Shell 练习题(四)
Shell 练习题(四)
- 1.输出带颜色文本
- 2.创建自定义指令 “ user ”,可以直接执行(#user -add xx),要求该指令具备以下语法和功能:
- 3.basename和dirname
- 4.添加一个新组为 class1 ,然后添加属于这个组的 30 个用户,用户名的形式为 stdxx ,其中 xx 从 01 到 30
- 5.写一个sed命令,修改/tmp/input.txt 文件的内容?
- 6.使用for循环在/oldboy目录下通过随机大小写10个字母加固定字符串oldboy批量创建10个html文件
- 7.将以上文件名中的oldboy全部改成oldgirl(用for循环实现),并且html改成大写。
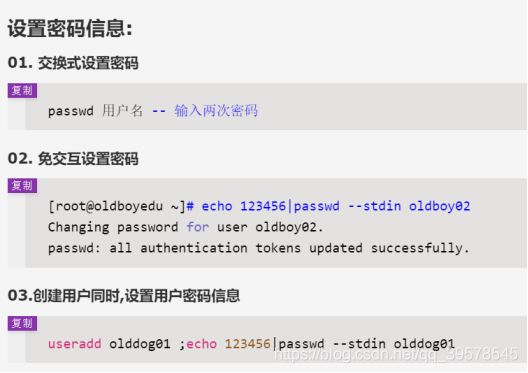
- 8.批量创建10个系统帐号oldboy01-oldboy10并设置密码(密码为随机8位字符串)
- 9.写一个脚本,实现判断10.0.0.0/24网络里,当前在线用户的IP有哪些
- 10.2>/dev/null和>/dev/null 2>&1和2>&1>/dev/null的区别
- 11.分别实现以脚本传参以及read读入的方式比较2个整数大小。以屏幕输出的方式提醒用户比较结果。注意:一共是开发2个脚本。当用脚本传参以及read读入的方式需要对变量是否为数字、并且传参个数做判断
- 12.打印选择菜单,一键安装Web服务
- 13.批量检查多个网站地址是否正常
- 14.用shell处理以下内容
- 1、按单词出现频率降序排序实践
- 2、按字母出现频率降序排序
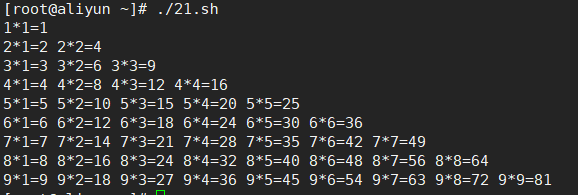
- 15.输出九九乘法表
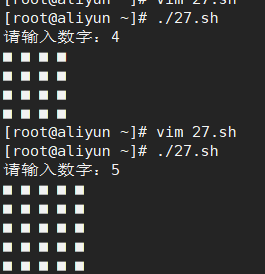
- 16.输出正方形,可接收用户输入的数字
- 17.输出等腰三角形,可接收用户输入的数字
1.输出带颜色文本
带背景色:
echo -e “\033[字背景颜色;文字颜色m字符串\033[0m”
例如: echo -e "\033[41;36m something here \033[0m"
其中41的位置代表底色, 36的位置是代表字的颜色
不带背景色:
echo -e “\033[31m字符串\033[0m”
-e:激活转义字符。
语法
echo(选项)(参数)选项
选项
-e:激活转义字符。使用-e选项时,若字符串中出现以下字符,则特别加以处理,而不会将它当成一般文字输出:
- \a 发出警告声;
- \b 删除前一个字符;
- \c 最后不加上换行符号;
- \f 换行但光标仍旧停留在原来的位置;
- \n 换行且光标移至行首;
- \r 光标移至行首,但不换行;
- \t 插入tab;
- \v 与\f相同;
- \ 插入\字符;
- \nnn 插入nnn(八进制)所代表的ASCII字符;
参数
变量:指定要打印的变量。
实例
用echo命令打印带有色彩的文字:
文字色:
echo -e "\e[1;31mThis is red text\e[0m"
This is red text
\e[1;31m 将颜色设置为红色
\e[0m 将颜色重新置回
颜色码:重置=0,黑色=30,红色=31,绿色=32,黄色=33,蓝色=34,洋红=35,青色=36,白色=37
字背景颜色范围:40----49
40:黑
41:深红
42:绿
43:黄色
44:蓝色
45:紫色
46:深绿
47:白色
字颜色:30-----------39
30:黑
31:红
32:绿
33:黄
34:蓝色
35:紫色
36:深绿
37:白色
下面举例说明一下:
$echo -e “a\bdddd” //前面的a会被擦除
dddd
$echo -e “a\adddd” //输出同时会发出报警声音
adddd
$echo -e “a\ndddd” //自动换行
2.创建自定义指令 “ user ”,可以直接执行(#user -add xx),要求该指令具备以下语法和功能:
a.#user -add 用户名 【添加用户】
b.#user -del 用户名 【删除用户及其家目录】
3.basename和dirname
$(basename $file .c) 过滤后缀名
basename表示取 file名字,过滤后缀.c。输出“file”。 main.c ——> main
basename 是去除目录后剩下的名字
example:shell>temp=/home/temp/1.test
shell>base=basename $temp
shell>echo $base
结果为:1.test
dirname 是取目录
example:shell>temp=/home/temp/1.test
shell>dir=dirname $temp
shell>echo $dir
结果为:/home/temp
basename命令用法
为basename指定一个路径,basename命令会删掉所有的前缀包括最后一个slash(‘/’)字符,然后将字符串显示出来。
格式:basename [pathname] [suffix]
basename [string] [suffix]
suffix为后缀,如果suffix被指定了,basename会将pathname或string中的suffix去掉。
示例一:basename /usr/bin/sort 【输出 sort】basename ./include/stdio.h .h 【输出 stdio,指定后缀为.h,删除第一个参数的文件名的后缀.h】
示例二:
#! /bin/bash
for file in *.bak;do
echo $file
base=`basename $file .bak`
echo $base done
结果:
1.bak
1
2.bak
2
4.添加一个新组为 class1 ,然后添加属于这个组的 30 个用户,用户名的形式为 stdxx ,其中 xx 从 01 到 30
#!/bin/bash
groupadd class1
for((i=1;i<31;i++))
do
if [ $i -le 10 ];then
useradd -g class1 std0$i
else
useradd -g class1 std$i
fi
done
5.写一个sed命令,修改/tmp/input.txt 文件的内容?
要求:
-
删除所有空行。
sed ‘/^$/d’ /tmp/input.txt -
一行中,如果包含“11111”,则在“11111”前面插入“AAA",在“11111”后面插入“BBB"。比如:将内容为0000111112222的一行改为0000AAA11111BBB2222。
sed ‘s#(11111)#AAA\1BBB#g’ /tmp/input.txt
\1 指的就是正则A中的第一个group,即第一个小括号所匹配到的内容。 AAA\1
6.使用for循环在/oldboy目录下通过随机大小写10个字母加固定字符串oldboy批量创建10个html文件
dir=/oldboy
[ -d "$dir" ] || mkdir -p $dir
for n in {1..10}
do
name=`tr -cd ['a-zA-Z'] </dev/urandom |head -c10` //生成随机数
touch $dir/${name}_oldboy.html
#touch $dir`echo $RANDOM|md5sum|cut -c -`_oldboy.html 大小写+数字
done
tr命令可以对来自标准输入的字符进行替换、压缩和删除。它可以将一组字符变成另一组字符
tr可以使用的字符类:
[:alnum:]:字母和数字
[:alpha:]:字母
[:cntrl:]:控制(非打印)字符
[:digit:]:数字
[:graph:]:图形字符
[:lower:]:小写字母
[:print:]:可打印字符
[:punct:]:标点符号
[:space:]:空白字符
[:upper:]:大写字母
[:xdigit:]:十六进制字符
使用方式:
tr ‘[:lower:]’ ‘[:upper:]’
生成固定长度的随机密码
head /dev/urandom | tr -dc A-Za-z0-9 | head -c 20
7.将以上文件名中的oldboy全部改成oldgirl(用for循环实现),并且html改成大写。
方法一:
#!/bin/bash
cd /oldboy
for n in `ls`
do
rename 'oldboy' 'oldgirl' $n | rename 'html' 'HTML' $n
done
方法二:
#!/bin/bash
cd /oldboy
for i in `ls`
do
mv $i `echo $i | sed -e 's#oldboy#oldgirl#g;s#html#HTML#g'`
done
-e script 允许多个脚本指令被执行. /和#都行,如果被替换的带有/就不行
8.批量创建10个系统帐号oldboy01-oldboy10并设置密码(密码为随机8位字符串)
for i in `seq 01 10`
do
useradd oldboy$i
password=`tr -cd 'a-zA-Z0-9' </dev/urandom |head -c8`
echo "$password |passwd --stdin oldboy$i"
# 免交互设置密码
done
9.写一个脚本,实现判断10.0.0.0/24网络里,当前在线用户的IP有哪些
#!/bin/bash
for I in `seq 1 255`
do
ping -c 1 10.0.0.$I &>/dev/null # 摒弃标准输出
if [ $? -eq 0 ] # 依据执行结果
then
echo -e "10.0.0.$I is up."
else
echo -e "10.0.0.$I is down."
fi
done
10.2>/dev/null和>/dev/null 2>&1和2>&1>/dev/null的区别
2>/dev/null
意思就是把错误输出到“黑洞”
/dev/null 2>&1
默认情况是1,也就是等同于1>/dev/null 2>&1。意思就是把标准输出重定向到“黑洞”,还把错误输出2重定向到标准输出1,也就是标准输出和错误输出都进了“黑洞”
2>&1 >/dev/null
意思就是把错误输出2重定向到标准出书1,也就是屏幕,标准输出进了“黑洞”,也就是标准输出进了黑洞,错误输出打印到屏幕
11.分别实现以脚本传参以及read读入的方式比较2个整数大小。以屏幕输出的方式提醒用户比较结果。注意:一共是开发2个脚本。当用脚本传参以及read读入的方式需要对变量是否为数字、并且传参个数做判断
#!/bin/bash
read -p "请输入第一个数字:" Num1
if [[ ! $Num1 =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]]
then
echo "你输入的不是一个正整数!请重新输入!"
fi
read -p "请输入第二个数字:" Num2
if [[ ! $Num2 =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]]
then
echo "你输入的不是一个正整数!请重新输入!"
fi
if [ $Num1 -gt $Num2 ];then
echo "$Num1 > $Num2,第一个数大于第二个数"
elif [ $Num1 -lt $Num2 ];then
echo "$Num1 < $Num2,第一个数小于第二个数"
else
echo "$Num1 = $Num2,第一个数等于第二个数"
fi
脚本传参
#!/bin/bash
if [ $# -ne 2 ];then
echo "你输入的位置参数不正确!值参数必须是两个!"
fi
Num1=$1
if [[ ! $Num1 =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]]
then
echo "你输入的不是一个正整数!请重新输入!"
fi
Num2=$2
if [[ ! $Num2 =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]]
then
echo "你输入的不是一个正整数!请重新输入!"
fi
if [ $Num1 -gt $Num2 ];then
echo "$Num1 > $Num2,第一个数大于第二个数"
elif [ $Num1 -lt $Num2 ];then
echo "$Num1 < $Num2,第一个数小于第二个数"
else
echo "$Num1 = $Num2,第一个数等于第二个数"
fi
12.打印选择菜单,一键安装Web服务
sh menu.sh
1.[install lamp]
2.[install lnmp]
3.[exit]
pls input the num you want:
要求:
1、当用户输入1时,输出“startinstalling lamp.”然后执行/server/scripts/lamp.sh,脚本内容输出"lampis installed"后退出脚本;
2、当用户输入2时,输出“startinstalling lnmp.”然后执行/server/scripts/lnmp.sh输出"lnmpis installed"后退出脚本;
3、当输入3时,退出当前菜单及脚本;
4、当输入任何其它字符,给出提示“Input error”后退出脚本。
5、要对执行的脚本进行相关条件判断,例如:脚本是否存在,是否可执行等。
PINK_COLOR='\E[1;35m'
RES='\E[0m'
cat << EOF
1.[install lamp]
2.[install lnmp]
3.[install mysql]
4.[install php]
5.[exit]
EOF
read -p"请输入一个参数:" a
case $a in
1)
echo -e "$BLUE_COLOR start installing lamp $RES"
lampScrirpts=/server/scripts/lamp.sh
[ -f $lampScripts ] && sh $lampScripts || exit1
;;
2)
echo -e "$PINK_COLOR start installing lnmp $RES"
lnmpScripts=/server/scripts/lnmp.sh
[ -f $lnmpScripts ] && sh $lnmpScripts || exit2
;;
3)
echo -e "$GREEN_COLOR start installing mysql $RES"
mysqlScripts=/server/sciprts/mysql.sh
[ -f $mysqlScripts ] && sh $mysqlScripts || exit3
;;
4)
echo -e "$PINK_COLOR start installing php $RES"
phpScripts=/server/scripts/php.sh
[ -f $phpScripts ] && sh $phpScripts || exit4
;;
*)
echo -e "$RED_COLOR input error $RES"
esac
13.批量检查多个网站地址是否正常
要求:shell数组方法实现,检测策略尽量模拟用户访问思路
http://www.etiantian.org
http://www.taobao.com
http://oldboy.blog.51cto.com
http://10.0.0.7
数组元素个数${#array[@]}
数组的所有元素${array[*]}
字符串长度${#str}
#!/bin/bash
array=(
http://www.etiantian.org
http://www.taobao.com
http://oldboy.blog.51cto.com
http://10.0.0.7 )
#check_url
wait(){
echo -n "wait 3s"for((i=0;i<3;i++))do
echo -n "."
sleep 1doneecho }
check_url(){
wget -T 5 -t 2 --spider $1 &>/dev/null
RETVAL=$?
if [ $RETVAL -eq 0 ];then
action "check $1" /bin/true
else
action "check $1" /bin/false
fi
return $RETVAL
}
main(){
wait
for((i=0;i<${#array[@]};i++))
do
check_url ${array[i]}
done
}
main
14.用shell处理以下内容
1、按单词出现频率降序排序!
2、按字母出现频率降序排序!
The months of learning in Old Boy education are the few months that I
think the time efficient is the most.I had also studied at other
training institutions before, but I was hard to understand what the
tutor said and hard to follow. It was just too much to learn with no
outline.
正则表达式
[\w-] 就是匹配任意字母和符号- (减号)
. = 就是匹配符号. (点)
1、按单词出现频率降序排序实践
方法1:传统老法
第一步:去特殊字符
sed 's/[,.]//g'

第二步:空格替换回车,将单词竖向排列,去重计数,然后出最终结果
sed 's/[,.]//g'

2、按字母出现频率降序排序
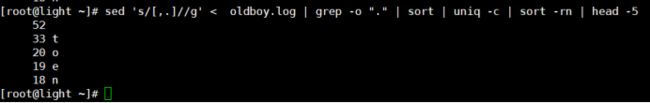
方法1:去空格特殊字符后,然后利用grep的-o将字符竖向排列后处理。
-o: 只输出符合 RE 的字符串
sed 's/[,.]//g' < oldboy.log | grep -o "." | sort | uniq -c | sort -rn | head -5
15.输出九九乘法表
#!/bin/bash
i=1
while [ $i -le 9 ]
do
for (( j=1;j<=9;j++ ))
do
[ $j -le $i ]&& echo -n "$i*$j=$((i*j)) "
done
echo " "
let i++
done
16.输出正方形,可接收用户输入的数字
#!/bin/bash
read -p "请输入数字:" a
for((i=1;i<=$a;i++))
do
for ((j=1;j<=$a;j++))
do
echo -e "■ \c"
done
echo
done
在\c 后,这一行后面的内容都不会输出,直接删掉了,
\c在这个程序的意思就是删除默认换行
17.输出等腰三角形,可接收用户输入的数字
#!/bin/bash
read -p "请输入数字:" a
for((i=1;i<=$a;i++))
do
for ((j=((2*${a}-2*${i}));j>=0;j--))
do
echo -e " \c"
done
for ((k=1;k<=((2*${i}-1));k++))
do
echo -e " *\c"
done
echo
done