关于分布式多文件自平衡云传输系统之补充-----对象序列化存储
文章目录
- XmlOperation测试
- ResourceXmlEditor
- ResourceXmlEditor 测试
- PropertiesEditor
对于分布式多文件自平衡云传输系统正文所述的对象与xml文件的转换是用了Java原生的XMLEncoder,XMLDecoder来实现的XmlOperation。
XmlOperation测试
package com.xd.mfct.test;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import com.xd.mfct.resource.ResourceBaseInfo;
import com.xd.mfct.resource.XmlOperation;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
ResourceBaseInfo resourceBaseInfo=new ResourceBaseInfo();
resourceBaseInfo.setName("QQ");
resourceBaseInfo.setAbsolutePath("C:\\Users\\48450\\Videos\\origin");
resourceBaseInfo.LoadResource();
ResourceBaseInfo resourceBaseInfo1=new ResourceBaseInfo();
resourceBaseInfo1.setName("Wechat");
resourceBaseInfo1.setAbsolutePath("C:\\Users\\48450\\Videos\\temp");
resourceBaseInfo1.LoadResource();
String resource1="C:\\Users\\48450\\Videos\\resource1.xml";
XmlOperation<ResourceBaseInfo> xmlOperation=new XmlOperation<>(resource1);
xmlOperation.addObject(resourceBaseInfo);
xmlOperation.addObject(resourceBaseInfo1);
}
}
实现的效果如图。
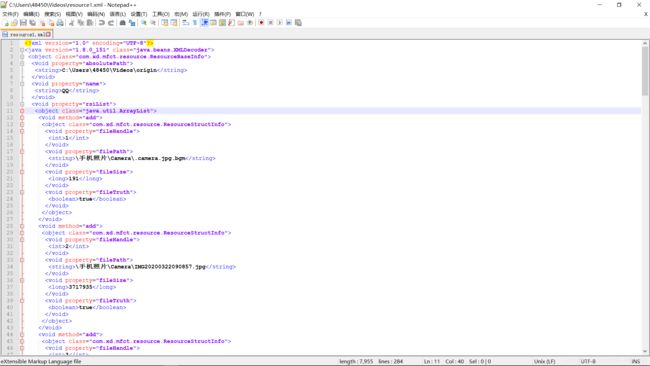
虽然通用性更强,但是可读性较差。因此,博主手写了一个ResourceBaseInfo序列化为xml文件的类。
ResourceXmlEditor
package com.xml.operation;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.List;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import javax.xml.transform.OutputKeys;
import javax.xml.transform.Transformer;
import javax.xml.transform.TransformerConfigurationException;
import javax.xml.transform.TransformerException;
import javax.xml.transform.TransformerFactory;
import javax.xml.transform.TransformerFactoryConfigurationError;
import javax.xml.transform.dom.DOMSource;
import javax.xml.transform.stream.StreamResult;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.GsonBuilder;
/**
* @author dingxiang
*用于存储ResourceBaseInfo对象
*/
public class ResourceXmlEditor {
public static final Gson gson=new GsonBuilder().create();
public static final String RESOURCE_TAG="resources";
private static volatile DocumentBuilder documentBuilder;
private static volatile Transformer transformer;
public ResourceXmlEditor() throws TransformerConfigurationException, ParserConfigurationException, TransformerFactoryConfigurationError {
init();
}
/**
* 初始化DocumentBuilder和Transformer
* @throws ParserConfigurationException
* @throws TransformerConfigurationException
* @throws TransformerFactoryConfigurationError
*/
private void init() throws ParserConfigurationException, TransformerConfigurationException, TransformerFactoryConfigurationError {
if (documentBuilder==null) {
synchronized (ResourceXmlEditor.class) {
if (documentBuilder==null) {
documentBuilder=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance()
.newDocumentBuilder();
transformer=TransformerFactory.newInstance()
.newTransformer();
}
}
}
}
/***
* 创建一个新的xml文件
* @param xmlFile
*/
private void createNewXml(File xmlFile) {
Document document=documentBuilder.newDocument();
Element element=document.createElement(RESOURCE_TAG);
element.setTextContent("\n");
document.appendChild(element);
saveXml(xmlFile, document);
}
//反射调用get方法获取属性值
private Object getFieldValue(Method[] methods,Class<?> klass,Object object,Field field) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
Method method=findMethod(methods,klass,field);
if (method!=null) {
return method.invoke(object);
}
return null;
}
/**
* 找到对应的方法,为反射执行获取属性值做准备
* @param methods
* @param klass
* @param field
* @return
* @throws NoSuchMethodException
* @throws SecurityException
*/
private Method findMethod(Method[] methods,Class<?> klass,Field field) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException {
field.setAccessible(true);
String fieldName=field.getName();
if (fieldName=="serialVersionUID") {
return null;
}
String methodName1="get" + fieldName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase()
+ fieldName.substring(1);
String methodName2="is" + fieldName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase()
+ fieldName.substring(1);
int methodNum=methods.length;
for(int i=0;i<methodNum;i++) {
Method method=methods[i];
String methodName=method.getName();
if (methodName1.equals(methodName)||methodName2.equals(methodName)) {
return klass.getDeclaredMethod(methodName, new Class<?>[]{});
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 判断paraType是否是符合转化的类型
* 对于map类型因没有使用,所以这里暂不做处理
* 读者有兴趣可以在此加上,并在makeElementByObject时增加对map类型的处理即可。
* @param paraType
* @return
*/
private boolean isRightType(Class<?> paraType) {
return paraType.isPrimitive()
||paraType.equals(String.class)
||paraType.isAssignableFrom(List.class);
}
/**
* 判断集合类中泛型是属于以下几种类型。
* @param klass
* @return
*/
private boolean isRightClass(Class<?> klass) {
if (klass.equals(Integer.class)
||klass.equals(Float.class)
||klass.equals(Double.class)
||klass.equals(Long.class)
||klass.equals(Boolean.class)
||klass.equals(Character.class)
||klass.equals(Short.class)
||klass.equals(Byte.class)
||klass.equals(String.class)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 将object转换成Element
* @param doc
* @param parentElement
* @param object
*/
private void makeElementByObject(Document doc,Element parentElement,Object object) {
Class<?> klass=object.getClass();
Element curElement=doc.createElement(klass.getSimpleName());
if (isRightClass(klass)) {
curElement.setTextContent(object.toString());
}else {
Method[] methods=klass.getDeclaredMethods();
Field[] fields=klass.getDeclaredFields();
int fieldNum=fields.length;
for (int i = 0; i<fieldNum; i++) {
Field field = fields[i];
Class<?> paraType=field.getType();
if (!isRightType(paraType)) {
continue;
}
String tagName=field.getName();
Element subElement=doc.createElement(tagName);
try {
Object objValue=getFieldValue(methods, klass, object, field);
if (objValue==null) {
continue;
}
if (paraType.isPrimitive()||paraType.equals(String.class)) {
subElement.setTextContent(objValue.toString());
}else{
subElement.setAttribute("class", objValue.getClass().getName());
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<Object> list=(List<Object>) objValue;
for(Object item:list) {
makeElementByObject(doc, subElement, item);
}
}
curElement.appendChild(subElement);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
parentElement.appendChild(curElement);
}
/**
* 插入新的对象
* @param xmlFilePath
* @param object
* @return
*/
public boolean insert(String xmlFilePath,Object object) {
File xmlFile = new File(xmlFilePath);
if (!xmlFile.exists()) {
int lastIndex = xmlFilePath.lastIndexOf("\\");
String xmlFileDirs = xmlFilePath.substring(0, lastIndex);
File xmlFileDirPath = new File(xmlFileDirs);
xmlFileDirPath.mkdirs();
createNewXml(xmlFile);
}
if (object == null) {
return false;
}
try {
Document doc = documentBuilder.parse(xmlFile);
Element root = (Element) doc.getElementsByTagName(RESOURCE_TAG).item(0);
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
makeElementByObject(doc, root, object);
saveXml(xmlFile, doc);
} catch (SAXException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
/**
* 将doc输出到xml文件
* @param xml
* @param doc
* @throws FileNotFoundException
* @throws TransformerException
*/
void saveXml(File xml,Document doc) {
try {
// 设置缩进
transformer.setOutputProperty(OutputKeys.INDENT, "yes");
//设置缩进量
transformer.setOutputProperty("{http://xml.apache.org/xslt}indent-amount", "4");
DOMSource source=new DOMSource();
source.setNode(doc);
StreamResult result=new StreamResult();
result.setOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(xml));
transformer.transform(source, result);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
ResourceXmlEditor 测试
package com.xd.mfct.test;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import javax.xml.transform.TransformerConfigurationException;
import javax.xml.transform.TransformerFactoryConfigurationError;
import com.xd.mfct.resource.ResourceBaseInfo;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, TransformerConfigurationException, ParserConfigurationException, TransformerFactoryConfigurationError {
ResourceBaseInfo resourceBaseInfo=new ResourceBaseInfo();
resourceBaseInfo.setName("QQ");
resourceBaseInfo.setAbsolutePath("C:\\Users\\48450\\Videos\\origin");
resourceBaseInfo.LoadResource();
ResourceBaseInfo resourceBaseInfo1=new ResourceBaseInfo();
resourceBaseInfo1.setName("Wechat");
resourceBaseInfo1.setAbsolutePath("C:\\Users\\48450\\Videos\\temp");
resourceBaseInfo1.LoadResource();
String resource2="C:\\Users\\48450\\Videos\\resource2.xml";
ResourceXmlEditor xmlEditor=new ResourceXmlEditor();
xmlEditor.insert(resource2, resourceBaseInfo);
xmlEditor.insert(resource2, resourceBaseInfo1);
}
}
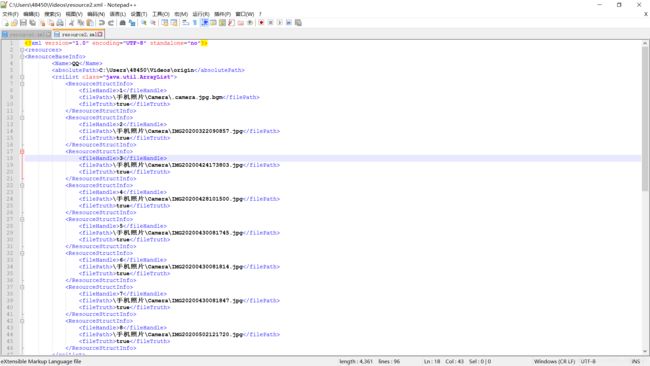
如图可见,可读性增强了很多。至于如何根据xml文件解析还原成对象,读者可参见XML文件解析及其工具制作,两者结合即可完成对象与xml文件的互转。
其实,很多情况下,我们对可读性的要求并不是那么高,而对于那种明显的有键值关系的数据,用properties文件来读写数据是更合适的,这里我使用fastjson来实现对象的序列化及反序列化。
PropertiesEditor
package com.xd.mfct.test;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.util.Properties;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
public class PropertiesEditor {
private Properties prop;
public PropertiesEditor() {
prop=new Properties();
}
/**
* 追加保存属性及值
* @throws IOException
*/
public void saveObject(String propertiesFilePath,String key,Object value) throws IOException {
File file=new File(propertiesFilePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
int lastIndex = propertiesFilePath.lastIndexOf("\\");
String propFileDirs = propertiesFilePath.substring(0, lastIndex);
File propFileDirPath = new File(propFileDirs);
propFileDirPath.mkdirs();
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("无法创建"+file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
//为防止写入时中文乱码,用Writer来写。
BufferedWriter writer=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(file,true)));
prop.setProperty(key,JSON.toJSONString(value));
prop.store(writer, key);
writer.close();
}
/**
* 读取属性及值
* @throws IOException
*/
public Object readObject(String propertiesFilePath,String key,Class<?> klass) throws IOException{
File file=new File(propertiesFilePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
System.out.println("该文件不存在!");
}
FileInputStream inputStream =new FileInputStream(propertiesFilePath);
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
prop.load(reader);
String value= prop.getProperty(key);
Object object=JSON.parseObject(value,klass);
inputStream.close();
reader.close();
return object;
}
}
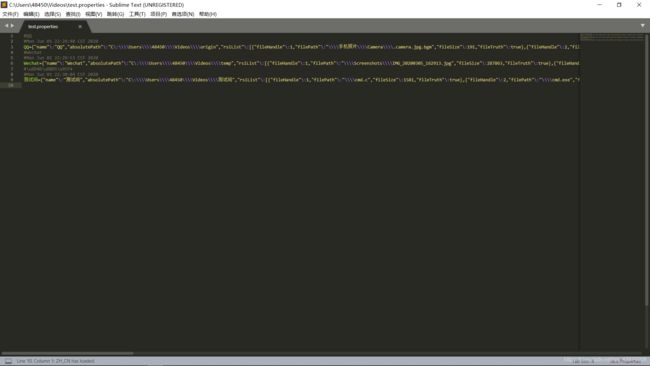
测试类及结果截图如下。
package com.xd.mfct.test;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import javax.xml.transform.TransformerConfigurationException;
import javax.xml.transform.TransformerFactoryConfigurationError;
import com.xd.mfct.resource.ResourceBaseInfo;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws TransformerConfigurationException, ParserConfigurationException, TransformerFactoryConfigurationError, IOException {
String properties1="C:\\Users\\48450\\Videos\\test.properties";
ResourceBaseInfo resourceBaseInfo=new ResourceBaseInfo();
resourceBaseInfo.setName("QQ");
resourceBaseInfo.setAbsolutePath("C:\\Users\\48450\\Videos\\origin");
resourceBaseInfo.LoadResource();
ResourceBaseInfo resourceBaseInfo1=new ResourceBaseInfo();
resourceBaseInfo1.setName("Wechat");
resourceBaseInfo1.setAbsolutePath("C:\\Users\\48450\\Videos\\temp");
resourceBaseInfo1.LoadResource();
PropertiesEditor editor=new PropertiesEditor();
editor.saveObject(properties1, resourceBaseInfo.getName(), resourceBaseInfo);
editor.saveObject(properties1, resourceBaseInfo1.getName(), resourceBaseInfo1);
Object object=
editor.readObject(properties1, resourceBaseInfo1.getName(), ResourceBaseInfo.class);
System.out.println(object);
}
}