计算机视觉:图像检索
一、图像检索原理概述
图像检索,简单的说,便是从图片检索数据库中检索出满足条件的图片,图像检索技术的研究根据描述图像内容方式的不同可以分为两类:
一类是基于文本的图像检索技术,简称TBIR,
一类为基于内容的图像检索技术,简称CBIR。
- 两类图像检索技术
基于文本的图像检索(TBIR)技术,其主要原理为利用文本描述,如文本描述图片的内容、作者等等的方式来检索图片;
基于图像的内容语义的图像检索技术(CBIR),利用图片的颜色、纹理及图片包含的物体、类别等信息检索图片,如给定检索目标图片,在图像检索数据库中检索出与它相似的图片。
基于图像的内容语义的图像检索包括相同物体图像检索和相同类别图像检索,检索任务分别为检索同一个物体地不同图片和检索同一个类别地图片。例如,行人检索中检索的是同一个人即同一个身份在不同场景不同摄像头下拍得的图片属于相同物体的图像检索,而在3D形状检索中则是检索属于同一类的物品,如飞机等。
- 图像检索技术的步骤
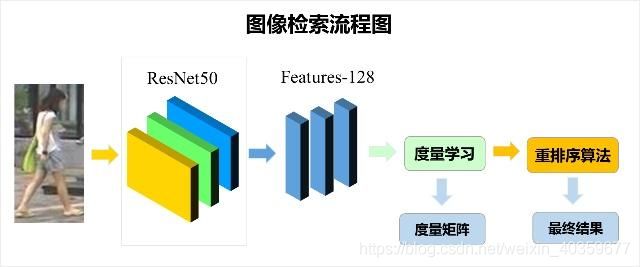
图像检索技术主要包含几个步骤,分别为:输入图片、特征提取、度量学习、重排序。
特征提取:即将图片数据进行降维,提取数据的判别性信息,一般将一张图片降维为一个向量;
度量学习:一般利用度量函数,计算图片特征之间的距离,作为loss,训练特征提取网络,使得相似图片提取的特征相似,不同类的图片提取的特征差异性较大。
重排序:利用数据间的流形关系,对度量结果进行重新排序,从而得到更好的检索结果。
二、基于BOW的图像检索原理
2.1 BoW词袋模型原理:
2.1.1模型简介
Bag-of-Words模型源于文本分类技术。在信息检索中,它假定对于一个文本,忽略其词序、语法和句法,将其仅仅看作是一个词集合,或者说是词的一个组合。文本中每个词的出现都是独立的,不依赖于其他词是否出现,或者说这篇文章的作者在任意一个位置选择词汇都不受前面句子的影响而独立选择的。
Bag-of-words在CV中的应用首先出现在Andrew Zisserman中为解决对视频场景的搜索,其提出了使用Bag-of-words关键点投影的方法来表示图像信息。后续更多的研究者归结此方法为Bag-of-Features,并用于图像分类、目标识别和图像检索。Bag-of-Features模型仿照文本检索领域的Bag-of-Words方法,把每幅图像描述为一个局部区域或关键点(Patches/Key Points)特征的无序集合,这些特征点可以看成一个词。这样,就能够把文本检索及分类的方法用到图像分类及检索中去。
使用某种聚类算法(如K-means)将特征进行聚类,每个聚类中心被看作是词典中的一个视觉词汇(Visual Word),相当于文本检索中的词,视觉词汇由聚类中心对应特征形成的码字(code word)来表示(可看当为一种特征量化过程)。所有视觉词汇形成一个视觉词典(Visual Vocabulary),对应一个码书(code book),即码字的集合,词典中所含词的个数反映了词典的大小。图像中的每个特征都将被映射到视觉词典的某个词上,这种映射可以通过计算特征间的距离去实现。然后,统计每个视觉词的出现与否或次数,图像可描述为一个维数相同的直方图向量,即Bag-of-Features。在Bag-of-Features方法的基础上,Andrew Zisserman进一步借鉴文本检索中TF-IDF模型(Term Frequency一Inverse Document Frequency)来计算Bag-of-Features特征向量。接下来便可以使用文本搜索引擎中的反向索引技术对图像建立索引,高效的进行图像检索。
Bag-of-Features更多地是用于图像分类或对象识别。在上述思路下对训练集提取Bag-of-Features特征,在某种监督学习(如:SVM)的策略下,对训练集的Bag-of-Features特征向量进行训练,获得对象或场景的分类模型;对于待测图像,提取局部特征,计算局部特征与词典中每个码字的特征距离,选取最近距离的码字代表该特征,建立一个统计直方图,统计属于每个码字的特征个数,即为待测图像的Bag-of-Features特征;在分类模型下,对该特征进行预测,从而实现对待测图像的分类。
2.1.2为什么要用BoW模型描述图像
SIFT特征虽然也能描述一幅图像,但是每个SIFT矢量都是128维的,而且一幅图像通常都包含成百上千个SIFT矢量,在进行相似度计算时,这个计算量是非常大的,通行的做法是用聚类算法对这些矢量数据进行聚类,然后用聚类中的一个簇代表BoW中的一个视觉词,将同一幅图像的SIFT矢量映射到视觉词序列生成码本,这样每一幅图像只用一个码本矢量来描述,这样计算相似度时效率就大大提高了。
2.1.3.构建BoW码本步骤
假设训练集有M幅图像,对训练图象集进行预处理。包括图像增强,分割,图像统一格式,统一规格等等。
提取SIFT特征。对每一幅图像提取SIFT特征(每一幅图像提取多少个SIFT特征不定)。每一个SIFT特征用一个128维的描述子矢量表示,假设M幅图像共提取出N个SIFT特征。
用K-means对2中提取的N个SIFT特征进行聚类,K-Means算法是一种基于样本间相似性度量的间接聚类方法,此算法以K为参数,把N个对象分为K个簇,以使簇内具有较高的相似度,而簇间相似度较低。聚类中心有k个(在BOW模型中聚类中心我们称它们为视觉词),码本的长度也就为k,计算每一幅图像的每一个SIFT特征到这k个视觉词的距离,并将其映射到距离最近的视觉词中(即将该视觉词的对应词频+1)。完成这一步后,每一幅图像就变成了一个与视觉词序列相对应的词频矢量。
构造码本。码本矢量归一化因为每一幅图像的SIFT特征个数不定,所以需要归一化。测试图像也需经过预处理,提取SIFT特征,将这些特征映射到为码本矢量,码本矢量归一化,最后计算其与训练码本的距离,对应最近距离的训练图像认为与测试图像匹配。设视觉词序列为{眼睛 鼻子 嘴}(k=3),则训练集中的图像变为:
第一幅图像:[1 0 0]
第二幅图像:[5 3 4]
…
当然,在提取sift特征的时候,可以将图像打成很多小的patch,然后对每个patch提取SIFT特征。
总结一下,整个过程其实就做了三件事,首先提取对n幅图像分别提取SIFT特征,然后对提取的整个SIFT特征进行KMeans聚类得到k个聚类中心作为视觉单词表(或者说是词典),最后对每幅图像以单词表为规范对该幅图像的每一个SIFT特征点计算它与单词表中每个单词的距离,最近的+1,便可得到该幅图像的码本。实际上第三步是一个统计的过程,所以BoW中向量元素都是非负的。Yunchao Gong 2012年NIPS上有一篇用二进制编码用于图像快速检索的文章就是针对这类元素是非负的特征而设计的编码方案。
2.2 BOF(Bag of features)原理:
2.2.1. BOF概述
Bag-of-Features模型仿照文本检索领域的Bag-of-Words方法,把每幅图像描述为一个局部区域/关键点(Patches/Key Points)特征的无序集合。使用某种聚类算法(如K-means)将局部特征进行聚类,每个聚类中心被看作是词典中的一个视觉词汇(Visual Word),相当于文本检索中的词,视觉词汇由聚类中心对应特征形成的码字(code word)来表示(可看当为一种特征量化过程)。所有视觉词汇形成一个视觉词典(Visual Vocabulary),对应一个码书(code book),即码字的集合,词典中所含词的个数反映了词典的大小。图像中的每个特征都将被映射到视觉词典的某个词上,这种映射可以通过计算特征间的距离去实现,然后统计每个视觉词的出现与否或次数,图像可描述为一个维数相同的直方图向量,即Bag-of-Features。
Bag-of-Features更多地是用于图像分类或对象识别。在上述思路下对训练集提取Bag-of-Features特征,在某种监督学习(如:SVM)的策略下,对训练集的Bag-of-Features特征向量进行训练,获得对象或场景的分类模型;对于待测图像,提取局部特征,计算局部特征与词典中每个码字的特征距离,选取最近距离的码字代表该特征,建立一个统计直方图,统计属于每个码字的特征个数,即为待测图像之Bag-of-Features特征;在分类模型下,对该特征进行预测从实现对待测图像的分类。
2.2.2. 基于SIFT特征构建BoF的步骤
这边sift算法原理省略SIFT原理
1、SIFT特征提取 :提取训练集中所有图像的SIFT特征,设有MM幅图像,共得到NN个SIFT特征。
2、构建视觉词汇表 对提取到的NN个SIFT特征进行聚类,得到KK个聚类中心,组成图像的视觉词汇表。
3、图像的视觉词向量表示,统计每幅图像中视觉词汇的出现的次数,得到图像的特征向量。在检索时,该特征向量就代表该幅图像。统计时,计算图像中提取到的SIFT特征点到各个视觉词(聚类中心)的距离,将其归类到聚类最近的视觉词中。
2.3 K-means聚类算法
聚类(Clustering)是一种无监督学习算法,其目的是将数据集中的样本划分为若干个不相交的子集,每个子集称为一个簇(Cluster)。聚类的时候并不关心某一类是什么,只根据数据的相似性,将数据划分到不同的组中。每个组内的成员具有相似的性质。
聚类算法可以分为三类:
原型聚类,此类算法假设聚类结构能够通过一组原型描述,这里原型指的是样本空间中具有代表性的点。
密度距离,该类算法假设聚类结构能够通过样本分布的紧密程度来确定。
层次聚类,在不同的层次对数据集进行划分,从而形成树形的聚结构。
K-Means算法是原型聚类的一种,对于给定的样本集,按照样本之间的距离大小,将样本集划分为K个簇。让簇内的点尽量紧密的连在一起,而让簇间的距离尽量的大。
如果用数据表达式表示,假设簇划分为(C1,C2,…Ck),则我们的目标是最小化平方误差E:
其中μi是簇Ci的均值向量,有时也称为质心,表达式为:
K-Means算法基本流程:
随机初始化 K 个聚类中心
重复下述步骤直至算法收敛:
对应每个特征,根据距离关系赋值给某个中心/类别
对每个类别,根据其对应的特征集重新计算聚类中心
三、代码及实现过程
图像搜索(代码运行流程)
1.生成代码所需要的模型文件
#获取图像列表
imlist = get_imlist('first1000/')
nbr_images = len(imlist)
#获取特征列表
featlist = [imlist[i][:-3]+'sift' for i in range(nbr_images)]
#提取文件夹下图像的sift特征
for i in range(nbr_images):
sift.process_image(imlist[i], featlist[i])
2.将模型数据导入数据库
在python\Lib文件夹之下可以看到一个sqlite3的包,说明python3自带数据库包,不需要安装pysqlite库,所以需要更改PCV\imagesearch中的imagesearch.py文件第三行为from sqlite3 import dbapi2 as sqlite
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pickle
from PCV.imagesearch import imagesearch
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from sqlite3 import dbapi2 as sqlite
from PCV.tools.imtools import get_imlist
##要记得将PCV放置在对应的路径下
#获取图像列表
imlist = get_imlist('D:/Visual_Studio_Code/data/first1000/')##记得改成自己的路径
nbr_images = len(imlist)
#获取特征列表
featlist = [imlist[i][:-3]+'sift' for i in range(nbr_images)]
# load vocabulary
#载入词汇
with open(r'D:\Visual_Studio_Code\data\first1000\vocabulary.pkl', 'rb') as f:
voc = pickle.load(f)
#创建索引
indx = imagesearch.Indexer('testImaAdd.db',voc)
indx.create_tables()
# go through all images, project features on vocabulary and insert
#遍历所有的图像,并将它们的特征投影到词汇上
for i in range(nbr_images)[:1000]:
locs,descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
indx.add_to_index(imlist[i],descr)
# commit to database
#提交到数据库
indx.db_commit()
con = sqlite.connect('testImaAdd.db')
print (con.execute('select count (filename) from imlist').fetchone())
print (con.execute('select * from imlist').fetchone())
3.测试
# index of query image and number of results to return
#查询图像索引和查询返回的图像数
q_ind = 0
nbr_results = 40
# regular query
# 常规查询(按欧式距离对结果排序)
res_reg = [w[1] for w in src.query(imlist[q_ind])[:nbr_results]]
print ('top matches (regular):', res_reg)
# load image features for query image
#载入查询图像特征
q_locs,q_descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[q_ind])
fp = homography.make_homog(q_locs[:,:2].T)
# RANSAC model for homography fitting
#用单应性进行拟合建立RANSAC模型
model = homography.RansacModel()
rank = {}
# load image features for result
#载入候选图像的特征
for ndx in res_reg[1:]:
locs,descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[ndx]) # because 'ndx' is a rowid of the DB that starts at 1
# get matches
matches = sift.match(q_descr,descr)
ind = matches.nonzero()[0]
ind2 = matches[ind]
tp = homography.make_homog(locs[:,:2].T)
# compute homography, count inliers. if not enough matches return empty list
try:
H,inliers = homography.H_from_ransac(fp[:,ind],tp[:,ind2],model,match_theshold=4)
except:
inliers = []
# store inlier count
rank[ndx] = len(inliers)
# sort dictionary to get the most inliers first
sorted_rank = sorted(rank.items(), key=lambda t: t[1], reverse=True)
res_geom = [res_reg[0]]+[s[0] for s in sorted_rank]
print ('top matches (homography):', res_geom)
# 显示查询结果
imagesearch.plot_results(src,res_reg[:8]) #常规查询
imagesearch.plot_results(src,res_geom[:8]) #重排后的结果
class Indexer(object):
def __init__(self,db,voc):
""" Initialize with the name of the database
and a vocabulary object. """
self.con = sqlite3.connect(db)
self.voc = voc
def __del__(self):
self.con.close()
def db_commit(self):
self.con.commit()
def get_id(self,imname):
""" Get an entry id and add if not present. """
cur = self.con.execute(
"select rowid from imlist where filename='%s'" % imname)
res=cur.fetchone()
if res==None:
cur = self.con.execute(
"insert into imlist(filename) values ('%s')" % imname)
return cur.lastrowid
else:
return res[0]
def is_indexed(self,imname):
""" Returns True if imname has been indexed. """
im = self.con.execute("select rowid from imlist where filename='%s'" % imname).fetchone()
return im != None
def add_to_index(self,imname,descr):
""" Take an image with feature descriptors,
project on vocabulary and add to database. """
if self.is_indexed(imname): return
print ('indexing', imname)
# get the imid
imid = self.get_id(imname)
# get the words
imwords = self.voc.project(descr)
nbr_words = imwords.shape[0]
# link each word to image
for i in range(nbr_words):
word = imwords[i]
# wordid is the word number itself
self.con.execute("insert into imwords(imid,wordid,vocname) values (?,?,?)", (imid,word,self.voc.name))
# store word histogram for image
# use pickle to encode NumPy arrays as strings
self.con.execute("insert into imhistograms(imid,histogram,vocname) values (?,?,?)", (imid,pickle.dumps(imwords),self.voc.name))
def create_tables(self):
""" Create the database tables. """
self.con.execute('create table imlist(filename)')
self.con.execute('create table imwords(imid,wordid,vocname)')
self.con.execute('create table imhistograms(imid,histogram,vocname)')
self.con.execute('create index im_idx on imlist(filename)')
self.con.execute('create index wordid_idx on imwords(wordid)')
self.con.execute('create index imid_idx on imwords(imid)')
self.con.execute('create index imidhist_idx on imhistograms(imid)')
self.db_commit()
class Searcher(object):
def __init__(self,db,voc):
""" Initialize with the name of the database. """
self.con = sqlite3.connect(db)
self.voc = voc
def __del__(self):
self.con.close()
def get_imhistogram(self,imname):
""" Return the word histogram for an image. """
im_id = self.con.execute(
"select rowid from imlist where filename='%s'" % imname).fetchone()
s = self.con.execute(
"select histogram from imhistograms where rowid='%d'" % im_id).fetchone()
# use pickle to decode NumPy arrays from string
return pickle.loads(s[0])
def candidates_from_word(self,imword):
""" Get list of images containing imword. """
im_ids = self.con.execute(
"select distinct imid from imwords where wordid=%d" % imword).fetchall()
return [i[0] for i in im_ids]
def candidates_from_histogram(self,imwords):
""" Get list of images with similar words. """
# get the word ids
words = imwords.nonzero()[0]
# find candidates
candidates = []
for word in words:
c = self.candidates_from_word(word)
candidates+=c
# take all unique words and reverse sort on occurrence
tmp = [(w,candidates.count(w)) for w in set(candidates)]
tmp.sort(key=cmp_to_key(lambda x,y:operator.gt(x[1],y[1])))
tmp.reverse()
# return sorted list, best matches first
return [w[0] for w in tmp]
def query(self,imname):
""" Find a list of matching images for imname. """
h = self.get_imhistogram(imname)
candidates = self.candidates_from_histogram(h)
matchscores = []
for imid in candidates:
# get the name
cand_name = self.con.execute(
"select filename from imlist where rowid=%d" % imid).fetchone()
cand_h = self.get_imhistogram(cand_name)
cand_dist = sqrt( sum( self.voc.idf*(h-cand_h)**2 ) )
matchscores.append( (cand_dist,imid) )
# return a sorted list of distances and database ids
matchscores.sort()
return matchscores
def get_filename(self,imid):
""" Return the filename for an image id. """
s = self.con.execute(
"select filename from imlist where rowid='%d'" % imid).fetchone()
return s[0]
def tf_idf_dist(voc,v1,v2):
v1 /= sum(v1)
v2 /= sum(v2)
return sqrt( sum( voc.idf*(v1-v2)**2 ) )
def compute_ukbench_score(src,imlist):
""" Returns the average number of correct
images on the top four results of queries. """
nbr_images = len(imlist)
pos = zeros((nbr_images,4))
# get first four results for each image
for i in range(nbr_images):
pos[i] = [w[1]-1 for w in src.query(imlist[i])[:4]]
# compute score and return average
score = array([ (pos[i]//4)==(i//4) for i in range(nbr_images)])*1.0
return sum(score) / (nbr_images)
# import PIL and pylab for plotting
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
def plot_results(src,res):
""" Show images in result list 'res'. """
figure()
nbr_results = len(res)
for i in range(nbr_results):
imname = src.get_filename(res[i])
subplot(1,nbr_results,i+1)
imshow(array(Image.open(imname)))
axis('off')
show()
4.建立演示程序及Web应用
课本中用了web服务器来演示我们的成果。使用前,我们需要先安装CherryPy包,直接运行
class SearchDemo:
def __init__(self):
# 载入图像列表
self.path = 'first1000/'
#self.path = 'D:/python_web/isoutu/first500/'
self.imlist = [os.path.join(self.path,f) for f in os.listdir(self.path) if f.endswith('.jpg')]
#self.imlist = get_imlist('./first500/')
#self.imlist = get_imlist('E:/python/isoutu/first500/')
self.nbr_images = len(self.imlist)
print (self.imlist)
print (self.nbr_images)
self.ndx = list(range(self.nbr_images))
print (self.ndx)
# 载入词汇
# f = open('first1000/vocabulary.pkl', 'rb')
with open('first1000/vocabulary.pkl','rb') as f:
self.voc = pickle.load(f)
#f.close()
# 显示搜索返回的图像数
self.maxres = 10
#header and footer html
self.header = """
Image search
"""
self.footer = """

