DownloadProvider介绍
一、介绍
DownloadProvider提供了一个保存数据的格式,如content://downloads/my_downloads/1,或content://downloads/all_downloads/2。第三方应用可以使用DownloadManager的enqueue(Request)方法来请求下载,并可以使用ContentResolver的query()方法来查询,注意这里只能查到他自己的下载记录。访问all_downloads需要具备权限android.permission.ACCESS_ALL_DOWNLOADS,这个权限的声明如下:
先看一下DownloadProvider的配置:
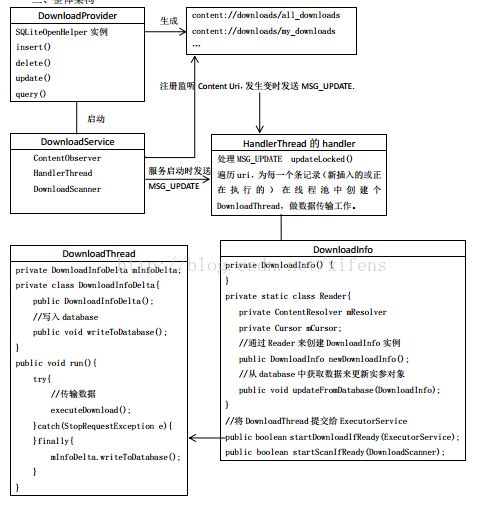
三、DownloadProvide的设计
1. 继承自ContentProvider,并实现增删改查的方法;
2. 包含一个内部类实现SQLiteOpenHelper,创建数据库;
3. 启动DownloadService服务,用于处理下载任务,这是整个流程的核心。
四、DownloadService服务在Downloadprovider刚创建时会启动DownloadService,之后当每有下载任务时也会启动该服务。
启动一个下载任务的流程是这样的:
Clients:
Uriuri = Uri.parse(“http://.../xxx.jpg”);
DownloadManager.Requestrequest = new Request(uri);
DownloadManagermDownloadManager =
(DownloadManager)getSystemService(Context.DOWNLOAD_SERVICE);
longdownId = mDownloadManager.enqueue(request);
DownloadManager:
[frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/DownloadManager.java]
publiclong enqueue(Request request) {
ContentValues values =request.toContentValues(mPackageName);
//插入到content://downloads/my_downloads中,返回值为要插入记录的contenturi.
Uri downloadUri = mResolver.insert(Downloads.Impl.CONTENT_URI,values);
long id =Long.parseLong(downloadUri.getLastPathSegment());
return id;
}
DownloadProvider:
[packages/providers/DownloadProvider]
/**Inserts a row in the database*/
@Override
publicUri insert(final Uri uri, final ContentValues values) {
ContentValuesfilteredValues = new ContentValues();
...
long rowID = db.insert(DB_TABLE, null,filteredValues);
if (rowID == -1) {
Log.d(Constants.TAG, "couldn'tinsert into downloads database");
return null;
}
notifyContentChanged(uri,match);
// Alwaysstart service to handle notifications and/or scanning
final Context context = getContext();
context.startService(new Intent(context,DownloadService.class));
return ContentUris.withAppendedId(Downloads.Impl.CONTENT_URI,rowID);
}4.1 DownloadService的设计
1. 包含一个private内部类,继承自ContentObserver。并注册监听方法,当content provider的内容发生改变时接收通知。
监听的Uri是content://downloads/all_downloads,需要ACCESS_ALL_DOWNLOADS权限。
2. 在onStartCommand()中保存调用该service的Id,并调用enqueueUpdate()。
在handlerThread中处理处理下载任务。
3. 处理下载任务的思路
当新的下载请求发出时,DownloadManager会往content://downloads/my_
downloads中插入一条记录,并再次启动DownloadService,在onStartCommand()中发送消息给HandlerThread的Handler,由handler在新的线程中处理。
处理流程大致是:遍历整个content://downloads/all_downloads,为新插入的记录构建DownloadInfo对象,并添加到HashMap
5. 几个要思考的问题
5.1 多线程的管理
每一个下载任务对应一个线程,即DownloadThread,采用ThreadPoolExecutor来管理线程。功能需求是:
① 最多允许maxThread个线程同时存在,多余的线程要排队等待;
② 各个线程相互独立,即任务互不依赖;
③ 当一个任务结束后,为了节省资源要终止该线程。
实现方法:
private final ExecutorService mExecutor = buildDownloadExecutor();
private static ExecutorService buildDownloadExecutor() {
final int maxConcurrent = Resources.getSystem().getInteger(
com.android.internal.R.integer.config_MaxConcurrentDownloadsAllowed);
// Create a bounded thread pool for executing downloads; it creates
// threads as needed (up to maximum) and reclaims them when finished.
final ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
maxConcurrent, maxConcurrent, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue());
executor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);
return executor;
} 5.2 显示界面的刷新
界面的刷新对应于content uri的更新,处理的思路是:
在一个无限循环中,从输入流中读取数据到输出流对应的文件中,每次读取的阈值是4096 bytes,每读取一次便调用updateProgress(),在updateProgress()中判断如果下载字节数的增量大于4096字节(4kb)并且距离上一次的时间间隔大于1500ms时,通过ContentResolver更新数据库,更新的内容有当前已经下载的bytes数。
如果读取到的字节数为-1,表示文件已全部读取完毕,跳出循环。
具体实现如下
privatevoid transferData(InputStream in, OutputStream out)
throws StopRequestException {
final byte data[] = newbyte[Constants.BUFFER_SIZE]; //4096 bytes
for (;;) {
int bytesRead =readFromResponse(state, data, in);
if (bytesRead == -1) { // success,end of stream already reached
handleEndOfStream(state);
return;
}
state.mGotData = true;
writeDataToDestination(state, data,bytesRead, out);
state.mCurrentBytes += bytesRead;
reportProgress(state);
checkPausedOrCanceled(state);
}
}
}5.3 下载异常的抛出
1. STATUS_BAD_REQUEST
初始化java.net.URL.URL(String spec)时,如果String参数未指定protocol或未知的protocol时,将MalformedURLException异常封装为StopRequestException,status为STATUS_BAD_REQUEST;
2. 与HttpURLConnection相关的异常,status有HTTP_UNAVAILABLE、HTTP_INTERNAL_ERROR、STATUS_CANNOT_RESUME等;
3.与网络连接相关的异常,status有STATUS_WAITING_FOR_NETWORK、STATUS_QUEUED_FOR_WIFI;
4.IOException
主要是从网络中读取数据、往手机存储设备上写数据时发生的异常,status为STATUS_HTTP_DATA_ERROR;
5. 尝试次数太多的异常
status为STATUS_TOO_MANY_REDIRECTS。
6. 未知的异常STATUS_UNKNOWN_ERROR
5.4 下载异常的捕捉
在DownThread的run()中对异常进行了捕捉,主要是StopRequestException及除它之外的异常。StopRequestException中加入了表示状态的变量。捕捉到异常后将:文件名、mimeType、状态信息(status),出错信息(如果不为null),出错次数等在数据库中更新。
public void run() {
try{
//下载任务
}catch(StopRequestException error){
//初始化StopRequestException实例
}catch(Throwable ex) {
//初始化StopRequestException实例
}finally {
//将异常信息写入数据库
}
}
class StopRequestException extends Exception {
private final int mFinalStatus;
public StopRequestException(int finalStatus, String message,Throwable t){
super(message, t);
mFinalStatus =finalStatus;
}
public int getFinalStatus() {
return mFinalStatus;
}
}5.5 下载完成时发送广播
android.intent.action.DOWNLOAD_COMPLETE,附加本次下载的Id。
5.6 下载的文件扫描流程
在DownloadInfo中定义了扫描文件的方法。
逻辑如下:
public boolean startScanIfReady(DownloadScanner scanner) {
synchronized (this) {
//是否需要扫描,如果需要则发送扫描请求。
finalboolean isReady = shouldScanFile();
if (isReady) {
scanner.requestScan(this);
}
return isReady;
}
}所使用的一个重要的类就是DownloadScanner,它的工作是:
当mConnection.connect( )与MediaScanner建立连接时onMediaScannerConnected()会被调用;当扫描一个文件完成时,onScanCompleted()会被调用。为了实现异步的扫描,引入了HashMap
5.7 DownloadScanner类的设计:
1. 实现MediaScannerConnectionClient接口。
publicinterface MediaScannerConnectionClient extends OnScanCompletedListener {
//当客户端连接上MediaScanner service时回调该方法
public void onMediaScannerConnected();
//当mediascanner扫描一个文件结束时,回调该方法。path是该文件的路径;
//如果扫描成功则uri为添加到media database中的uri值;否则为null。
public void onScanCompleted(String path,Uri uri);
}
2. 内部静态类ScanRequest
private static class ScanRequest {
public final long id;
public final String path;
public final String mimeType;
public final long requestRealtime;
//构造方法
public ScanRequest(long id, Stringpath, String mimeType) {
this.id = id;
this.path = path;
this.mimeType = mimeType;
this.requestRealtime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
}
//执行扫描操作
public void exec(MediaScannerConnectionconn) {
conn.scanFile(path, mimeType);
}
}5.8 通知管理—DownloadNotifier
发送通知的流程分析:
有三种类型的通知:TYPE_ACTIVE、TYPE_WAITING、TYPE_COMPLETE。
使用Notification.Builder类来构建通知内容,如下:
//通知发出的时间
builder.setWhen(longwhen)
//显示在status bar上的通知图标,三种类型的icon是不一样的
builder. setSmallIcon(inticon)
//当该notification被点击时的PendingIntent
builder.setContentIntent(PendingIntentintent)
//当被点击时该通知可以自动取消
builder.setAutoCancel(boolean)
//设置这个notification为on-going状态
builder.setOngoing(boolean)
//当该Notification被删除时,会调用的PendingIntent
builder.setDeleteIntent(PendingIntent);
builder.setProgress(setProgress(int max, int progress, boolean indeterminate)
builder.setContentTitle(CharSequencetitle);
builder.setContentText(CharSequence title);
mNotifManager.notify(tag,0, notif);5.9 数据传输
通过java.net.URL获取Http连接,由HttpURLConnection得到InputSream,下载网络文件。
private void transferData(State state, HttpURLConnection conn)
throws StopRequestException {
InputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
try {
//通过HttpURLConnection获取输入流
try {
in = conn.getInputStream();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new StopRequestException(STATUS_HTTP_DATA_ERROR, e);
}
try {
//定义输出流,参数true表示追加到文件末尾
out = new FileOutputStream(state.mFilename, true);
}catch (IOException e) {
throw new StopRequestException(STATUS_FILE_ERROR, e);
}
//传输数据
transferData(state, in, out);
}finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(in); //关闭输入流
try {
if (out != null) out.flush(); //刷新
if (outFd != null) outFd.sync();
} catch (IOException e) {
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(out); //关闭输出流
}
}
}