1.相关的两个方法
/* The context ClassLoader for this thread */
private ClassLoader contextClassLoader;
/**
* Returns the context ClassLoader for this Thread. The context
* ClassLoader is provided by the creator of the thread for use
* by code running in this thread when loading classes and resources.
* If not {@linkplain #setContextClassLoader set}, the default is the
* ClassLoader context of the parent Thread. The context ClassLoader of the
* primordial thread is typically set to the class loader used to load the
* application.
*
* If a security manager is present, and the invoker's class loader is not
* {@code null} and is not the same as or an ancestor of the context class
* loader, then this method invokes the security manager's {@link
* SecurityManager#checkPermission(java.security.Permission) checkPermission}
* method with a {@link RuntimePermission RuntimePermission}{@code
* ("getClassLoader")} permission to verify that retrieval of the context
* class loader is permitted.
*
* @return the context ClassLoader for this Thread, or {@code null}
* indicating the system class loader (or, failing that, the
* bootstrap class loader)
*
* @throws SecurityException
* if the current thread cannot get the context ClassLoader
*
* @since 1.2
*/
@CallerSensitive
public ClassLoader getContextClassLoader() {
if (contextClassLoader == null)
return null;
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
ClassLoader.checkClassLoaderPermission(contextClassLoader,
Reflection.getCallerClass());
}
return contextClassLoader;
}
返回当前线程的contextClassLoader。contextClassLoader由线程创建者提供,供在此线程中运行的代码使用(加载类和资源)。如果没有调用getContextClassLoader,则默认为父线程的contextClassLoader。原始线程的contextClassLoader通常设置为用于加载应用程序的类加载器,也即AppClassLoader。
/**
* Sets the context ClassLoader for this Thread. The context
* ClassLoader can be set when a thread is created, and allows
* the creator of the thread to provide the appropriate class loader,
* through {@code getContextClassLoader}, to code running in the thread
* when loading classes and resources.
*
* If a security manager is present, its {@link
* SecurityManager#checkPermission(java.security.Permission) checkPermission}
* method is invoked with a {@link RuntimePermission RuntimePermission}{@code
* ("setContextClassLoader")} permission to see if setting the context
* ClassLoader is permitted.
*
* @param cl
* the context ClassLoader for this Thread, or null indicating the
* system class loader (or, failing that, the bootstrap class loader)
*
* @throws SecurityException
* if the current thread cannot set the context ClassLoader
*
* @since 1.2
*/
public void setContextClassLoader(ClassLoader cl) {
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPermission(new RuntimePermission("setContextClassLoader"));
}
contextClassLoader = cl;
}
设置当前线程的contextClassLoader。
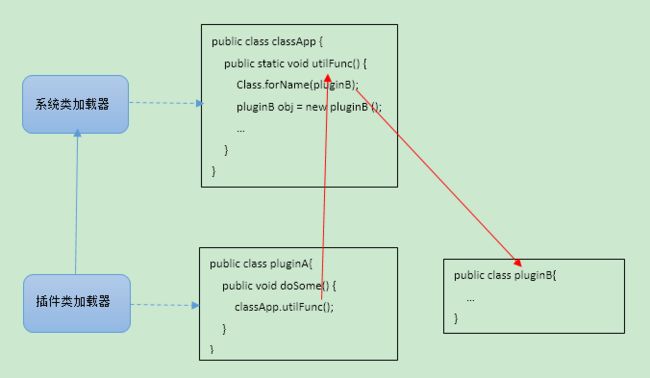
2.类加载器倒置
- 应用代码包含一个助手方法,其调用Class.forName(className),该className指定是是包含在插件JAR中的类
- 插件类中调用了该助手方法
助手方法utilFunc()的类由系统类加载器加载,这也是Class.forName使用类加载器(参考Class.forName(String)类加载器分析)。但是对于系统类加载器来说,插件JAR中的类是不可见的,这种现象称为类加载器倒置。
解决方法:
- 1)助手方法可以要求插件类的类加载器作为一个参数传递给它
- 2)助手方法可以要求将插件类的类加载器设置成为当前线程的上下文类加载器。
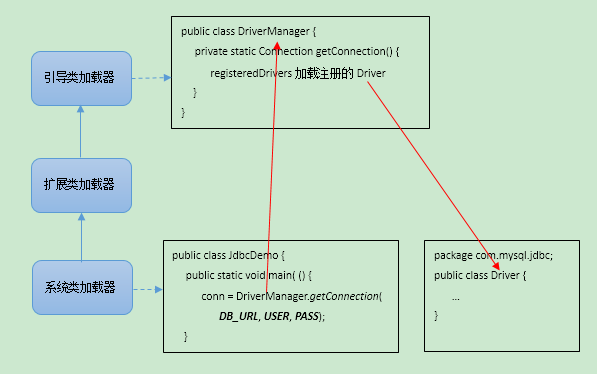
3.SPI
Java提供了很多服务提供者接口(Service Provider Interface,SPI),允许第三方为这些接口提供实现。常见的 SPI 有 JDBC、JCE、JNDI、JAXP 和 JBI 等。
这些 SPI 的接口由 Java 核心库来提供,而这些 SPI 的实现代码则是作为 Java 应用所依赖的 jar 包被包含进类路径(CLASSPATH)里。SPI接口中的代码经常需要加载具体的实现类。那么问题来了,SPI的接口是Java核心库的一部分,是由引导类加载器来加载的;SPI的实现类是由系统加载器来加载的。引导类加载器是无法找到 SPI 的实现类的,因为依照双亲委派模型,BootstrapClassloader无法委派AppClassLoader来加载类
3.1 JDBC
public class JdbcDemo {
...
@Test
public void QueryStatementDemo() {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
List users = new ArrayList<>();
try {
// STEP 2: 注册mysql的驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// STEP 3: 获得一个连接
System.out.println("Connecting to database...");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, USER, PASS);
// STEP 4: 创建一个查询
System.out.println("Creating statement...");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
3.1.1 Class.forName()
加载类Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver")时,会运行com.mysql.jdbc.Driver的静态代码块:
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
public Driver() throws SQLException {
}
static {
try {
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException var1) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
}
public static void registerDriver(java.sql.Driver driver,
DriverAction da)
throws SQLException {
/* Register the driver if it has not already been added to our list */
if (driver != null) {
registeredDrivers.addIfAbsent(new DriverInfo(driver, da));
} else {
// This is for compatibility with the original DriverManager
throw new NullPointerException();
}
println("registerDriver: " + driver);
}
// List of registered JDBC drivers
private final static CopyOnWriteArrayList registeredDrivers = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
将驱动注册到DriverManger的静态域registeredDrivers中,这是一个CopyOnWriteArrayList数据结构。
3.1.2 DriverManager.getConnection
@CallerSensitive
public static Connection getConnection(String url,
String user, String password) throws SQLException {
java.util.Properties info = new java.util.Properties();
if (user != null) {
info.put("user", user);
}
if (password != null) {
info.put("password", password);
}
return (getConnection(url, info, Reflection.getCallerClass()));
}
private static Connection getConnection(
String url, java.util.Properties info, Class caller) throws SQLException {
/*
* When callerCl is null, we should check the application's
* (which is invoking this class indirectly)
* classloader, so that the JDBC driver class outside rt.jar
* can be loaded from here.
*/
ClassLoader callerCL = caller != null ? caller.getClassLoader() : null;
if (callerCL == null) {
callerCL = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
}
if (url == null) {
throw new SQLException("The url cannot be null", "08001");
}
println("DriverManager.getConnection(\"" + url + "\")");
ensureDriversInitialized();
// Walk through the loaded registeredDrivers attempting to make a connection.
// Remember the first exception that gets raised so we can reraise it.
SQLException reason = null;
for (DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) {
// If the caller does not have permission to load the driver then
// skip it.
if (isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerCL)) {
try {
println(" trying " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
Connection con = aDriver.driver.connect(url, info);
if (con != null) {
// Success!
println("getConnection returning " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
return (con);
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
if (reason == null) {
reason = ex;
}
}
} else {
println(" skipping: " + aDriver.getClass().getName());
}
}
// if we got here nobody could connect.
if (reason != null) {
println("getConnection failed: " + reason);
throw reason;
}
println("getConnection: no suitable driver found for "+ url);
throw new SQLException("No suitable driver found for "+ url, "08001");
}
分析各个类的加载器:
System.out.println(JdbcDemo.class.getClassLoader());
System.out.println(com.mysql.jdbc.Driver.class.getClassLoader());
System.out.println(com.mysql.jdbc.Driver.class.getClassLoader().getParent());
System.out.println(DriverManager.class.getClassLoader()
结果:
sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@18b4aac2
sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@27082746
null
这里DriverManager融合两种方式正确加载第三方提供的驱动类:
- 1)Reflection.getCallerClass() 该方法是@CallerSensitive,可以获得最终调用者的类信息即JdbcDemo,该类的类加载器是AppClassLoader,跟com.mysql.jdbc.Driver一样。
- 2)当callerCL为null时,callerCL = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader() 还可以获取线程的contextClassLoader,默认情况下该类加载器就是AppClassLoader。