spring源码(四)自定义标签
spring自定义标签
- 自定义标签也叫自定义命名空间
- 自己实现一套自定义标签
- 具体实现
- 源码解析
自定义标签也叫自定义命名空间
用过dubbo的同学应该都知道怎么在xml中配置服务的发布与引用,而且配置dubbo的配置文件是被spring容器加载的,原生的spring可是没有< dubbo:xxx >这样的标签的,spring是如何解析和加载这种标签的对象呢
自己实现一套自定义标签
如何构建其实网上都有很多实现,主要分为以下几个步骤:
- 在资源文件夹MATE-INF下创建spring.schemas和spring.handlers;
- 创建标签元素定义的xsd文件,并在spring.schemas中指定xsd位置;
- 创建命名空间处理器NamespaceHandler,并在spring.handlers中指定处理器位置;
- 创建解析对应标签元素的解析器BeanDefinitionParser;
- 在配置文件中使用我们的自定义标签;
具体实现
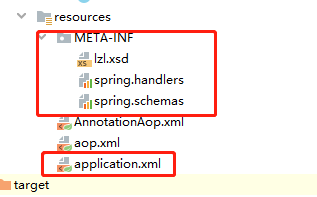
spring.schemas的内容提示自定义标签xsd文件的位置
//这里的key和value,如果value对于的位置没有找到xsd文件,就会去key的路径网上下载
http\://www.lzl.com/schema/lzl/lzl.xsd=META-INF/lzl.xsd
spring.handlers的内容指定了标签的命名空间处理器所在位置
http\://www.lzl.com/schema/lzl=com.lzl.springscope.selfNameSpace.LZLNameSpaceHandler
xsd文件是我们最需要考虑如何设计的
配置文件引入自定义标签
实现自定义的命名空间处理器
public class LZLNameSpaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
@Override
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("person",new LZLBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
实现自定义的解析器
public class LZLBeanDefinitionParser extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser {
public void doParse(Element element, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder){
String name = element.getAttribute("name");
if(null!= name && name.length()>0){
builder.addPropertyValue("name",name);
}
String sex = element.getAttribute("sex");
if(null!= name && name.length()>0){
builder.addPropertyValue("sex",sex);
}
String age = element.getAttribute("age");
if(null!= name && name.length()>0){
builder.addPropertyValue("age",Integer.valueOf(age));
}
builder.getRawBeanDefinition().setBeanClass(Person.class);
}
// protected Class getBeanClass(Element element) {
// String clazz = element.getAttribute("class");
// if(clazz!=null&&clazz.length()>0){
// try {
// return Class.forName(clazz);
// } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// return Person.class;
// }
// }
// return Person.class;
// }
}
这里解析器的原理是首先spring把xml文件解析成dom元素,然后调用对应的命名空间处理器来对指定的元素进行解析,解析的主要逻辑是根据dom元素的属性来构建一个beanDefinition,这里需要注意的一点生成的beanDefinition要指定beanClass,才能在之后构建成你想要的bean,最后把构建好的beanDefinition注册到容器中,放到beanDefinitionMap中。
源码解析
首先看spring是如何加载配置文件的
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:application.xml");
在构造函数中,spring把配置文件的路径存到成员变量configLocations中,然后调用主流程refresh()方法
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
在refresh方法的主流程中
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
我们需要跟到刷新beanFactory的方法中refreshBeanFactory()
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}
在AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext类中,我们可以看到这里开始了加载beanDefinition
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
在AbstractXmlApplicationContext类中,创建了XmlBeanDefinitionReader来加载beanDefinition,并且取的资源就是我们传进来的配置文件。
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
在XmlBeanDefinitionReader类中实现了如何加载资源文件,先将资源文件传成数据流的形式,然后根据dom解析成dom元素,并创建BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 来实现解析dom元素。
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
}
Set currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
在DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类中解析dom元素,主要有两种模式,一种是含有bean、alias、import标签的元素使用默认的解析逻辑,其他的采用委托的方式,使用用户自定义的解析器去解析。
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// Any nested elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
preProcessXml(root);
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
在BeanDefinitionParserDelegate类中首先找到元素对应的命名空间处理器,然后调用注册在容器中对应元素的解析器beanDefinitionParser
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBd) {
String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(ele);
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler == null) {
error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele);
return null;
}
return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}
在NamespaceHandlerSupport类中调用自定义解析器解析元素,并注册beanDefinition
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
return findParserForElement(element, parserContext).parse(element, parserContext);
}