响应式特点
- 数据响应式
修改数据时,视图自动更新,避免繁琐Dom操作,提高开发效率
- 双向绑定
数据改变,视图随之改变。视图改变,数据随之改变
- 数据驱动
开发时仅需要关注数据本身,不需要关心数据如何渲染到视图
官方教程: https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/reactivity.html
MDN: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Object/defineProperty
vue 2.x 基于 defineProperty 实现数据捕捉
当你把一个普通的 JavaScript 对象传入 Vue 实例作为 data 选项,Vue 将遍历此对象所有的 property,并使用 Object.defineProperty 把这些 property 全部转为 getter/setter。
Object.defineProperty 是 ES5 中一个无法 shim 的特性,这也就是 Vue 不支持 IE8 以及更低版本浏览器的原因。
下面是一段模仿 vue 实现数据捕捉的代码
interface Vue{
data: {
[prop: string]: any
}
[prop: string]: any
}
let vm: Vue = {
data: {
name: 'Tom',
age: 22,
},
}
//数据劫持
function proxyData(vm: Vue){
Object.keys(vm.data).forEach(key => {
console.log(key, vm.data[key])
vm[key] = vm.data[key];
Object.defineProperty(vm, key, {
enumerable: true, //可枚举
configurable: true, //可配置:删除或重定义
get(){
console.log('getter:', vm.data[key]);
return vm.data[key];
},
set(newVal){
console.log('setter', newVal);
if (newVal === vm.data[key]){
return;
}
vm.data[key] = newVal;
document.querySelector('#app')!.textContent = vm.data[key];
}
})
})
}
proxyData(vm);
vm.name = 'karolina'; //模拟数据发生改变,视图改变
console.log(vm);
// {
// name: "karolina"
// age: 33
// data:{
// name: "karolina"
// age: 33
// }
// }
Vue 3.x 基于 Proxy 代理捕捉数据
MDN: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Proxy
ES6 提供 Proxy 捕捉器, 相比于 Object.defineProperty 代理整个对象而非属性,代码上更简洁,性能上由浏览器优化更快
同样下面是一段模仿 vue 实现数据捕捉的代码
let data ={
name: 'Tom',
age: 22,
};
let vm = new Proxy(data, {
get(target: any, key){
if (key in target){
console.log('getter: ',key, target[key]);
return target[key];
}
},
set(target: any, key, newVal,){
console.log('setter: ',key, target[key]);
if (target[key] === newVal){
return false;
}
target[key] = newVal;
document.querySelector('#app')!.textContent = target[key];
return true;
},
})
vm.name = 'Karolina';
console.log(vm);
console.log(vm.age);
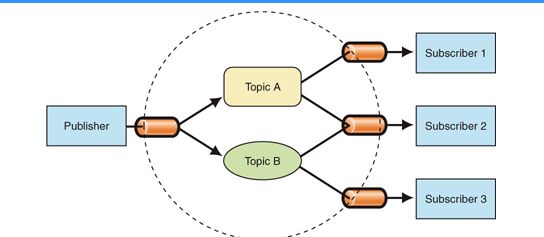
发布订阅模式
在“发布者-订阅者”模式中,称为发布者的消息发送者不会将消息编程为直接发送给称为订阅者的特定接收者。
这意味着发布者和订阅者不知道彼此的存在。存在第三个组件,称为代理或消息代理或事件总线,它由发布者和订阅者都知道,它过滤所有传入的消息并相应地分发它们。
换句话说,pub-sub是用于在不同系统组件之间传递消息的模式,而这些组件不知道关于彼此身份的任何信息。经纪人如何过滤所有消息?实际上,有几个消息过滤过程。最常用的方法有:基于主题和基于内容的。
- 订阅者(subscriber)需要在
事件中心注册事件 - 发布者(publisher)需要于
事件中心触发事件 - 订阅者和发布者无需知道对方身份
Vue中的发布订阅模式
https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/migration.html#dispatch-和-broadcast-替换
下面是Vue的发布订阅伪代码,用于兄弟组件之间通信
//事件中心
let eventHub = new Vue();
//ComponetA.vue 订阅者
willDo: function(){
eventHub.$on('will-do', (text)=>{console.log(text)});
}
//ComponetB.vue 发布者
willDo: function(){
eventHub.$emit('will-do', {text: 'Hello'});
}
下面手写代码来模拟Vue的发布订阅模式实现
//存储主题和句柄,主题为事件名,句柄为hanlder
interface ITopicMap {
[prop: string]: Array,
}
//事件中心,封装订阅和发布事件
class EventCenter {
public topicMap:ITopicMap = {};
$on(topic: string, handler: Function): void{
this.topicMap[topic] = this.topicMap[topic] || [];
this.topicMap[topic].push(handler);
}
$emit(topic: string, ...params: any){
if (topic in this.topicMap){
this.topicMap[topic].forEach((handler)=>{
handler(...params);
})
}
}
}
//测试
let hub: EventCenter = new EventCenter();
//订阅者注册事件
hub.$on('click', ()=>{console.log('you click me')});
hub.$on('custom', (name: string, age: 12)=>{console.log(`your name is ${name}, and age is ${age}`)});
//发布者触发事件
hub.$emit('click'); //you click me
hub.$emit('custom', 'Tom', 22); //your name is Tom, and age is 22
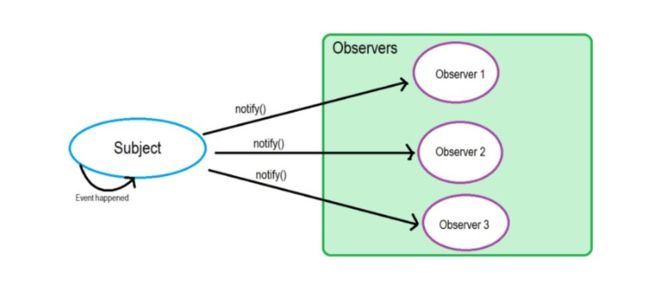
Vue中的观察者模式
当对象间存在一对多关系时,则使用观察者模式(Observer Pattern)。比如,当一个对象被修改时,则会自动通知依赖它的对象。观察者模式属于行为型模式。
-
观察者
wacher | observer通过update()描述当事件发生时需要做的事情 -
目标
Dep | subject需要添加认识观察者,通过notify()通知触发观察者事件 -
没有事件中心,观察者和目标需要知道对方身份,抽象耦合
-
手写代码模拟vue中观察者模式实现
class Watcher {
constructor(public update: Function){}
}
class Dep {
public watcherList: Array = [];
addWatcher(watcher: Watcher){
this.watcherList.push(watcher);
}
notify(...params: any){
this.watcherList.forEach(watcher => {
watcher.update(...params);
})
}
}
//创建事件目标
let dep = new Dep();
let watcher = new Watcher(
(name:string)=>{console.log(`my name is ${name}`)}
);
//目标添加观察者对象
dep.addWatcher(watcher);
//事件触发通知
dep.notify('Tim'); //my name is Tim
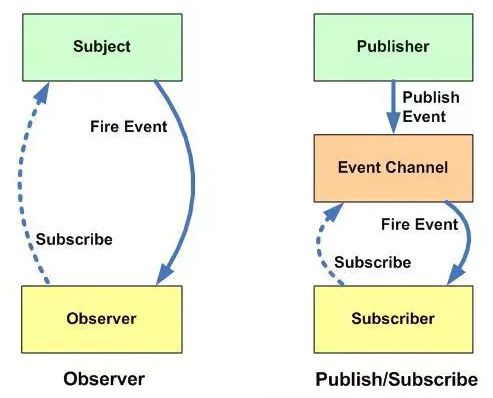
老生常谈的 观察者模式 与 发布订阅模式 区别
- 在观察者模式中,主体维护观察者列表,因此主体知道当状态发生变化时如何通知观察者。然而,在发布者/订阅者中,发布者和订阅者不需要相互了解。它们只需在中间层消息代理(或消息队列)的帮助下进行通信。
- 在发布者/订阅者模式中,组件与观察者模式完全分离。在观察者模式中,主题和观察者松散耦合。
- 观察者模式主要是以同步方式实现的,即当发生某些事件时,主题调用其所有观察者的适当方法。发布服务器/订阅服务器模式主要以异步方式实现(使用消息队列)。
- 发布者/订阅者模式更像是一种跨应用程序模式。发布服务器和订阅服务器可以驻留在两个不同的应用程序中。它们中的每一个都通过消息代理或消息队列进行通信。
其他行为模式参考
其他行为模式学习网站: https://www.runoob.com/design-pattern/observer-pattern.html