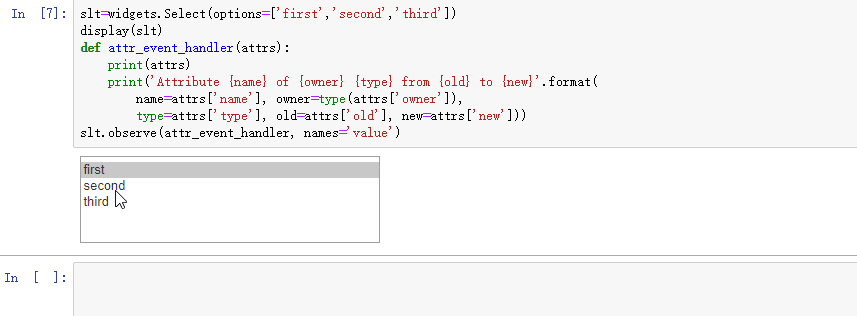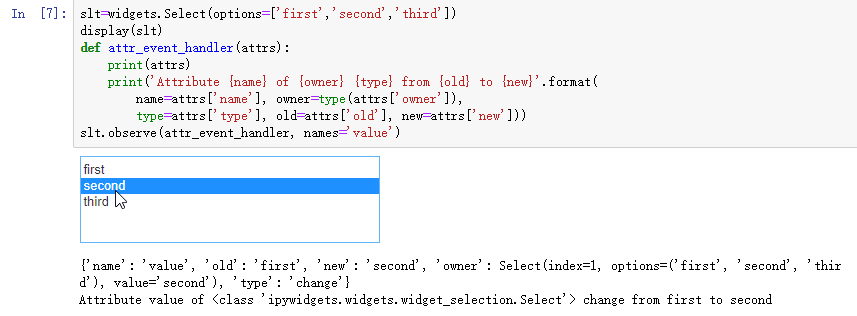
运行后,Select控件默认选中第一行(first),鼠标单击选中第二行后,会触发attr_event_handler,因为这里observe的names参数不是数组而是仅有一个value属性,因此传递到attr_event_handler的也不是数组,不需要用for遍历。
注意:如果初始化后用户仍选取第一行(或不作选取),是不会触发
observe事件的,因此要做好用户不作选取的应对方案
以下控件都需要使用observe事件
- 前文介绍的选项类控件
widgets.IntSlider:可拖动的滚动条,构造函数的形参包括:- value:初始值
- min:最小值
- max:最大值
- step:可调整的最小步长
widgets.FloatSilder:也是滚动条,但value是浮点数widgets.DatePicker:日期选取widgets.ColorPicker:颜色选取- 其它不常用控件
更多控件请访问ipywidgets官方文档
控件属性同步 - Link方法
上文中所介绍的控件属性,本质其实并不是Python Class的
attributes,而是traitlets。Traitlets是一个可以为Class定义类型安全的属性的框架,见Traitlets文档。Ipywidget中对traitlets的说明是:
Traitlets is an IPython library for defining type-safe properties on configurable objects. For this tutorial you do not need to worry about the configurable piece of the traitlets machinery. The sync=True keyword argument tells the widget framework to handle synchronizing that value to the browser.
widgets.link((widget, name),...):同步多个控件的traitlets属性(通常是'value'):caption = widgets.Label(value='slider1和slider2的值将同步变化') sliders1, slider2 = widgets.IntSlider(description='Slider 1'),\ widgets.IntSlider(description='Slider 2') l = widgets.link((sliders1, 'value'), (slider2, 'value')) display(caption, sliders1, slider2)
widgets.dlink((source, name), (target, name), transform=None):单向连接(directional_link),即:target的指定属性跟随source的指定属性变化,而source的指定属性不随target的指定属性变化。由name指定属性(通常是'value')。caption = widgets.Label(value='source的values变化将反映在target1上') source, target1 = widgets.IntSlider(description='Source'),\ widgets.IntSlider(description='Target 1') dl = widgets.dlink((source, 'value'), (target1, 'value')) display(caption, source, target1)
link与dlink会返回一个对象,对此对象调用unlink()方法将解除绑定。l.unlink() dl.unlink()
控件布局与样式 - Layout与Style属性
控件通过layout属性控制布局,用于调整控件大小与位置;通过style属性控制样式,用于调整色彩与字体。
在控件初始化时,可以指定形参layout为ipywidgets.Layout的实例,需要引用:
from ipywidgets import Layout
例如:
b = widgets.Button(description='(50% width, 80px height) button',
layout=Layout(width='50%', height='80px'))
b1 = Button(description='Another button with the same layout', layout=b.layout)
display(b, b1)

如果不想额外引用Layout,也可以在初始化之后再设置控件的layout属性:
b = widgets.Button(description='(50% width, 80px height) button')
b.layout.width='50%'
b.layout.height='80px'
b1 = Button(description='Another button with the same layout')
b1.layout = b.layout
Style的用法与Layout相似,既可以在初始化时指定,也可以初始化后指定。例如:
b1 = Button(description='Custom color')
b1.style.button_color = 'lightgreen'
b1

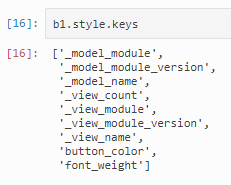
可以通过widget.style.keys查看一个控件的所有可用样式:
除了自己指定Style外,ipywidgets还为许多控件预定义了许多type_style,以便快速获取常用的样式。
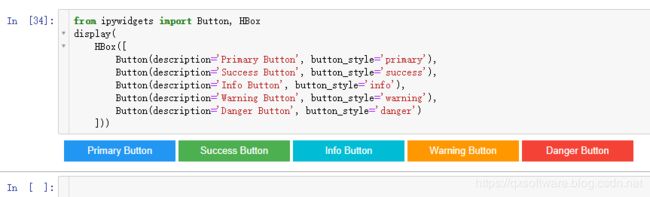
例如,Button.button_style可以在以下5种常用按钮中选择:['primary', 'success', 'info', 'warning', 'danger']
from ipywidgets import Button, HBox
display(
HBox([
Button(description='Primary Button', button_style='primary'),
Button(description='Success Button', button_style='success'),
Button(description='Info Button', button_style='info'),
Button(description='Warning Button', button_style='warning'),
Button(description='Danger Button', button_style='danger')
]))
Layout实际使用的是CSS样式,常用的有:
- Sizes
- height
- width
- max_height
- max_width
- min_height
- min_width
- Display
- visibility
- display
- overflow
- overflow_x
- overflow_y
- Box model
- border
- margin
- padding
- Positioning
- top
- left
- bottom
- right
- Flexbox
- order
- flex_flow
- align_items
- flex
- align_self
- align_content
- justify_content
- Grid layout
- grid_auto_columns
- grid_auto_flow
- grid_auto_rows
- grid_gap
- grid_template
- grid_row
- grid_column
详情参见Layout and Styling
感谢NickeManarin开发的ScreenToGif,一个很好用的GIF截屏工具。