4springboot的yml文件使用
文章目录
- 1yml文件语法
- 1.1yml文件
- 1.2实体类
- 1.3测试
- 2yml文件和 properties转换
- 3@Value
- 3.1application. properties
- 3.2使用
- 3.3@Value获取值和@ConfigurationProperties获取值比较
- 4加载指定的配置文件
- 4.1PropertySource
- 4.2@Configuration
- 5profile
- 5.1第一种方式
- 5.2 yml支持多文档块方式
1yml文件语法
1.1yml文件
server:
port: 8080
person:
lastName: hello
age: 18
boss: false
birth: 2017/12/12
maps: {k1: v1,k2: 12}
lists:
‐ lisi
‐ zhaoliu
dog:
name: 小狗
age: 12
1.2实体类
/**
* 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中
* @ConfigurationProperties:告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定;
* prefix = "person":配置文件中哪个下面的所有属性进行一一映射
*
* 只有这个组件是容器中的组件,才能容器提供的@ConfigurationProperties功能;
* @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")默认从全局配置文件中获取值;
*
*/
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String lastName;
private Integer age;
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
}
1.3测试
package com.example.junit.Controller;
import com.example.junit.pojo.Person;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
class HelloControllerTest {
@Autowired
Person person;
@Test
void print() {
System.out.print(person);
}
}
运行:
Person{lastName='hello', age=18, boss=false, birth=Tue Dec 12 00:00:00 CST 2017, maps={k1=v1, k2=12}, lists=[‐ lisi ‐ zhaoliu], dog=Dog{name='小狗', age=12}}
2yml文件和 properties转换
application.yml
server:
port: 8080
person:
lastName: hello
age: 18
boss: false
birth: 2017/12/12
maps: {k1: v1,k2: 12}
lists:
‐ lisi
‐ zhaoliu
dog:
name: 小狗
age: 12
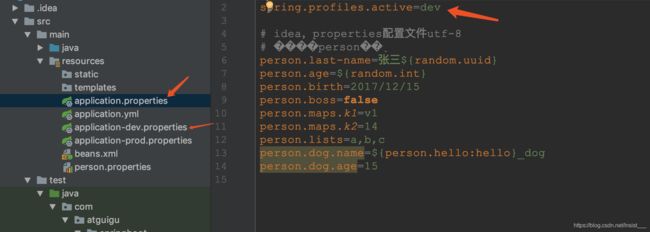
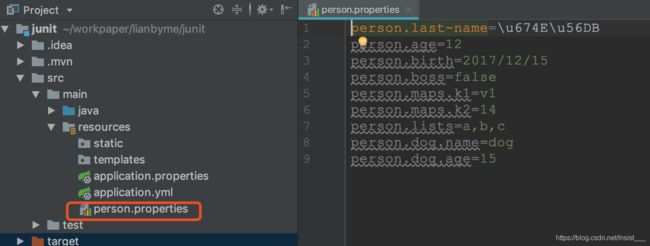
application.properties:
person.last-name=李四
person.age=12
person.birth=2017/12/15
person.boss=false
person.maps.k1=v1
person.maps.k2=14
person.lists=a,b,c
person.dog.name=dog
person.dog.age=15
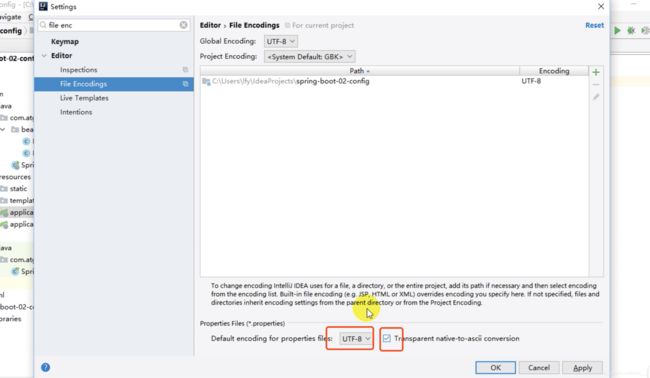
注意:
properties配置文件在idea中默认utf-8可能会乱码
idea 的编码时utf-8
propertis 的编码时ascli
修改:
3@Value
3.1application. properties
person.last-name=李四
person.age=12
person.birth=2017/12/15
person.boss=false
person.maps.k1=v1
person.maps.k2=14
person.lists=a,b,c
person.dog.name=dog
person.dog.age=15
3.2使用
@Component
public class Person2 {
@Value("${person.last-name}")
private String lastName;
@Value("#{11*2}")
private Integer age;
@Value("true")
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
//@Value("${person.maps}")不支持复杂类型
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
3.3@Value获取值和@ConfigurationProperties获取值比较
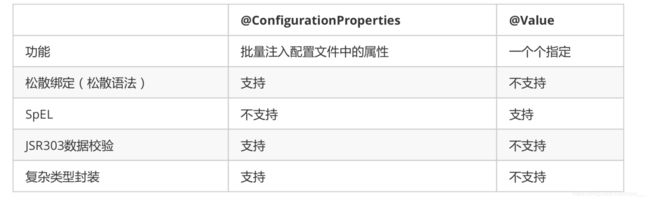
配置文件yml还是properties他们都能获取到值;
如果说,我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用@Value; 如果说,我们专门编写了一个javaBean来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties;
4加载指定的配置文件
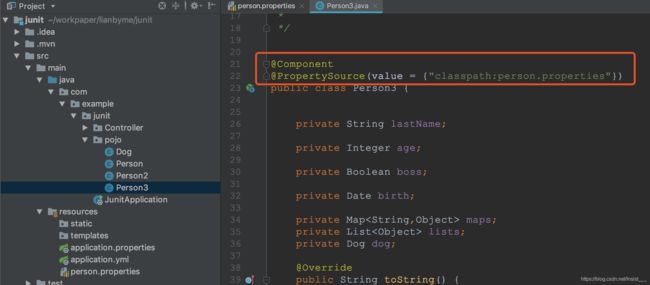
4.1PropertySource
@PropertySource(value = {“classpath:person.properties”})
4.2@Configuration
使用@Bean给容器中添加组件
package com.atguigu.springboot.config;
import com.atguigu.springboot.service.HelloService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @Configuration:指明当前类是一个配置类;就是来替代之前的Spring配置文件
*
* 在配置文件中用5profile
5.1第一种方式
5.2 yml支持多文档块方式
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles:
active: prod
‐‐‐
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: dev
‐‐‐
server:
port: 8084
spring:
profiles: prod #指定属于哪个环境