使用SpringJDBC+SpringMVC+JSP实现三层架构
三层架构就是把一个程序的业务划分为表现层+业务逻辑层+数据访问层,可以有效的实现程序的高内聚与低耦合。处于练习和巩固知识的目的。我花了一下午时间把它实现了。
为了实现这种三层模型,我使用SpringJDBC进行数据库的访问,实现了数据访问层(DAO)。使用SpringMVC进行前后端的分离,有了更清晰的业务逻辑,实现了业务逻辑层(Service)。使用JSP作为前端的展示页面,实现了表现层(Web)。
现在用这三层结构模拟实现一个用户登录/注册的小页面,用户的数据用MySQL存储。
话不多说先上代码,注释很详细的
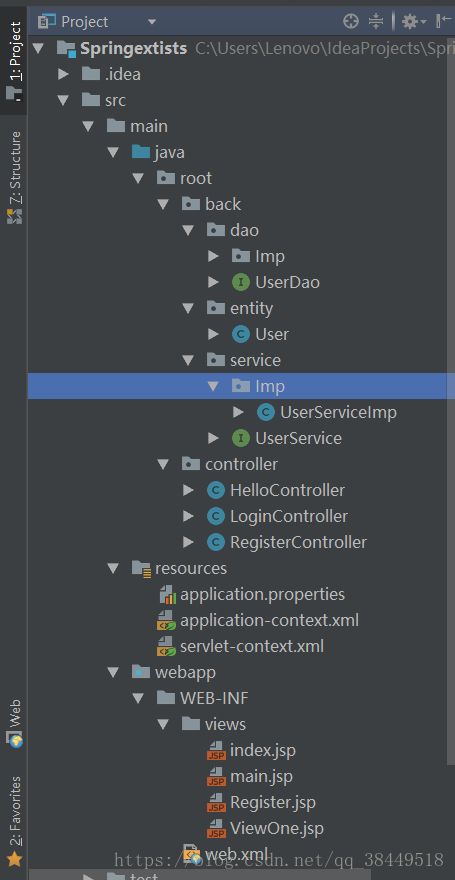
一、项目结构
在这里说一下,我用的IDE是idea
二、pom.xml
Maven项目的配置文件,一般来说没有什么太大的改动的话,可以直接CV
4.0.0
spring.mvc
spring
1.0-SNAPSHOT
war
org.springframework
spring-framework-bom
4.3.9.RELEASE
pom
import
org.springframework
spring-context
org.springframework
spring-jdbc
org.springframework
spring-web
org.springframework
spring-aspects
org.springframework
spring-webmvc
javax.servlet
javax.servlet-api
3.1.0
provided
com.google.code.gson
gson
2.8.2
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.16.16
com.alibaba
druid
1.1.2
mysql
mysql-connector-java
5.1.43
org.slf4j
slf4j-api
1.7.25
ch.qos.logback
logback-classic
1.2.3
org.apache.maven.plugins
maven-compiler-plugin
3.7.0
1.8
1.8
三、web.xml
Web项目的一些配置文件,里面配置了前端控制器(DispatcherServlet),这个项目很简单,我并没有配置Filter和Listener
contextConfigLocation
classpath:application-context.xml
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
DispatcherServlet
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
contextConfigLocation
classpath:servlet-context.xml
DispatcherServlet
/
四、application-context.xml
SpringIOC容器的配置,里面有数据访问层和业务逻辑层的各种Bean,还有数据源等等......
五、servlet-context.xml
SpringMVC前端控制器的配置,里面配置了视图解析器以及模型类的Bean
主要的配置差不多完了,现在主要看三层架构的实现
数据访问层
首先定义接口,因为数据访问层只需要向业务逻辑层提供接口就可以了,这就是典型的接口式编程,实现类我们是可以随便换的
UserDao(数据访问层接口):
package root.back.dao;
import root.back.entity.User;
public interface UserDao {
//登录的时候检验是否存在用户
User login(User user);
//用户注册
Integer insert(User user);
//检查用户名是否存在
boolean exist(String userName);
}
嗯嗯还有实现类,项目简单,只有一个
UserDaoImp(数据访问层实现类)
package root.back.dao.Imp;
import root.back.dao.UserDao;
import root.back.entity.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
@Repository
public class UserDaoImp implements UserDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public User login(User user) {
String sql = "select id, userName,password from message where userName=? and password=?";
List userList = jdbcTemplate.query(sql,
new Object[]{
user.getUserName(),
user.getPassword()
},
new UserRowMapper());
if (userList.isEmpty() || userList.size() > 1) {
return null;
} else {
return userList.get(0);
}
}
@Override
public Integer insert(User user) {
String sql = "insert into message (userName,password) values (?,?)";
return jdbcTemplate.update(sql, user.getUserName(), user.getPassword());
}
@Override
public boolean exist(String username) {
String sql = "select count(id) from message where userName=?";
//query相关的方法主要执行查询类的sql语句
int count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new Object[]{username}, Integer.class);
return count > 0;
}
public static class UserRowMapper implements RowMapper {
@Override
public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
User user = new User();
user.setId(rs.getString("id"));
user.setUserName(rs.getString("userName"));
user.setPassword(rs.getString("password"));
return user;
}
}
}
现在对底层数据的访问就已经结束了,接下来只需要向上一层提供接口就行了
业务逻辑层
这一层主要用的是SpringMVC的Controller还有一些对接数据访问层接口的类。以下是业务逻辑层的流程:
当用户访问url的时候,SpringMVC查找到对应的Controller来处理用户的请求,Controller获取到用户请求中的参数,调用一些类来进行业务逻辑的识别,之后调用数据访问层的接口。并根据数据访问层返回的信息结果决定应该把哪个视图呈现给用户。
LoginController:
package root.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import root.back.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
//处理登录请求的后端控制器
//注意:@RequestParam注解中的required注解对表单提交中的属性是没有用的,就算不填它也会默认为空字符串,它只对GET请求中
//在url后加的key-value的属性有限制作用
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = {"/test"})
public class LoginController {
private static final String CURRENT_USER = "Now_user";
//业务层接口
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
//如果是GET方法请求的话,就直接给用户返回登录的页面,此页面表单请求的方法为POST
@RequestMapping(value = {"/login"},method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public ModelAndView LoginGet(){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("index");
return modelAndView;
}
//该方法主要是用来处理表单提交上来的请求的,@RequestParam中的value属性就是表单中的属性名
//可以通过这种方法重新定义参数的名字
@RequestMapping(value = {"login"},method = {RequestMethod.POST})
//让请求的url后面必须跟上一个叫做userName的属性,是用户的用户名
public ModelAndView LoginPost(@RequestParam(value = "userName") String userName,
//请求的url后必须跟上password属性,为用户当前的密码
@RequestParam(value = "password") String password,
//Spring MVC框架集成了Servlet请求响应等一系列参数,可以在有需要的时候使用
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpSession session) {
//这里是和后端交互的代码,如果是用户登录的话就在数据库中查找对应的用户信息
if(userName.isEmpty() || password.isEmpty()){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("error","用户名或密码为空");
modelAndView.setViewName("index");
return modelAndView;
}
//用户名和密码不为空,进入登录的业务层
//如果登录业务失败,说明用户已经注册过了
if(!userService.login(userName, password)){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("error","用户名或密码错误");
modelAndView.setViewName("index");
return modelAndView;
}
//到了这里就说明用户登录成功了
// System.out.println("用户名是:" + userName + "密码是:" + password);
//使用session进行会话跟踪
session.setAttribute(CURRENT_USER, userName);
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
try {
//我的chrome这里只能选择GBK的编码方式,其他方式会出现乱码
//把用户名和密码作为模型数据塞到ModelAndView中
modelAndView.addObject("userName", new String(userName.getBytes(), "GBK"));
modelAndView.addObject("password",new String(password.getBytes(),"GBK"));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//视图名选择主界面
modelAndView.setViewName("main");
return modelAndView;
}
}
RegisterController:
package root.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import root.back.service.UserService;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = {"/test"})
public class RegisterController {
public static final String CURRENT_USER = "Now_user";
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping(value = {"/register"},method = {RequestMethod.GET})
public ModelAndView RegisterGet(){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("Register");
return modelAndView;
}
@RequestMapping(value = {"register"},method = {RequestMethod.POST})
public ModelAndView Register(@RequestParam(value = "userName") String userName,
@RequestParam(value = "password") String password,
HttpSession session, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response){
//假设用户名或者密码为空就继续回到当前页面
if(userName.isEmpty() || password.isEmpty()){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("error","用户名或密码为空");
modelAndView.setViewName("Register");
return modelAndView;
}
if(userService.exist(userName)){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("error","该用户已经注册过了");
modelAndView.setViewName("Register");
return modelAndView;
}
//用户名和密码的判空和重复性已经判定完了,说明用户注册成功了
session.setAttribute(CURRENT_USER,userName);
//把用户的信息加入数据库
userService.register(userName,password);
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("userName",userName);
map.put("password",password);
map.put("SuccessMassage","注册成功");
modelAndView.addAllObjects(map);
modelAndView.setViewName("index");
return modelAndView;
}
}
UserService(业务层接口):
package root.back.service;
public interface UserService {
boolean login(String userName, String password);
boolean register(String userName, String password);
boolean exist(String userName);
}
UserServiceImp(业务层实现类,进行简单的业务处理)
package root.back.service.Imp;
import root.back.dao.UserDao;
import root.back.entity.User;
import root.back.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
//业务层代码,只需要对用户提交的信息做一些判定和包装
//不进行任何底层数据的访问工作,只用对web层返回业务的执行结果(true/false)
@Repository
public class UserServiceImp implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Override
public boolean login(String userName, String password) {
if(userName.isEmpty() || password.isEmpty()){
return false;
}
//把用户的用户名和密码装配成一个User对象
User user = new User();
user.setUserName(userName);
user.setPassword(password);
//如果返回不为空的话,就说明用户表中有且只有一条信息,就是该用户的id
//所以说明登陆成功
return userDao.login(user) != null;
}
//用户注册的业务层
@Override
public boolean register(String userName, String password) {
if(userName.isEmpty() || password.isEmpty()){
return false;
}
//如果数据库中有该用户的信息,那肯定是不能注册了
if(userDao.exist(userName)){
return false;
}
//现在该用户可以注册了,继续把用户名和密码包装成类,交给Dao层进行数据库存储
User user = new User();
user.setUserName(userName);
user.setPassword(password);
//存储成功就说明数据库的行数改动为1,只要在这里进行判断就可以了
//同样的,业务层只需要告诉web层业务执行成功或者失败
return userDao.insert(user) == 1;
}
@Override
public boolean exist(String userName) {
if(userName.isEmpty()){
return false;
}
return userDao.exist(userName);
}
}
表现层
表现层都是一些JSP页面,很好理解,这个小程序主要的地方还是在SpringMVC的Controller上
1、index.jsp(登录界面)
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
登录界面
2、Resgister.jsp(注册界面)
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
注册页面
3、main.jsp(主界面)
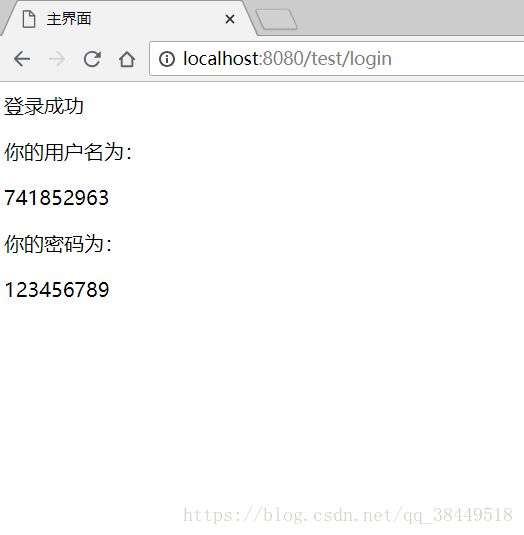
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
主界面
登录成功
你的用户名为:${userName}
你的密码为:${password}
现在来测试一下吧
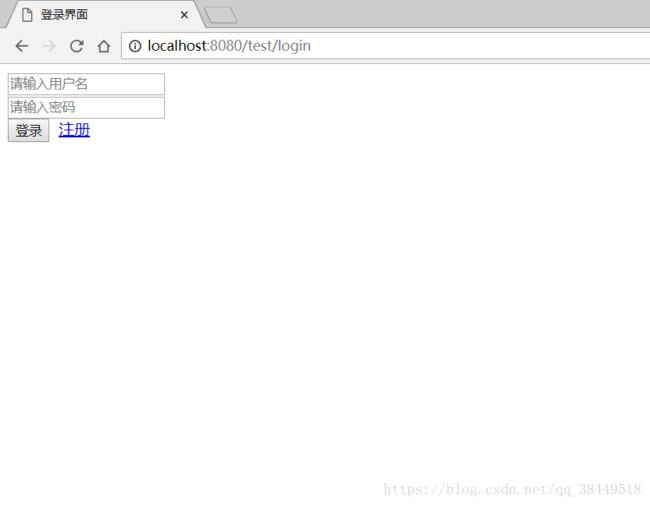
首先到登录界面上
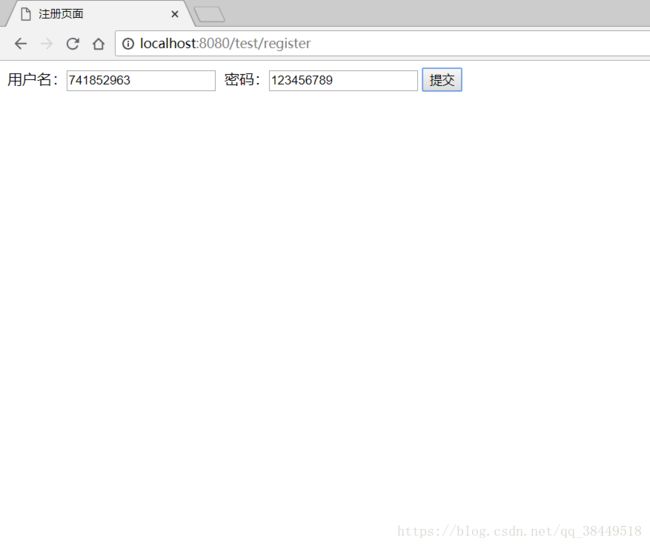
现在还没有用户,注册一个!
好了,点击提交!
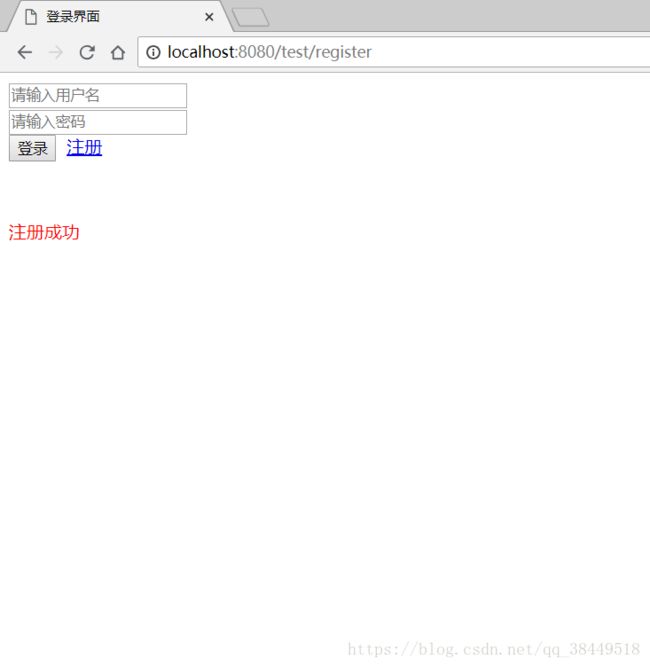
嗯现在我们可以在数据库中看到刚刚注册的用户了
现在直接登录!
好了现在成功了,从前端到后端已经连起来了。
今天总结到这里,编码问题我还没有弄,这只是练习,仅供个人学习使用。