C语言实现简单的客户端和服务器模型
最近刚刚开始学习网络编程,今天看了童永清的《Linux C编程实战》一书,在看到这本书网络编程后面的部分,有一个实现面向连接的Client/Server实例,在此将它整理了一下,并加上一些自己的备注,希望对大家有所帮助。
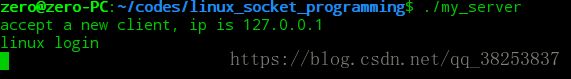
先简要介绍一下这个实例:客户端通过IP和端口号向服务器发起连接,服务器收到连接后,打印客户端的IP,并请求客户端用户名和密码,客户端输入用户名和密码,服务器检查用户名和密码是否匹配,若匹配成功,则服务器在终端打印该用户已登录,客户端退成程序。
一、服务器端源代码
//my_server.c
#include 二、客户端源代码
#include 三、读取数据以及错误处理
头文件的定义:
//my_recv.h
#ifndef _MY_RECV_H
#define _MY_RECV_H
#define BUFSIZE 1024
void my_err(const char *err_string, int line);
int my_recv(int conn_fd, char *data_buf, int len);
#endif源代码:
//my_recv.c
#include 五、运行并测试程序
首先运行服务端程序:
./my_server./my_client -a 127.0.0.1 -p 6666